When a point of the component is subjected to a sufficiently large disturbance stress, a crack is formed after a sufficient number of cycles, and this phenomenon is called fatigue. Fatigue fracture is the main cause of failure of engineering structures and components. In the current application and research, there are four main types of fatigue testing methods:
1. Nominal stress and strain method;
2. Local stress and strain method;
3. Energy method;
4. Fracture mechanics method.
This article briefly introduces the four types of methods and their applications.
1. Nominal stress method
The nominal stress method is a method of applying a rated stress test to a standard component, and is classified into stress fatigue and strain fatigue according to the relationship between the maximum cyclic stress and the yield stress.
First, stress fatigue is introduced, which is defined as stress fatigue if the maximum cyclic stress Smax is less than the yield stress Sy. Due to the stress fatigue test, the material life is more than 104 times, so stress fatigue is also called high cycle fatigue. According to the theory of stress fatigue, the stress S of the metal material and the number N of cycles of the failure are nonlinearly distributed. Available power functions: take the logarithm: , or use exponential: take the logarithm to represent, this method is called S-N method. The results were analyzed using the S-N curve, or the p (survival rate)-S-N curve in the actual test.
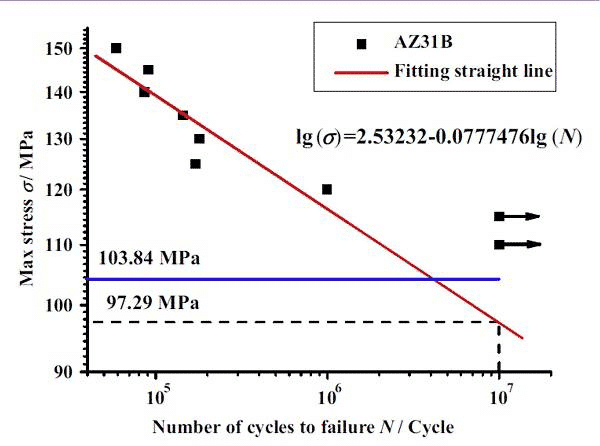
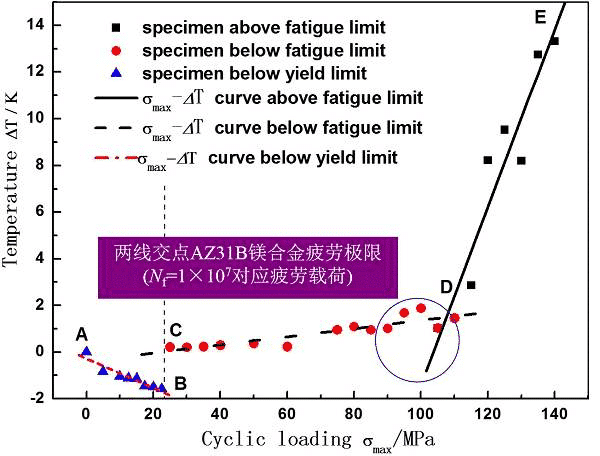
Stress fatigue is generally used for the material fatigue S-N curve. As shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2, the fatigue limit of the AZ31B magnesium alloy (the stress ratio is 0.1 and the fatigue life is 107 corresponding to the fatigue load) is tested by the lifting method. The fatigue limit of the AZ31B magnesium alloy sample in the figure is 97.29 MPa.
Figure 1. AZ31B magnesium alloy fatigue test
Figure 2. AZ31B magnesium alloy fatigue test S-N curve
Strain fatigue is applied to the testing of high load, low design life components. The definition is: if the maximum cyclic stress Smax is greater than the yield stress Sy, it is strain fatigue. The stress fatigue test is used to study the component at high load and low frequency. For example, during the service life of the pressure vessel, the total number of cycles is on the order of 104. Therefore, strain is used as the fatigue performance parameter description. Stress fatigue is also known as low cycle fatigue.
Based on strain fatigue research scholars put forward the following theory, the stress-strain (Remberg-Osgood elastoplastic stress-strain) relationship of materials:
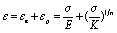
In the formula, the εe elastic strain amplitude, εp is the plastic strain amplitude.
In the constant amplitude symmetric strain test, due to the plastic deformation of the material, the stress cannot be reduced by the original path when the strain is reduced, and the stress-strain curve is annular. This curve is called the hysteresis loop. As the number of cycles increases, the same strain amplitude stress will increase or decrease. The response of this stress corresponding to the change is called cyclic hardening or cyclic softening. The cycle is enough for several cycles, and some materials will form a stable hysteresis loop.
In strain fatigue, a stress-strain curve is used to describe the cyclic hardening or cyclic softening tendency of the material. For materials with a symmetrical hysteresis loop curve, it is called Massing material.
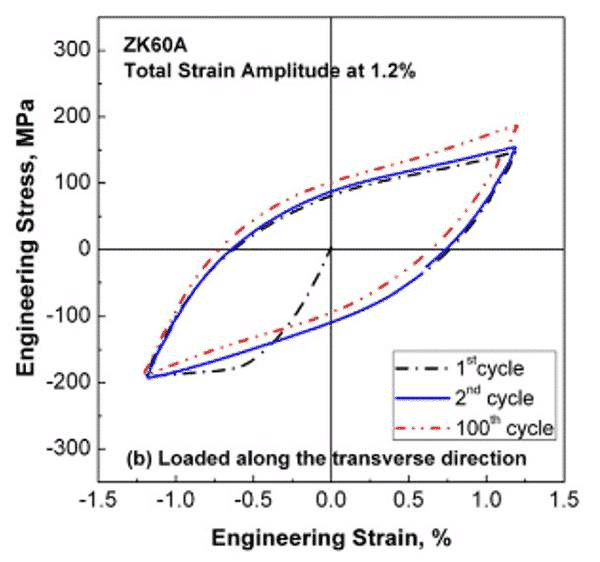
The figure below shows the σ-ε curve of ZK60 magnesium alloy loaded in the rolling direction and transverse direction. In the lateral direction, the cyclic hardening phenomenon is obvious.
Figure 3. ZK60A magnesium alloy load along the rolling σ-ε curve
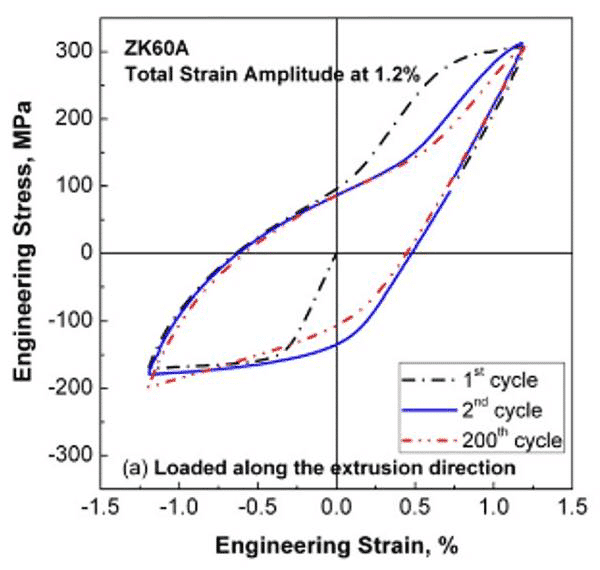
Figure 4. ZK60A magnesium alloy load along the transverse σ-ε curve
2. Local stress and strain method
For the notched specimens and the stress-concentrated components, the local stress-strain analysis is used. The current research shows that the fatigue life of the members is the local maximum strain and stress, and the concept of stress concentration factor is proposed. It is suitable for calculating the life of material crack formation and the prediction of residual fatigue life of components.
The theory proposed by the local stress method has the Neuber formula (stress concentration formula)
Minner theory (fatigue cumulative damage theory): The fatigue life of a member under constant stress S is N, then the damage through n cycles is:
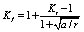
If subjected to ni cycles under k constant stress Si, the total damage can be defined as:
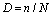
The damage criteria are:
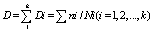
The application of the local stress method is shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
Figure 5. Fatigue life prediction of notched specimens
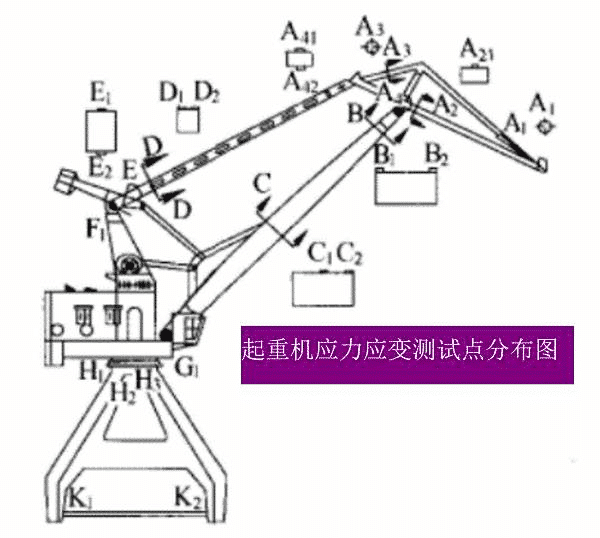
Figure 6. Crane fatigue life prediction (crane stress and strain test point distribution map)
The stress concentration point fatigue life is calculated according to the following formula:
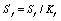
Where: Sf – equivalent stress smooth sample fatigue life
Figure 6 The fatigue life calculation method of the crane is to input the time history map of different test points and input the fatigue life equation of each point, and calculate the residual fatigue life of each point. The default life minimum point is the remaining fatigue life of the device. For cranes, scholars have suggested that the cumulative damage value D of ordinary steel reaches 0.68.
3.energy method
Infrared thermography is a method for predicting fatigue performance based on the energy constant law of material fatigue process. The fatigue thermal imaging method is based on the thermodynamic energy U, kinetic energy K and other forms of energy dissipation in the process of fatigue. The sum of the energy changes E and the thermal change Q absorbed or dissipated by the object should be the work W acting on the object. the same.
Fatigue thermal imaging has the advantages of non-destructive, real-time, non-contact. At the same time, due to the nonlinear relationship between energy dissipation and fatigue load, and the error of temperature dissipation using heat dissipation, it is still not suitable for industrial measurement.
The current research has proposed the following predictive model theory, Luong method, ?Tmax and fatigue life Nf are as follows:
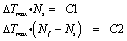
Where: C1, C2 are constants.
Therefore, the fatigue limit can be predicted by the two-wire method. Based on the heat dissipation, scholars have proposed the following models:
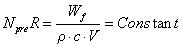
R-temperature rise slope
The following is a study of the fatigue thermal imaging method by the team of teacher Zhang Hongxia from Taiyuan University of Technology. The fatigue life of AZ31B Mg alloy was quickly predicted by thermal imaging. It is only necessary to test the temperature rise of the first stage of the sample to predict the fatigue limit of the material according to the two-line method. Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, respectively.
Figure 7. Surface temperature of AZ31B magnesium alloy sample with different cycle times in fatigue test
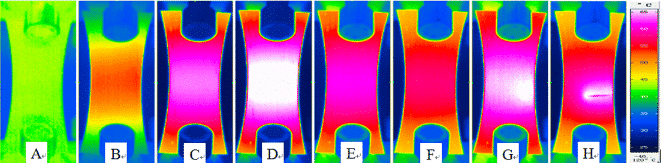
Figure 8. AZ31B fatigue process sample surface temperature curve
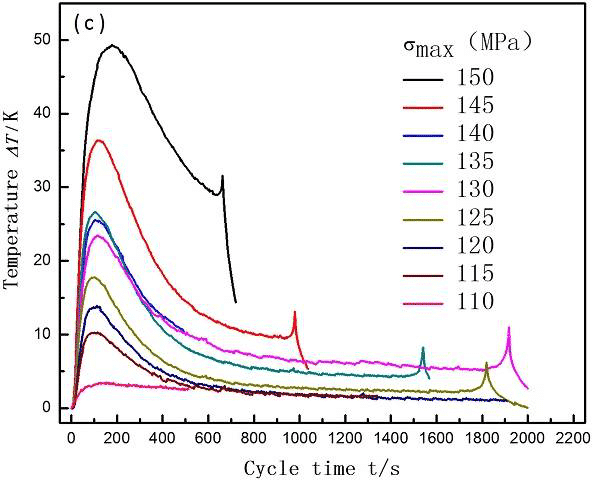
Figure 9. The variation of temperature with fatigue load
4. Fracture mechanics method
Linear elastic fracture mechanics is the theoretical basis for studying fatigue crack growth. Fatigue crack propagation can also be quantitatively described by the stress intensity factor K.
Under the fatigue load, the rate of change a of the crack length a with the number of cycles N, da/dN, is the rate of fatigue crack growth, reflecting the speed of crack propagation. For a given crack length a, da/dN increases with increasing cyclic stress amplitude ?σ (the larger ?σ, the larger ?K). Based on this phenomenon, scholars have studied da/dN-?K (crack propagation). The rate-stress intensity increase curve, the curve can be divided into three zones: low rate, medium rate, high rate zone. The Paris formula states that there is a linear relationship between the stable extension of the medium rate:
Empirical formula for the shape of the crack tip:
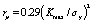
Fatigue crack formation and expansion can be unified under the framework of damage mechanics.
The following is a study of the crack growth rate of AZ31B magnesium alloy, and evaluate the stable expansion rate of AZ31B.
Figure 10. Schematic diagram of the fatigue crack tip competition mechanism
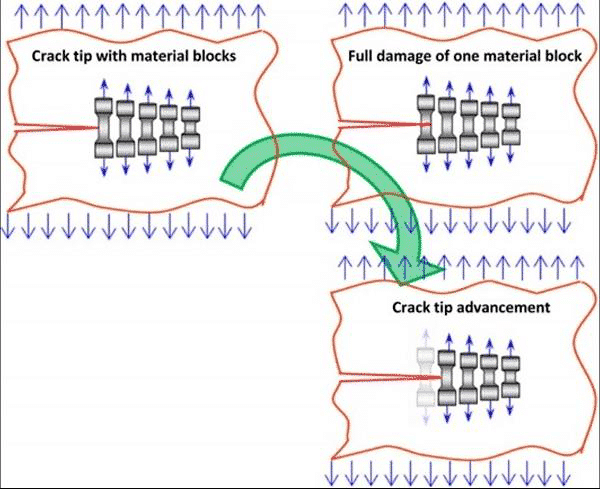
Figure 11. Schematic diagram of three different regions of the stress-strain field at the crack tip
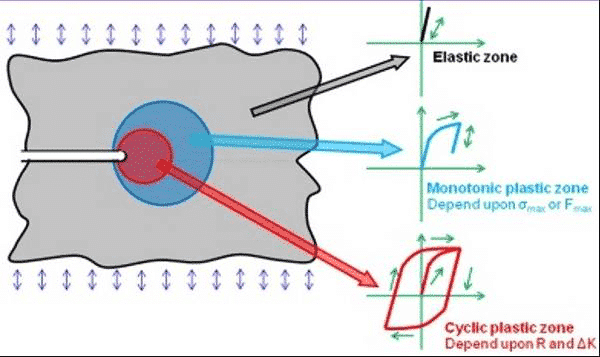
Figure 12. Schematic diagram of the a-N curve of the fatigue crack tip competition mechanism
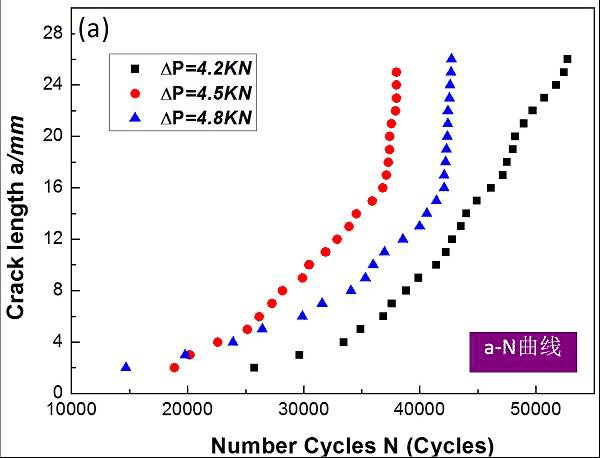
Figure 13. Schematic diagram of da/dN-ΔK curve for fatigue crack tip competition mechanism
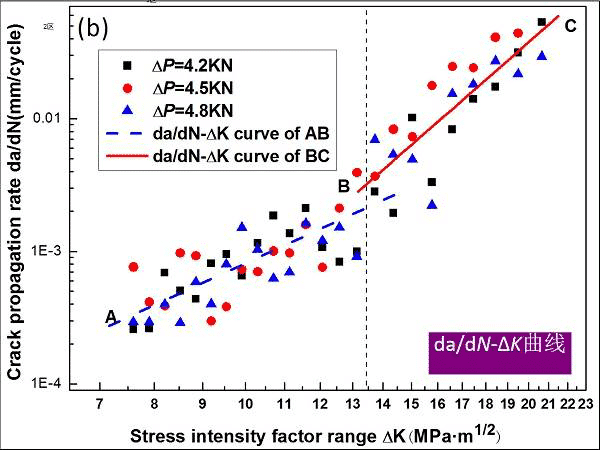
AB segment (medium rate zone):da/dN=4.57×10-7(ΔK)3.25 (7.2<ΔK≤13.5 MPa?m1/2)
BC segment (high rate zone):da/dN=3.16×10-10(ΔK)6.21(13.5<ΔK≤22.1 MPa?m1/2)
Conclusion:
The four types of methods are different in application. The nominal stress method and the local stress method are suitable for the material and component performance test in the industrial field. The energy method can predict the fatigue life of the material, and the fracture mechanics method successfully unifies the fatigue crack formation and expansion.









