It is well known that there are two important performance indicators for hard metal alloys: hardness and strength. These two factors are often difficult to balance, much like a seesaw. However, the addition of rhenium to high-temperature alloys can significantly enhance the toughness and high-temperature deformation resistance of materials, including iron-based, nickel-based, and cobalt-based high-temperature alloys.
Characteristics of hyper?carbide
hyper?carbide?materials, built upon the foundation of general hard metal alloy constituents, incorporate one or several refractory high-temperature metallic components from hyper?alloys, such as rhenium, ruthenium, osmium, molybdenum, vanadium, tantalum, niobium, etc. This modification imparts exceptional characteristics including higher strength, hardness, and temperature resistance compared to conventional hard metal alloys.
One particularly notable effect is observed when trace amounts of rhenium are introduced into hard metal alloys. This addition significantly enhances and improves the physical properties of hard metal alloy materials, particularly in terms of red hardness and alloy stiffness (elastic modulus). Rhenium applies a solid solution strengthening effect to the existing binding phase metals (iron, cobalt, nickel series) in hard metal alloys, particularly in the realm of high-speed cutting and precision machining of challenging-to-process materials like nickel-based high-temperature alloys, heat-resistant stainless steels, titanium alloys, tungsten-molybdenum-tantalum-niobium-zirconium-hafnium class special alloys. The utilization of cutting tools and precision molds made from these newly developed hyper?carbide?materials presents an extraordinary cost-performance advantage, replacing conventional tools in a remarkable manner.
The Principle of Rhenium Enhancement in carbide?Performance
People have come to recognize that adding rhenium to the binder of WC-based hard metal alloys can enhance their high-temperature performance.
Figure 1 schematically depicts the W-Co-Re-C phase diagram under conditions of 9wt% Re + 6wt% Co. This diagram, based on literature and experimental results, is compared with a redrawn phase diagram of WC-Co under conditions of 10wt% Co. Considering that the density of Re is significantly higher than that of Co, the WC-Co-Re hard metal alloy with 9wt% Re and 6wt% Co contains almost the same proportion of binder phase in terms of volume as the WC-Co material with 10wt% Co.
From Figure 1, it is evident that the W-Co-Re-C phase diagram differs from the W-Co-C phase diagram. The following are characteristics of the W-Co-Re-C phase diagram:
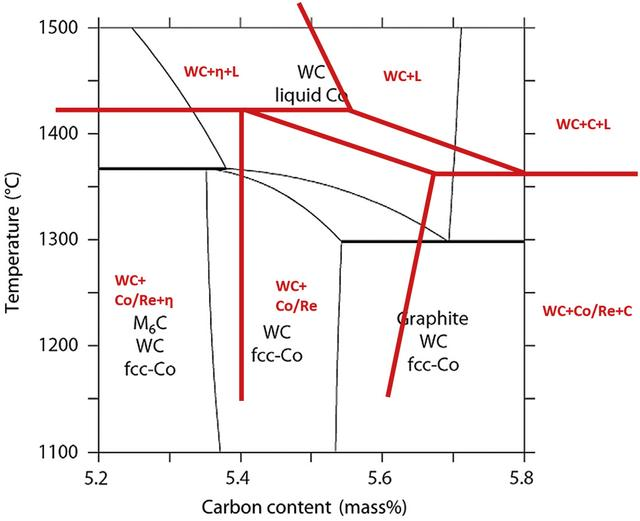
Firstly, in the W-Co-Re-C phase diagram, all melting points shift towards higher temperatures. Therefore, compared to traditional WC-Co materials, WC-Co-Re hard metal alloys require sintering at higher temperatures.
Secondly, for WC-Co-Re hard metal alloys, the two-phase region without the η phase and free carbon slightly shifts towards the higher end at higher carbon contents. This shift is relatively minor but still needs to be considered in the preparation of WC-Co-Re hard metal alloys. It’s worth noting that the width of the two-phase regions in the W-Co-Re-C phase diagram is similar to that in the W-Co-C phase diagram.
Lastly, the addition of rhenium to the binder significantly expands the region where the equilibrium of WC + η phase + liquid phase exists at temperatures above approximately 1430°C. This implies that if medium- to low-carbon and low-carbon content WC-Co-Re hard metal alloys are rapidly cooled from the sintering temperature, they might contain the η phase instead of decomposing into thermodynamically stable WC + Co/Re mixtures. Therefore, post-sintering WC-Co-Re hard metal alloys must be cooled at relatively low cooling rates to ensure complete decomposition of the η phase.
Figure 2 illustrates this, showing that batches of WC-Co-Re with medium to low carbon content contain the encapsulated η phase after rapid cooling, while they don’t contain the η phase after slow cooling.
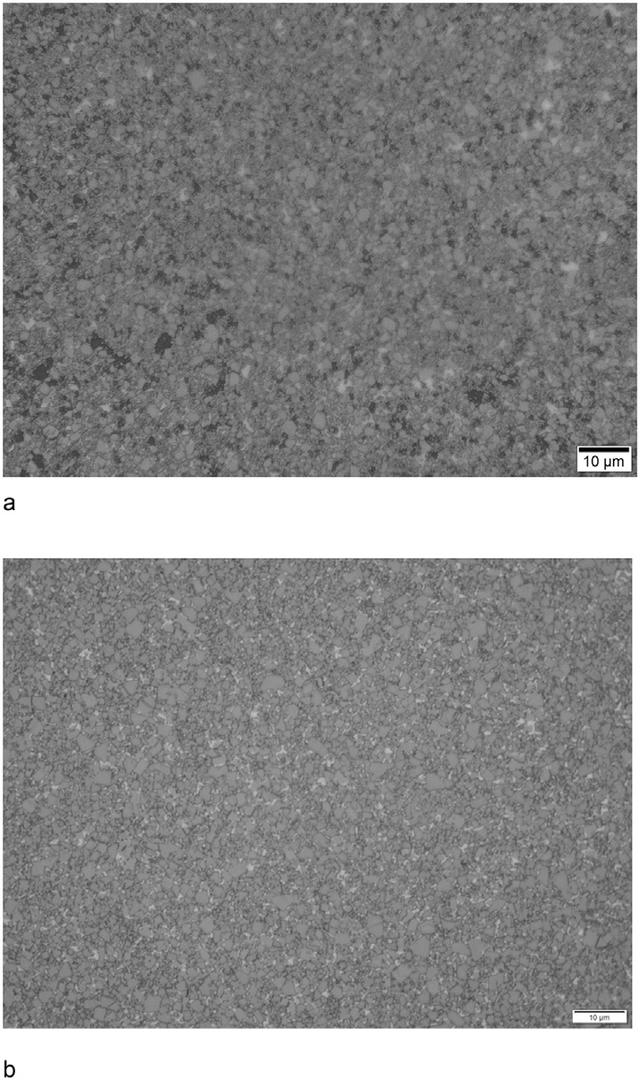
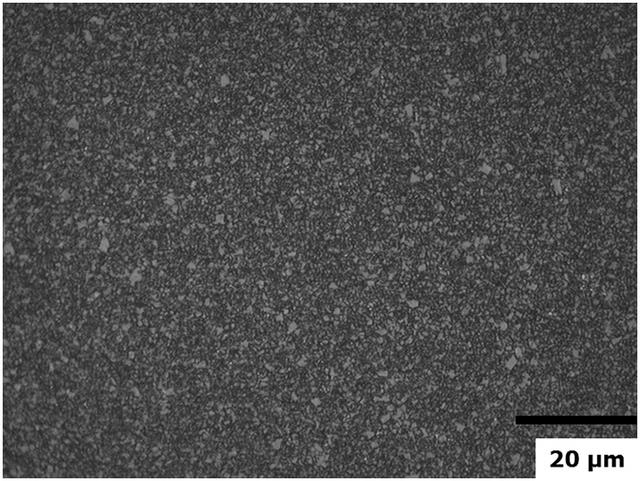
Figures 3 and 4 present the typical microstructures of medium-grained WC-Co-Re hard metal alloy, compared to traditional WC-Co materials prepared from the same level of WC powder. From Figure 3, it is evident that the microstructure of WC-Co-Re hard metal alloy is noticeably finer than that of traditional WC-Co hard metal alloy. Thus, rhenium serves as a potent inhibitor of WC grain growth, restraining the coarsening process of WC. According to research findings, rhenium tends to concentrate at the WC/binder grain boundaries. Therefore, it can be inferred that the role of inhibiting WC grain growth in WC-Co-Re materials is analogous to the inhibitory action of traditional grain growth inhibitors at WC-Co interfaces.
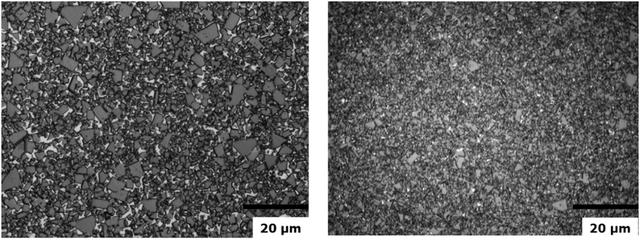
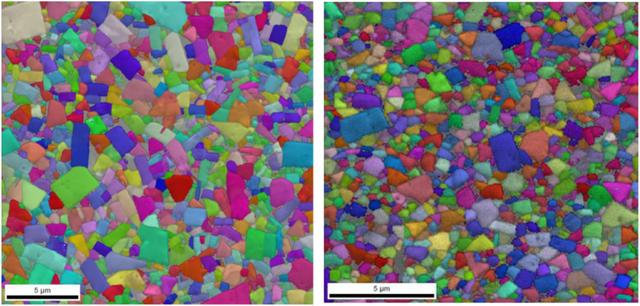
Sub-micron WC-Co-Re hard metal alloys are commonly used in high-temperature and high-pressure components, where the role of rhenium in inhibiting grain growth is crucial. This is significant as it eliminates the need to add conventional grain growth inhibitors to sub-micron WC-Co-Re hard metal alloys. Figures 4 and 5 depict the microstructure of sub-micron WC-Co-Re hard metal alloy without grain growth inhibitors, exhibiting fine and uniform particles without exceptionally large WC grains. The sintering temperature for this hard metal alloy is 1520°C, notably higher than the typical sintering temperature for sub-micron WC-Co alloys.
Performance of hyper?carbide?WC-Co-Re
Research has revealed that WC-Co-Re hard metal alloys exhibit significantly improved physical and mechanical properties at high temperatures. The curves in Figure 6 indicate that the hardness of WC-Co-Re material remains more stable as the temperature decreases (20-800°C) compared to traditional WC-Co hard metal alloys. Operating temperatures of 300°C and 500°C are common for HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature) components. In comparison to conventional WC-Co materials, the hardness of WC-Co-Re hard metal alloy reduces by nearly two times at these two temperatures. Increased thermal hardness is crucial for manufacturing tools used for nickel-based high-temperature alloys or other heat-generating materials. These tools require cutting edges with high thermal stability and mechanical robustness.
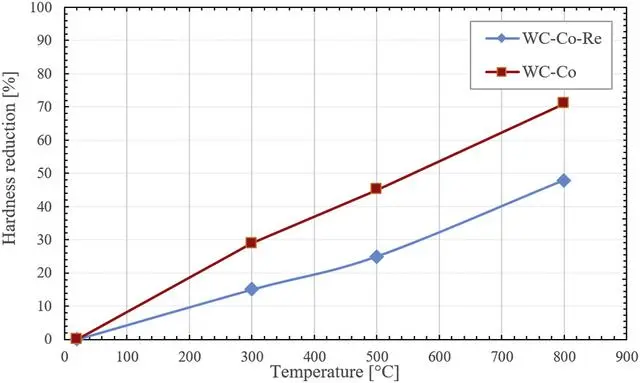
Fig. 6. The hardness variation with temperature when comparing sub-micron WC-Co-Re cemented carbide containing 5. 5 wt % Co + 3. 7 wt % Re with traditional sub-micron cemented carbide containing 6 wt % Co
Figure 6 illustrates the variation of hardness with temperature for sub-micron WC-Co-Re hard metal alloy containing 5.5 wt% Co + 3.7 wt% Re, compared to the traditional sub-micron hard metal alloy with 6 wt% Co.
Based on the previously mentioned higher thermal hardness of WC-Co-Re hard metal alloy, it can be inferred that Re-containing hard metal alloys exhibit improved high-temperature creep resistance. In fact, as depicted in Figure 7, the WC-Co-Re hard metal alloy achieves the same compressive stress rate value under a significantly higher load than conventional WC-Co material. This suggests that the Co-Re binder demonstrates significantly enhanced high-temperature creep performance.
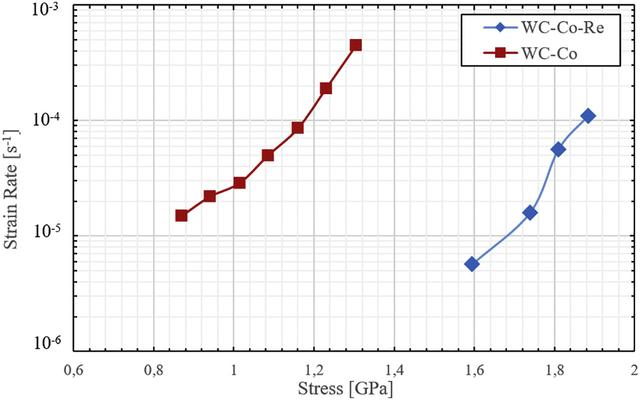
Figure 7 illustrates the relationship between strain rate and compressive stress for WC-Co-Re and WC-Co hard metal alloys at 800°C.









