Introduction
Usually, the metal material is a polycrystal composed of a large number of crystal grains. When the grain orientation of a polycrystal is concentrated around a certain reference plane (or direction) of a macroscopic material, it is called a preferred orientation, and the texture is Preferred orientation of polycrystals. In a broad sense, the phenomenon that the grain orientation deviates from the random distribution in the polycrystal can be called texture.
In metallic materials, the existence of texture phenomena is universal. The external temperature field, electromagnetic field, strain field and anisotropy inside the crystal can cause texture. For example, the preferred orientation of the grain during deformation is the crystal slip/slip surface and the moment effect during stretching. the result of. Industrial materials commonly have casting texture, deformation texture, recrystallization texture and phase change texture, among which the deformation texture and recrystallization texture are studied more.
Texture representation
(1) Description of crystal orientation and common types of texture
The so-called crystal orientation refers to the three crystal axes of the crystal (such as [100], [010], [001] axis) in a given reference coordinate system (such as rolling direction RD, lateral TD and normal ND in the rolling plate) The relative orientation within. When actually describing the crystal orientation, different reference frames are set due to different deformation conditions. For example, for the most common rolling deformation, the three axes of the reference frame are usually set to the rolling direction (RD) and the rolling surface. The direction (ND) and the transverse direction of the rolled sheet, that is, the direction perpendicular to the rolling direction (TD), assuming an orientation is expressed as (110) [1-12], indicating the (110) plane of the unit cell at this time. Parallel to the rolling surface, the [1-12] direction is parallel to the rolling direction.
The type of texture mainly depends on the nature of the metal and the processing method, etc. Among them, there are rolling texture, drawing texture and the like. The rolling texture is the texture that occurs during rolling deformation. It is characterized in that a certain crystal plane {hkl} of each grain is parallel to the rolling surface, and a direction <uvw> is parallel to the rolling direction. The rolling texture is usually expressed as {hkl}<uvw>. Unidirectional stretching and drawing deformation cause a certain direction of the polycrystalline grains to be parallel to the stretching or drawing direction. The texture thus formed is called silk texture, also called fiber texture, parallel to stretching. Or the crystal orientation <uvw> of the drawing direction.
(2) pole figure
The pole figure is an orientation distribution pattern representing a selected crystal plane {hkl} of each grain in the material to be tested on the polar projection projection map containing the direction of the sample coordinate system. This figure is called a {hkl} pole figure. Figure 1 is the {111} pole figure of the Cu-30%Zn alloy after 96% rolling. It can be known from the orientation analysis that the texture component in the material is mainly {110}<1-12> texture. Also known as brass texture.
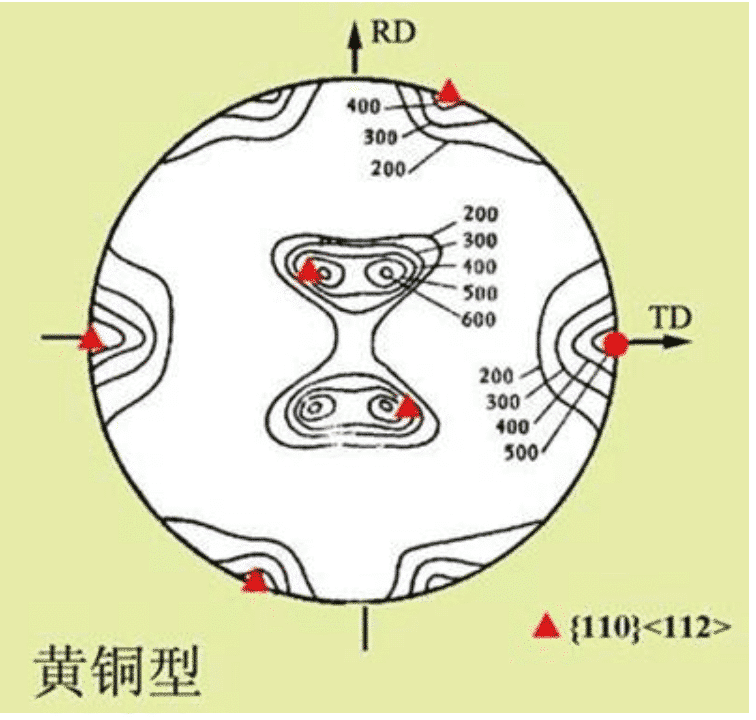
Fig.1 {111} pole figure of Cu-30%Zn alloy after 96% rolling
(3) inverse pole diagram
In contrast to the pole figure, the inverse pole figure is a graph depicting the spatial distribution of a certain appearance characteristic of a polycrystalline material parallel to the material in the crystal coordinate system. The three axes of the reference coordinate system generally take the three crystal axes of the crystal or the low-index crystal orientation. For the cubic system, since there are 24 symmetry, only the part of [001]-[101]-[111] is selected. Describe. The inverse pole figure is generally used to describe the silk texture. Figure 2 shows the reverse pole figure of a hot rolled low carbon steel parallel to the normal ND direction. It can be seen that there are <111> and <100> silk weaves in the material. Structure.
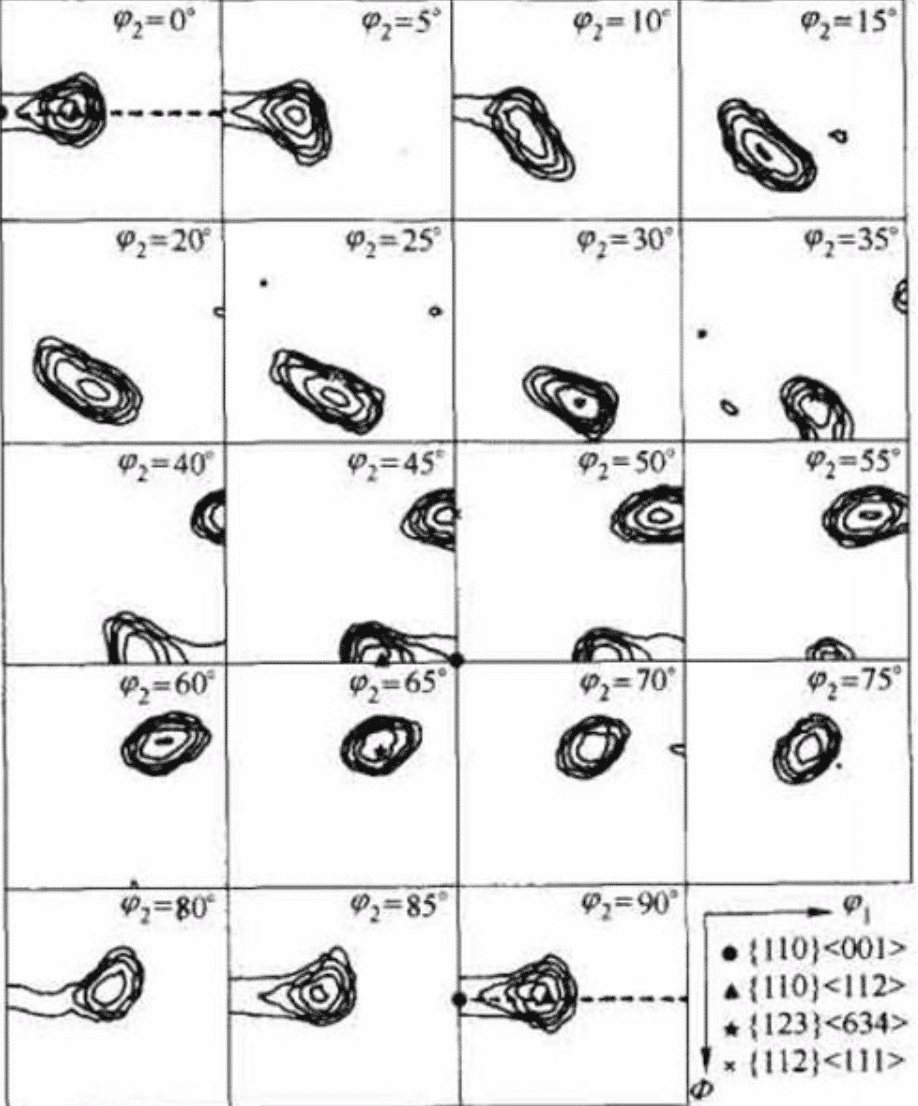
Figure 2 ND reverse pole diagram of hot rolled mild steel
(4) Orientation distribution function
Pole and inverse pole figures use two-dimensional graphics to describe the orientation distribution of three-dimensional space, and they all have limitations. The distribution density f(g) of the spatial orientation g(φ1, Φ, φ2) can express the orientation distribution of the entire space, which is called the spatial orientation distribution function (ODF). The ODF is a three-dimensional figure calculated from the polar density distribution of the pole figure. Since it is inconvenient to use a three-dimensional diagram, it is generally represented by a set of sections fixed by φ2. Figure 3 shows the ODF of industrial pure aluminum after cold rolling by 95% deformation.
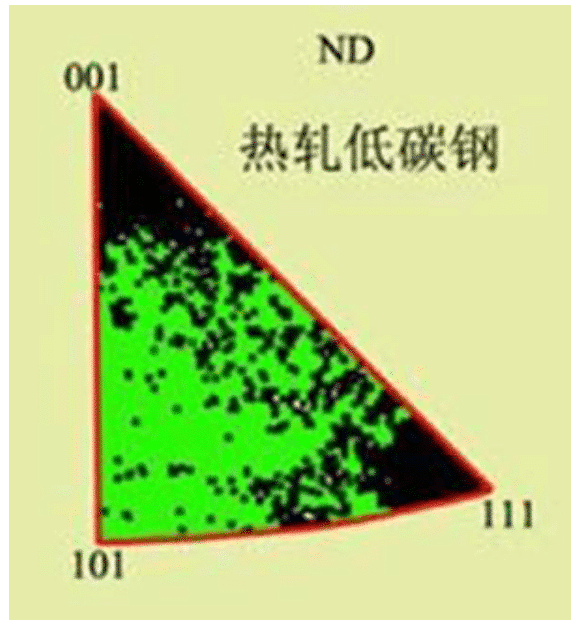
Fig. 3 ODF diagram of industrial pure aluminum after cold rolling with 95% deformation
Texture impact on performance
A large number of experimental results show that the properties of materials are 20%-50% affected by texture, and the texture affects the mechanics of elastic modulus, Poisson’s ratio, strength, toughness, plasticity, magnetic properties, conductance, and coefficient of linear expansion. Performance and physical properties, here are some examples of the effects of texture on material properties.
The most studied is the influence of texture on the static mechanical properties of the material. Figure 4 shows that a commercial magnesium alloy produces a strong base texture under the influence of the friction stir welding process, so that different parts of the material are pulled in different directions. The stretch performance shows a difference. For example, in the case of a sample processed by a friction welding (FSP) process, the tensile strength of the material in the width direction of the sample, that is, the transverse direction (TD), is significantly higher than the processing direction (PD), exhibiting remarkable anisotropy.
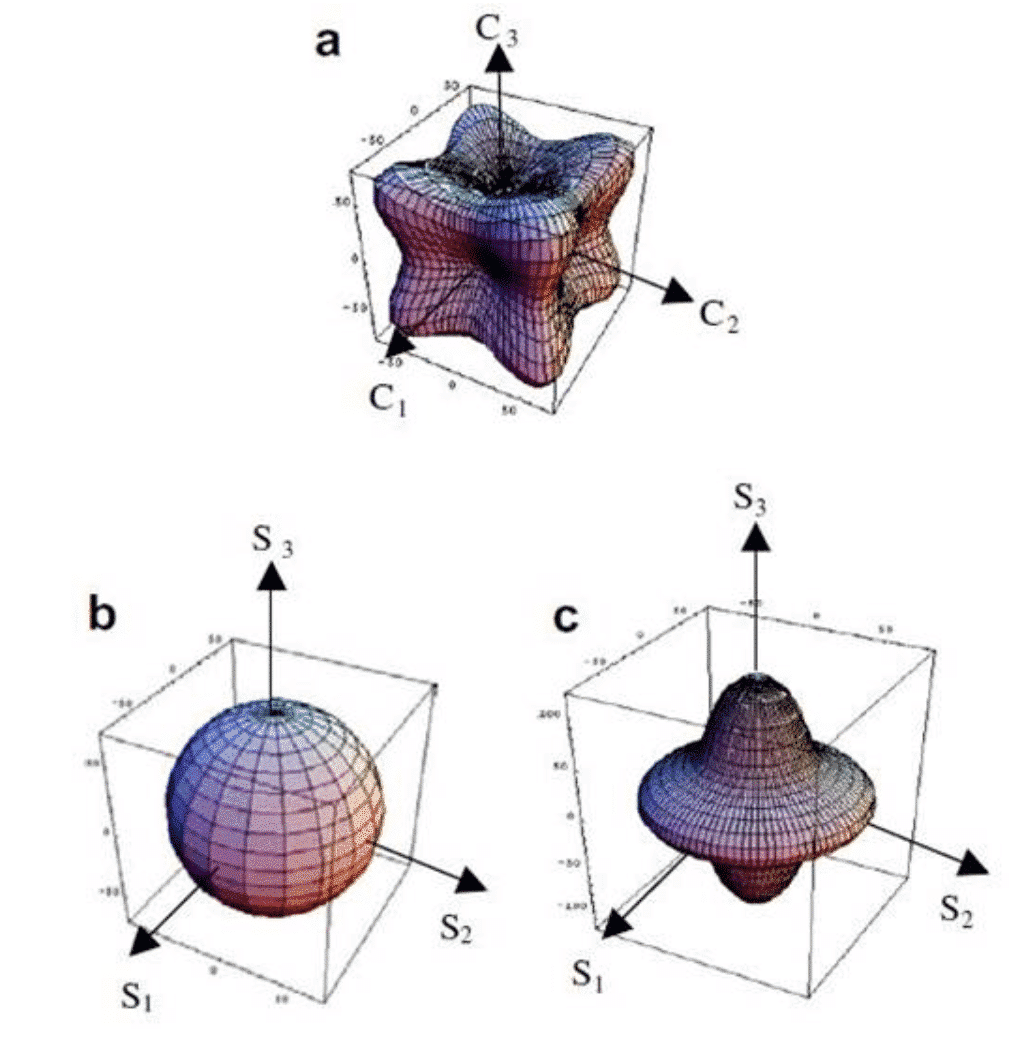
Fig.4 Tensile properties of different sample orientations after AZ31 magnesium alloy in original rolling state and friction stir welding
Texture also affects the elastic properties of the material. Figure 5 shows the effect of texture on the elastic modulus of a gold film. The three figures in the figure show the single crystal gold in the crystal coordinate system. The texture of the non-textured gold film in the sample coordinate system and the elastic modulus parameter of the gold film containing the silk texture in the sample coordinate system, it can be seen that the texture makes the elastic modulus of the material anisotropic along the The elastic modulus of the material in different directions shows a significant difference. The elastic modulus of the material in the S3 direction is 118 GPa, which is higher than the elastic modulus of 89.7 GPa in the S1 and S2 directions, and the minimum value of the elastic modulus is along the deviation S3. The direction is about 40 degrees and the modulus is only 60 GPa.
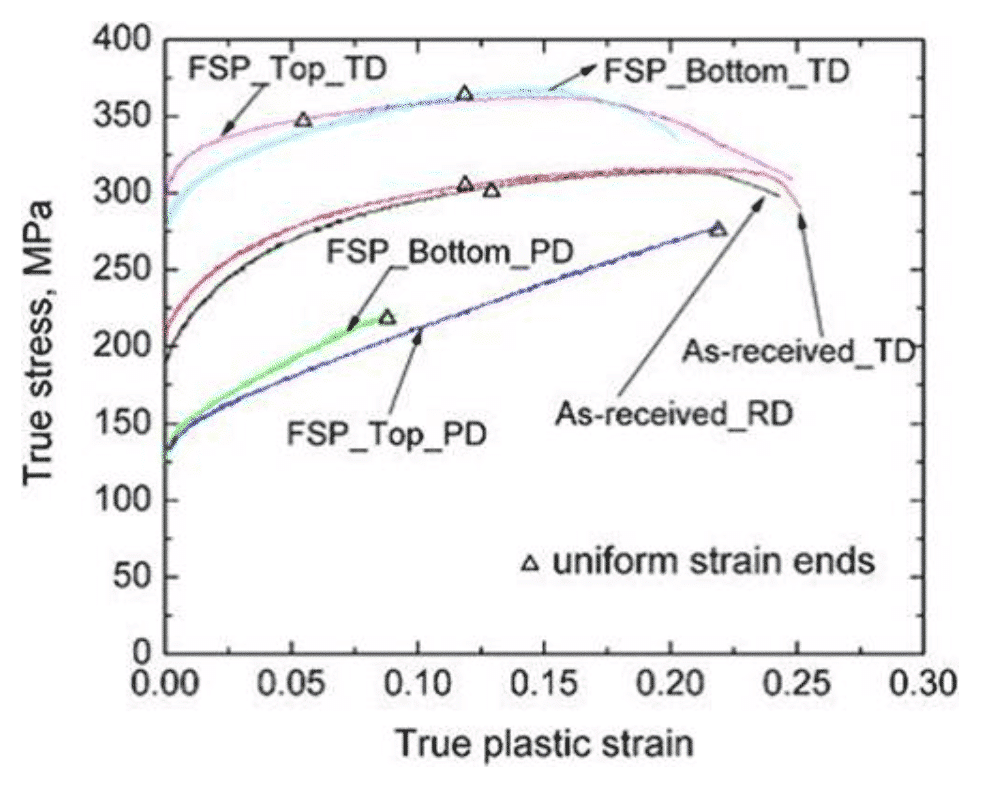
Fig. 5 Effect of texture on the elastic modulus of a gold film
The corrosion behavior is also affected by the texture. Figure 6 shows the Nyquist plot of the impedance spectrum of commercial pure titanium after undergoing different degrees of equal channel angular deformation. The number of times of deformation is different, and the microstructure and texture of the material are also Differently, it can be seen that the material has better corrosion resistance when it is not subjected to deformation (0 pass) in the initial state.
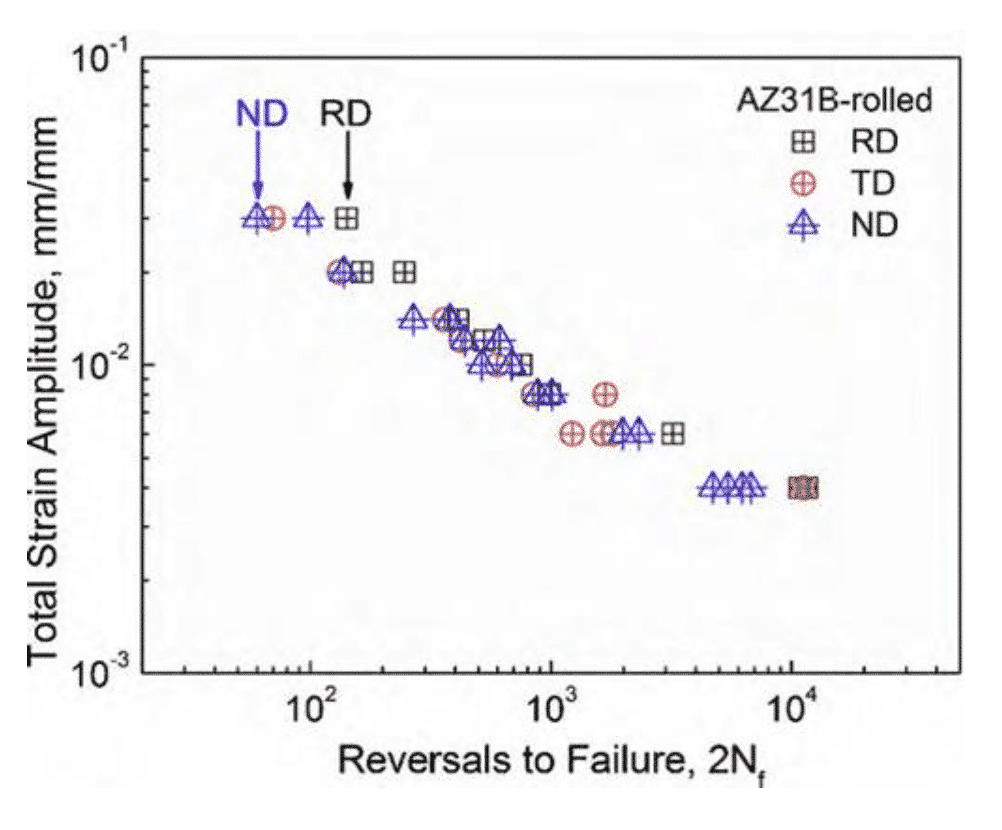
Fig.6 Effect of equal channel angular extrusion on Nyquist plot of commercial pure titanium impedance spectrum
The fatigue behavior of the material under dynamic cyclic loading is also affected by the texture. Figure 7 shows that the low-cycle fatigue behavior of a different orientation of a magnesium alloy after extrusion deformation will be different. It can be seen that in the case of the same total strain amplitude, the fatigue life of the material in the RD direction is generally better than the fatigue life in the ND direction.
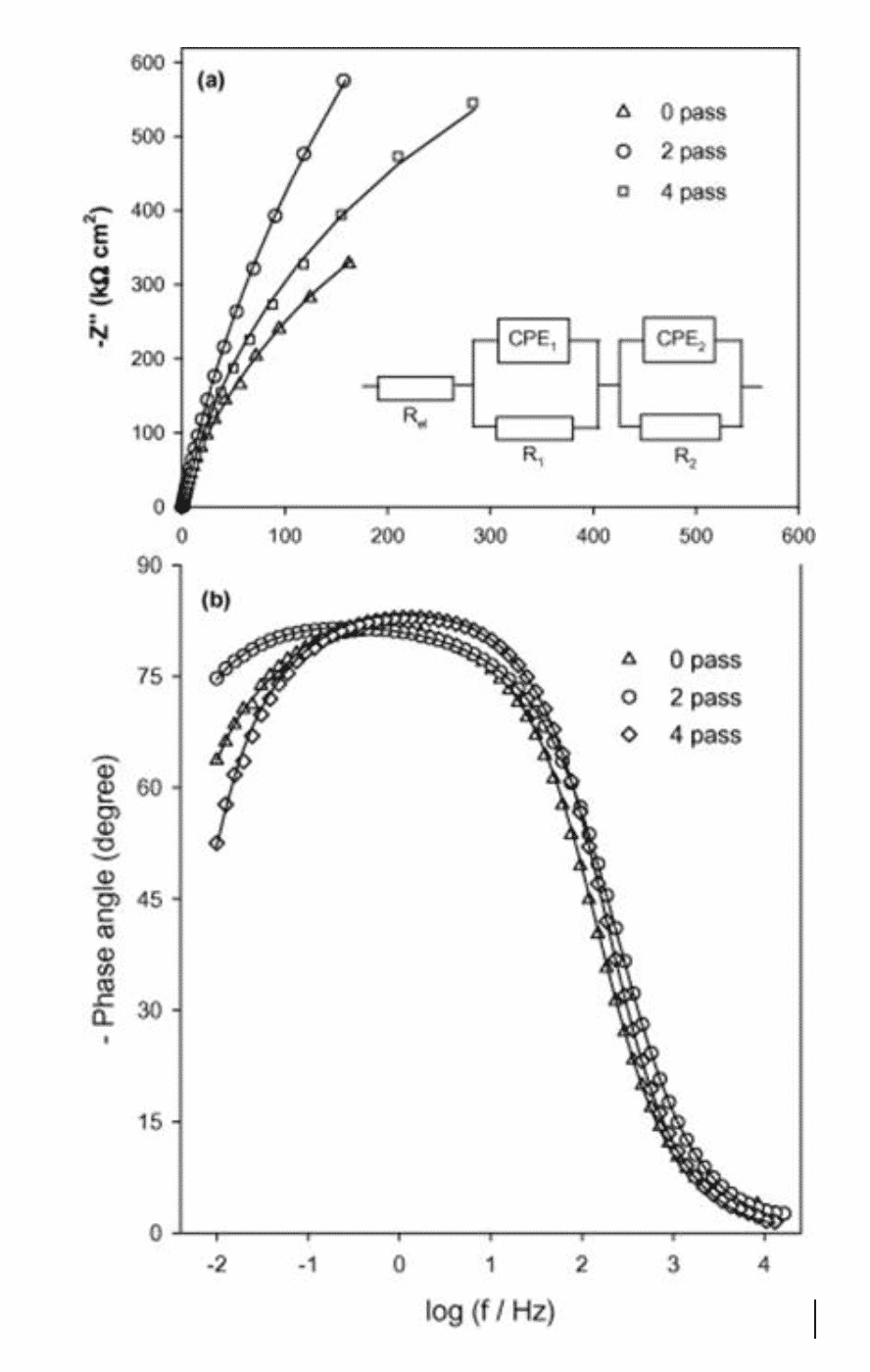
Fig. 7 Effect of texture on low cycle fatigue behavior of materials
Summary
In summary, the presence of texture is universal in metallic materials. The essence of the texture is that many grains are not distributed in a random orientation, which naturally leads to anisotropy in the properties of the material. The effect of texture on material properties is studied in order to better utilize the texture in the material to regulate the related properties of the material.









