Characteristics of non-magnetic carbide
Because non-magnetic carbide?is produced in high-temperature and high-pressure environments, it possesses excellent characteristics of high flexural strength and high hardness. If this type of carbide?is used as a material for molds, its service life can be several tens of times longer than that of ordinary molds, and its service life is very long. Furthermore, it can ensure that no burrs or powder sticking phenomena occur during the pressing process, guaranteeing both processing accuracy and surface quality. The subsequent machining results are also guaranteed.
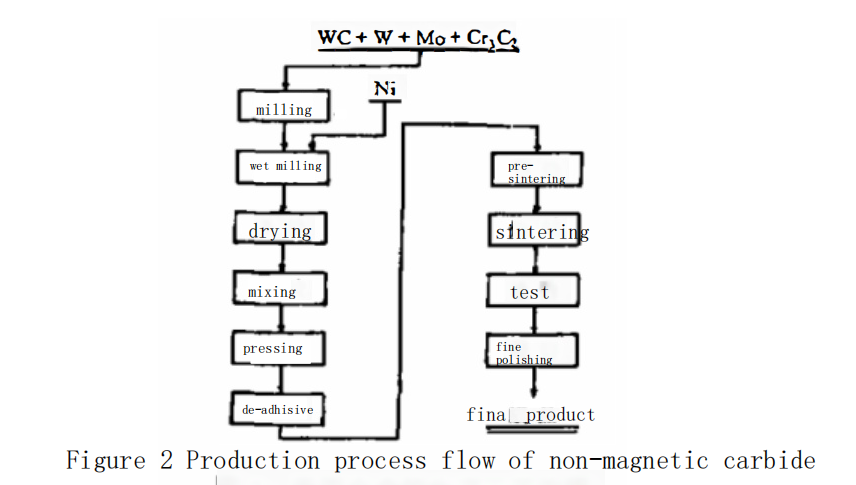
Preparation methods of non-magnetic carbide
The research and production of non-magnetic?carbide?materials represent a significant advancement in new types of?carbide?materials. Hard alloys are composed of refractory metal carbides from Groups IV A, V A, and VI A of the periodic table (such as tungsten carbide, WC), with iron-group transition metals (cobalt, Co; nickel, Ni; iron, Fe) as the binder phase, and are sintered using powder metallurgy techniques. Tungsten carbides mentioned above are non-magnetic, while Fe, Co, and Ni are magnetic, with Curie points of 770°C, 1120°C, and 354°C, respectively. Among them, the Curie point of Ni (nickel) is relatively low and can be lowered below room temperature using certain methods. Using Ni as a binder is an essential condition for producing non-magnetic alloys.
There are the following methods to obtain WC-Ni series non-magnetic hard alloy:
Strictly controlling the carbon content
WC-Ni alloys, like WC-Co alloys, are influenced by carbon content, which is the main factor affecting the solid solubility of W in the binder phase. In other words, the lower the carbon content in the carbide phase of the alloy, the greater the solid solubility of W in the Ni binder phase. This variation ranges from about 10% to 31%. When the solid solubility of W in the Ni binder phase exceeds 17%, the alloy becomes non-magnetic. The essence of this method lies in lowering the carbon content and increasing the solid solubility of W in the binder phase to achieve a non-magnetic hard alloy.
In practice, WC powder with a carbon content lower than the theoretical carbon content is often used, or W powder is added to the mixture to achieve the production of low-carbon alloys. However, it is quite challenging to solely rely on controlling the carbon content to produce non-magnetic alloys.
Adding chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), and tantalum (Ta)
High-carbon WC-10%Ni (wt% weight percentage) alloy exhibits ferromagnetic properties at room temperature. If more than 0.5% of Cr or Mo and more than 1% of Ta in metallic form are added, the high-carbon alloy can transition from ferromagnetic to non-magnetic. Adding Cr results in an alloy’s magnetism being independent of carbon content, similar to how Cr is significantly solubilized in the alloy’s binder phase as W is. On the other hand, alloys with added Mo or Ta can only transform into non-magnetic alloys under certain carbon content.
Since the solubility of Mo and Ta in the binder phase is relatively low, most of them extract carbon from WC to form corresponding carbides or solid solutions of carbides. As a result, the alloy composition shifts towards the low-carbon side, causing an increase in the solid solubility of W in the binder phase. In other words, the method of adding Mo or Ta is essentially achieved by lowering the carbon content to obtain a non-magnetic alloy. Although it’s not as easily controlled as adding Cr, this method is relatively easier to control in terms of carbon content compared to pure WC-10%Ni alloy, widening the carbon content range from 5.8-5.95% to 5.8-6.05%.
Adding NiB or Al.
Using NiB (nickel boride) with a boron content of 1-8% as the binder phase, and WC, TiC (titanium carbide), TaC (tantalum carbide), etc., as the hard phase, this alloy is produced through vacuum sintering at temperatures between 1300°C and 1450°C. When the boron content in the binder phase exceeds 8%, the flexural strength noticeably decreases.
The reason this alloy achieves non-magnetic properties is inferred to be either due to boron’s solubility in the binder phase causing a reduction in the alloy’s Curie point or because boron reacts with WC to generate new hard phases, resulting in the alloy becoming a low-carbon alloy.
In the WC-Ni alloy system, adding Al is also a method to achieve non-magnetic properties. For instance, an alloy with the composition of WC-0.75%Al-14.25%Ni displays weak magnetism at room temperature, with a flexural strength of 1670 MPa and a hardness of 87.4 HRA.
Among the production and preparation methods for non-magnetic alloys, the second method has been practically applied due to challenges in controlling the first method’s processes, and the third method hasn’t been industrialized due to its inferior performance.
VC addition method
Vanadium (V) is the most effective element in reducing the Curie point of nickel. Vanadium carbide (VC) is the most effective grain growth inhibitor in hard alloys, and increasing the content of vanadium carbide (VC) is a novel method for producing non-magnetic hard alloys.
Comparing the magnetic permeability of samples with a certain amount of added VC (reaching a specific null level) with the magnetic permeability of existing domestic non-magneticcarbideproducts, there is a noticeable decrease. It is also much lower than the magnetic permeability of non-magnetic steel. VC is limited in solid solubility within Ni, and excessive addition can lead to the precipitation of VC. From the perspective of producing non-magnetic alloys, a VC addition of 0.1-0.2% is sufficient to meet the requirements.
Adding 1% Cr3C2 to WC-10%Ni alloy also yields a non-magnetic alloy. However, in terms of magnetic permeability and temperature proximity (-6°C), the addition of Cr3C2 is relatively large and its non-magnetic effect is not as effective as adding VC.
Types of non-magnetic?carbide?products
Here are some products and applications that can be made using non-magnetic carbide:
Electronic device components
Due to its low magnetic properties, non-magnetic carbide?can be used to manufacture components in electronic devices, such as electronic magnetic induction elements, transformers, inductors, etc. This helps to prevent magnetic fields from interfering with the performance of the devices.
Medical instruments
In certain medical devices, non-magnetic carbide?can be used to manufacture certain components to prevent induction of magnetic fields in the equipment, ensuring the proper functioning of the devices.
Aerospace field
In the aerospace industry, non-magnetic carbide?can be utilized to manufacture sensitive instruments, equipment, and tools to prevent magnetic field interference with navigation and measurement systems.
Precision instruments
Non-magnetic carbide?also finds applications in manufacturing precision instruments, instruments, optical equipment, and the like, as magnetism can affect the accurate measurement and operation of these devices.
Nuclear industry
In the nuclear industry, non-magnetic carbide?can be used for certain nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) equipment and other nuclear magnetic applications to avoid the influence of external magnetic fields.
Mold industry
With the booming development of the magneto-electric industry, the demand for non-magnetic?carbide?molds is increasing, and the size of non-magnetic?carbide?molds is also growing. It’s well-known that under existing production process conditions, manufacturing small-volume WC-Ni alloy products is not a difficult task. However, producing large-volume (over 10 kg in mass) WC-Ni alloy mold materials that are completely non-magnetic and possess excellent mechanical properties is a challenging endeavor.
Based on practical experience, there are three main difficulties:
1Due to the large size, achieving uniform and consistent carbon content throughout the mold material is challenging. This is especially true for production processes that use rubber as a binder, where disparities are more pronounced. The most typical issue is that the surface exhibits normal properties while the interior suffers from carburization.
2The narrow carbon range required for the two-phase alloy with non-magnetic properties makes carbon control extremely difficult in actual production.
3The technical difficulty of preventing cracking during the debinding and sintering processes of large-volume products is high. Therefore, research on non-magnetic?carbide?molds is still in development.









