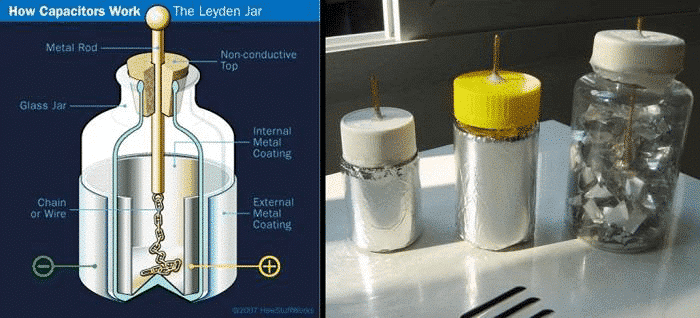
The concept of capacitors has been around for a long time. It was first known as the Leiden bottle. Its prototype is a glass bottle containing a hydrolyzed acid dielectric. The conductor immersed in acid and the metal foil coated on the outside of the glass bottle serve as two electrodes. The glass in between is used as a dielectric material, as shown in Figure 1. Berker filed a patent in 1757, describing that the electrical energy in the primary cell is stored by the charge stored in the dual cell immersed in the aqueous dielectric porous carbon material interface. What is an electrochemical capacitor (aka supercapacitor)? The first to be named is a large-capacity capacitor (per gram of farad capacity) developed by a hafnium oxide film system and a carbon double layer. How is such a large charge capacity achieved? Next we will find out what is going on.
Figure 1 Principle and physical map of the Leiden bottle
I. Classification and principle
Electrochemical capacitors are known to have several notable features: high power density (fast charge and discharge, second order), long cycle life, and relatively large energy density (slightly less than lithium-ion batteries), all of which depend on the energy storage mechanism. According to the principle of energy storage, electrochemical capacitors are generally divided into electric double layer capacitors and Faraday tantalum capacitors. Of course, mixing the two together is also called a hybrid capacitor. What are their respective energy storage mechanisms and how are they different from lithium-ion batteries? Below we briefly understand some of the basic energy storage principles and the difference with lithium-ion batteries, as shown in Figure 2.
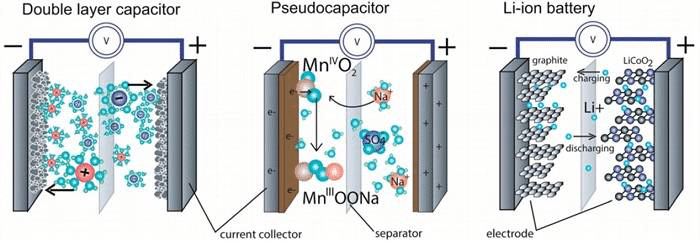
Fig. 2 Comparison of basic composition and energy storage mechanism of electric double layer capacitor, Faraday tantalum capacitor and lithium ion battery
In an electric double layer capacitor, charges are concentrated in a region near the surface, attracting positive and negative ions in the electrolyte, and thus an electrostatic field is formed between the electrode and the electrolyte for energy storage. Both poles each have a positive and negative charge pair, so it is called an electric double layer capacitor. This reaction is highly reversible physical adsorption, excellent cycle stability (> 100,000 times), and the rate of charge and discharge is extremely fast, but the energy is not high due to the limited charge. In a Faraday tantalum capacitor, a charge passes through the interface of the electrode electrolyte, and a surface of the variable valence substance in the electrode or embedded therein causes a redox reaction to combine with ions in the electrolyte to realize storage of the charge. The energy storage mechanism is different from the traditional electric double layer energy storage. Because some of these redox reactions are rapid reversible reactions on the surface of the electrode, and some are embedded reactions with a certain phase change, the cycle stability is worse than that of the electric double layer capacitor, but the stored energy is improved. For a lithium ion battery, it mainly relies on lithium ions in the electrolyte to be embedded and removed in the layered structure of the positive and negative electrodes during charge and discharge to realize charge storage and release. Under this mechanism, the stored energy is very large, but due to the phase change process, the charge transfer speed is slow, and the structure is easily collapsed, so the cycle performance is not high.
2.structure and development
The basic structure of the electrochemical capacitor is shown in FIG. 2, and mainly includes an electrode, an electrolyte, and a separator insulated between the two electrodes. Electrode materials and electrolytes are the two most important components, and the research obtained is very systematic. The following is a brief introduction to the research progress of the main electrode materials and electrolytes.
Electrode material
Research on electrode materials has been very mature. Most of the original electric double layer capacitors used carbon materials such as porous carbon, carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes and graphene. Although the carbon material has a small capacity and a low energy density, its load on the conductive substrate can be very high, which makes it widely and deeply applied in the field of commercialization. Of course, researchers have recently begun to activate carbon materials to achieve higher energy densities, which is expected to significantly increase the performance level of commercial grade carbon.
Due to the limited capacitance of carbon materials and insufficient energy storage, tantalum capacitors have gradually become a research hotspot. The main materials explored include metal oxides, conductive polymers, metal nitrides and, more recently, the study of hot metal carbides. The earliest widely studied is yttrium oxide, which has excellent electrochemical performance, but it is gradually gaining attention due to its low yield and high price. Many metal oxides are superior in performance, but have the disadvantage of poor electrical conductivity, which greatly affects the characteristics of rapid charging and discharging of electrochemical capacitors. The conductivity of the conductive polymer is superior to that of most metal oxides, and the performance is similar, but there is a problem that the cycle stability is poor. Metal nitrides have superior electrical conductivity and good energy storage capacity, but are easily oxidized during electrochemical cycling to reduce electrical conductivity, and cycle performance is not guaranteed. Metal carbides or carbonitrides and corresponding layered materials (such as Mxene, etc.) have received extensive attention from researchers in recent years and have great potential for development.
Electrolyte
The electrolyte system of electrochemical capacitors is gradually maturing with the development of electrodes. From the perspective of large classification, the electrolyte mainly includes an aqueous electrolyte and an organic electrolyte. The water-based electrolyte includes acid, acid and neutral, and has high ion conductivity, but is limited by the decomposition voltage limit of water (1.23 V), and its working voltage is low. Water-based electrolytes are used more in scientific research, but there are few commercial products. The type of organic electrolyte is relatively large, and its biggest characteristic is that the limit voltage is much higher than that of the aqueous electrolyte (2.7-3.7 V). Therefore, a high operating voltage can help the supercapacitor greatly increase its energy density. In commercial electrochemical capacitors, the vast majority of organic electrolytes are used.
Development of electrochemical capacitor structure
With the deepening and specificity of the research work, the shape of the device of the electrochemical capacitor has also developed a lot. The first commercially available supercapacitors were mainly of the wound type and the button type (same structure as the conventional battery), as shown in Figure 3.
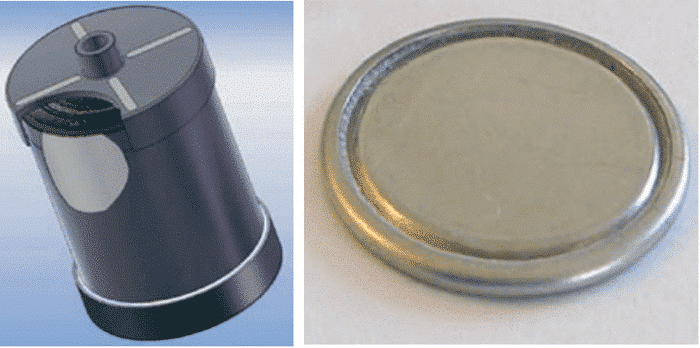
Figure 3 Winding and button type supercapacitors
With the gradual increase of demand, there are some shortcomings in the application surface of electrochemical capacitors for hard substrates. Flexible portable supercapacitors have become a research hotspot. The main advancement is that the substrate is a flexible conductive material such as carbon cloth, carbon paper, nickel foam, flexible metal sheets and self-supporting CNTs, etc., as shown in FIG4.
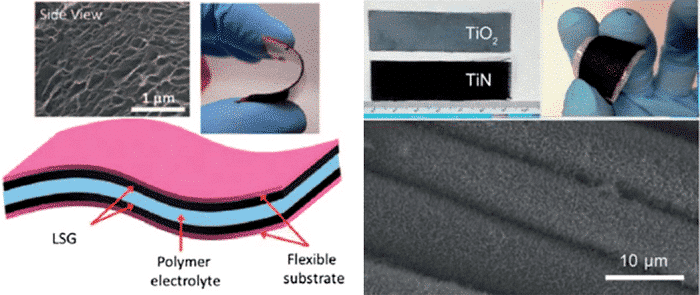
Figure 4 Flexible electrode materials for several flexible supercapacitors
The flexible supercapacitor can realize the convenient carrying of the energy storage unit, and the flexible electrochemical capacitor as shown in FIG. 5 drives the electronic watch as a watchband at the same time.
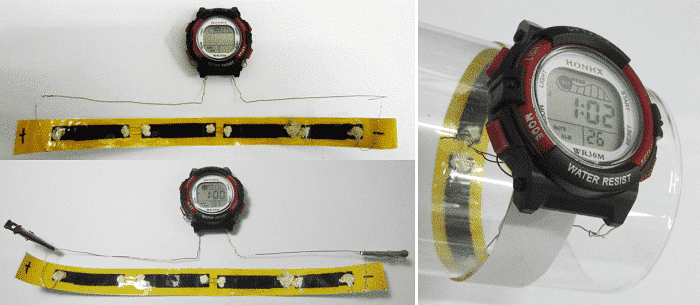
Figure 5 Some applications of two-dimensional flexible supercapacitors
Further, when it comes to wearable devices, the two-dimensional flexible substrate is still insufficient to meet any need for weaving. At this time, one-dimensional linear supercapacitors have also been developed. The effective weaving of the garment can be achieved by using these linear supercapacitors, as shown in some of Figure 6.
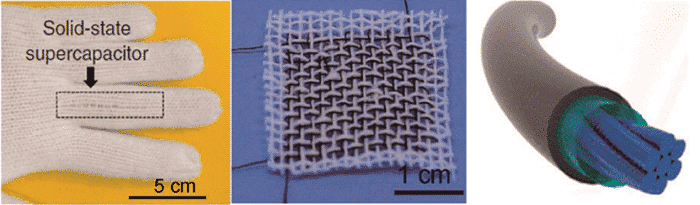
Figure 6 Weaving display of one-dimensional linear supercapacitor
3. the future and prospects
How will the future of supercapacitors develop? It is an energy storage device, but due to its principle limitation, the storage capacity is hard to exceed the battery (if it is more than a super capacitor), it should not have the same effect as the battery, but should be used as a battery. A powerful addition to the main power source. In this case, its development naturally depends on demand. When solar energy or wind power is used to store energy, its power is increased; when it is used as a backup power source, its energy storage is maximized. In short, it is to follow the needs.
I believe that in the near future, electrochemical capacitors will become an indispensable item in daily life, such as batteries, and become our good helper!









