
Spherical cast tungsten carbide powder is a new type of ultra-wear-resistant ceramic particle material. Compared with traditional tungsten carbide, spherical cast tungsten carbide has two significant advantages: first, it has a regular spherical appearance, good powder flowability, and wettability, which results in good integration with the surrounding tissue when added as particles, reducing the likelihood of stress concentration; second, the internal structure of the tungsten carbide particles is dense, with good toughness, fine grains, high hardness, and the coating has excellent wear resistance and is less likely to break under load. Due to its outstanding performance, spherical cast tungsten carbide powder is gradually replacing traditional tungsten carbide powder in the surface protection of components in mining machinery, oil machinery, construction industry, and foundries, significantly improving the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance of workpieces, and extending the service life of workpieces.
Introduction to the Methods of Spherical Cast Tungsten Carbide
Currently, the spherical cast tungsten carbide powders available in the market are mainly prepared by the following methods: induction remelting spheroidization, plasma remelting spheroidization, and plasma rotating electrode atomization.
The induction remelting spheroidization method involves heating the material in a reactor to the spheroidization temperature through induction heating, and the material moves forward slowly the vibration of the furnace tube. If the dispersion of the material is not well controlled, the molten droplets will grow due to collision and adhesion, making particle size control difficult. Moreover, during the operation, the powder must not come into contact with the reactor, otherwise it will affect the entire spheroidization process and cause material waste.
The plasma remelting spheroidization method uses casting tungsten carbide powder as the raw material and employs radiofrequency plasma flame to heat argon gas to a high temperature of 3000 to 10000 ℃, melting the casting tungsten carbide particles into a liquid state and directly quickly condensing them into spherical particles. This method can easily obtain fine-grained spherical tungsten carbide powder by controlling the particle size and composition of the raw material.
The plasma rotating electrode atomization method uses a tungsten carbide rod as the electrode, fixed within the rod material bin, and then subjected to plasma atomization under inert gas protection. The plasma arc melts the end face of the high-speed rotating rod, and under the action of centrifugal force, the molten droplets separate from the edge of the molten pool and solidify in the form of spherical particles. This technology avoids the difficulty of material dispersion at ultra-high temperatures during remelting spheroidization, and the obtained spherical tungsten carbide powder has a narrow particle size distribution range and is easy to control.
The following will study the chemical composition, micro-morphology, microstructure, microhardness, and other powder properties of spherical cast tungsten carbide powders prepared by different methods.

Chemical composition
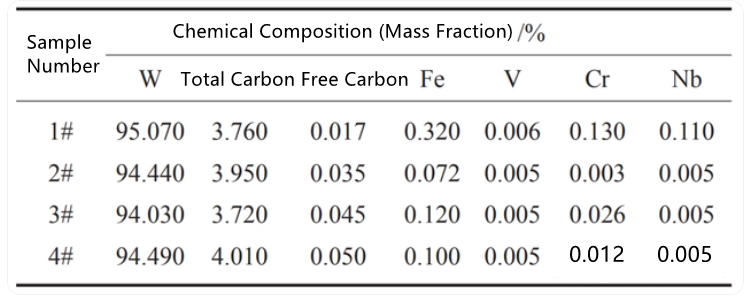
The table above shows the chemical composition of spherical cast tungsten karbür powder samples prepared by different methods. It can be observed that the main components of the spherical cast tungsten carbide powder are W and C elements, and all contain trace amounts of Fe, V, Cr, and Nb elements. The ideal spherical cast tungsten carbide should be a eutectic of WC and W2C, with an eutectic temperature of 2525 ℃ and a carbon content of 3.840% (by mass) at the eutectic point. From the data in the table, it can be seen that the total carbon content of the spherical cast tungsten carbide prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the smallest deviation from the theoretical eutectic carbon content, with the lowest free carbon content; the powder obtained by the induction remelting spheroidization method has the largest difference in total carbon content from the theoretical value, with a difference of 0.170% (by mass). This is due to the carbon content increase caused by the graphite tube heating method used in the induction remelting spheroidization process. In addition, by comparing samples 2#, 3#, and 4# with similar particle sizes, it can be determined that the powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the relatively lowest impurity content. However, the impurity content of sample 1# prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method is relatively high, which may be related to the quality of the cast tungsten carbide raw material rod. This suggests that, compared to other methods, the plasma rotating electrode atomization method can more accurately control the carbon content of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder, preventing overeutectic and hypoeutectic reactions caused by carburization and decarburization, and obtaining a nearly complete eutectic structure, which is crucial for improving the microstructure and properties of spherical cast tungsten carbide.
Microscopic morphology
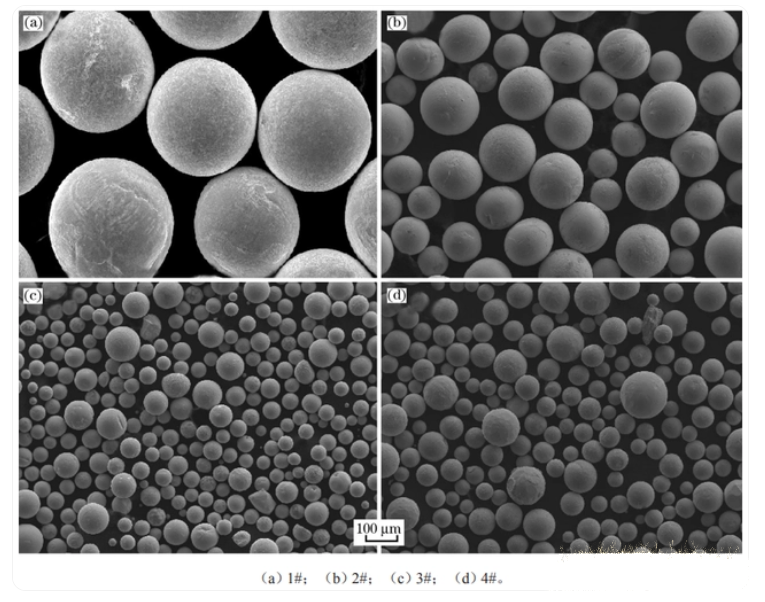
The image above shows the microscopic morphology of spherical cast tungsten carbide powders prepared by different methods. It can be observed that the spherical cast tungsten carbide powders prepared by the three methods are all regular and smooth, nearly spherical in shape.
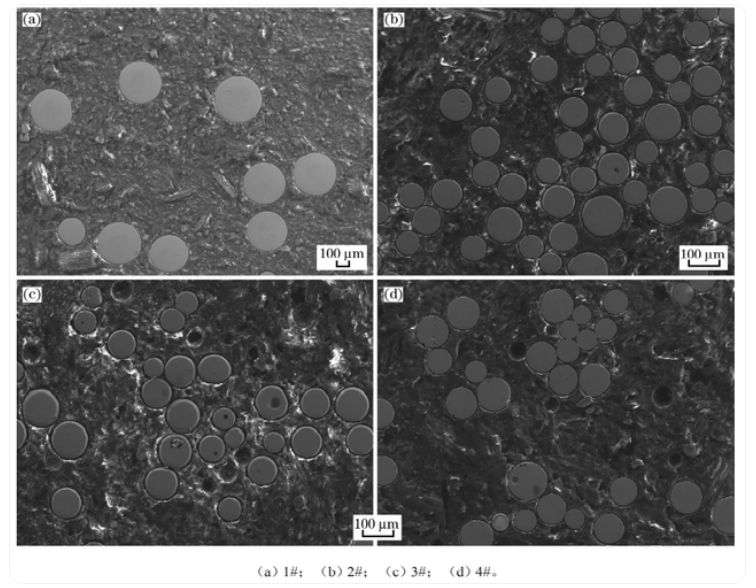
The image above shows the cross-sectional photos of spherical cast tungsten carbide powders prepared by different methods. As can be seen from (a) and (b), the spherical tungsten carbide powder particles prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method are dense with almost no defects. However, as seen in (c) and (d), there are some obvious pores within the spherical tungsten carbide powder particles prepared by the plasma remelting spheroidization method and the induction remelting spheroidization method, resulting in some hollow powders. The main reason for this is that the crushed tungsten carbide powder material used in the above methods is likely to contain residual pores from the casting process. During the short plasma or induction heating process, the interior of the crushed tungsten carbide powder is difficult to completely melt, leading to some residual pores within the particles.
Microstructure
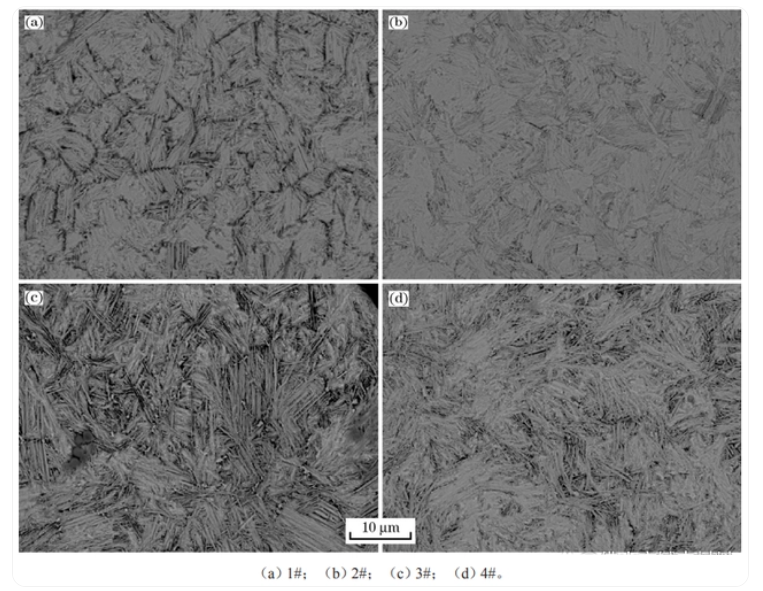
The image above shows the microstructure photos of spherical cast tungsten carbide powder particles after corrosion. It can be observed that the internal structure of the spherical tungsten carbide powder particles prepared by the three methods mainly consists of a typical fine acicular WC and W2C eutectic structure. Compared to the plasma remelting spheroidization method and the induction remelting spheroidization method, the spherical cast tungsten carbide powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has a denser eutectic structure. This is because, unlike the plasma remelting spheroidization method and the induction remelting spheroidization method, the plasma rotating electrode atomization method completely melts the cast tungsten carbide feedstock rod and then solidifies by being thrown out under the action of centrifugal force. During the crystallization of the molten cast tungsten carbide, the degree of undercooling is greater, nucleation is more rapid, and a larger number of crystal nuclei are generated, resulting in a finer and denser eutectic structure.
Microhardness
The table below shows the average microhardness of spherical cast tungsten carbide powders prepared by different methods. It can be seen that the microhardness of the spherical cast tungsten carbide powders prepared by the three methods is all above 2800 HV0.1, with the powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method having the highest microhardness, reaching 3045 HV0.1. This is mainly due to the finer eutectic structure within the spherical cast tungsten carbide prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method.
Other Physical Properties of spherical cast tungsten carbide
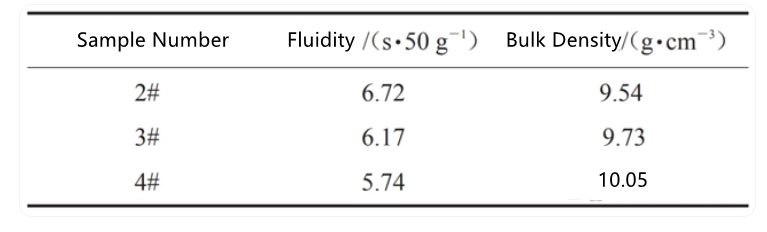
The table below shows the flowability and apparent density values of spherical cast tungsten carbide powders prepared by different methods. It can be seen that the powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the worst flowability and the smallest apparent density; whereas the powder prepared by the induction remelting spheroidization method has the best flowability and the largest apparent density.
??züm
(1) The spherical cast tungsten carbide prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method has the smallest deviation from the theoretical eutectic carbon content, the lowest free carbon content, and relatively low impurity content.
(2) The spherical tungsten carbide powder particles prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method are dense with almost no defects, and the eutectic structure is finer. The spherical tungsten carbide powder particles prepared by the plasma remelting spheroidization method and the induction remelting spheroidization method both have some obvious pores, resulting in some hollow powders.
(3) The spherical cast tungsten carbide powders prepared by the three methods mainly consist of WC and W2C phases.
(4) The microhardness of the spherical cast tungsten carbide powders prepared by the three methods is all above 2800 HV0.1, with the powder prepared by the plasma rotating electrode atomization method having the highest microhardness, reaching 3045 HV0.1. The powder prepared by the induction remelting spheroidization method has the best flowability and the largest apparent density.









