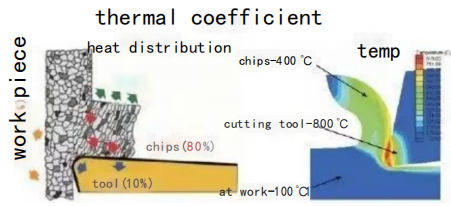
The components of the machining system absorb the heat generated during the metal cutting process. Typically, 10% of the heat enters the workpiece, 80% goes into the chips, and 10% enters the tool. Ideally, most of the heat is carried away by the chips, as high temperatures can shorten the tool life and damage the machined parts.
Let’s take milling as an example to analyze the factors that affect cutting heat and tool life, as well as how to improve them. The different thermal conductivity of the workpiece material and other machining factors significantly influence the distribution of heat. When machining a workpiece with poor thermal conductivity, more heat is transferred to the tool. Materials with higher hardness generate more heat during machining compared to materials with lower hardness. In general, higher cutting speeds increase heat generation, and higher feed rates increase the area of the cutting edge affected by high temperatures.
In intermittent cutting conditions, where milling operations are predominant, the selection of tool engagement arc, feed rate, cutting speed, and cutting edge geometry all have an impact on the generation, absorption, and control of heat.
Arc of engagement
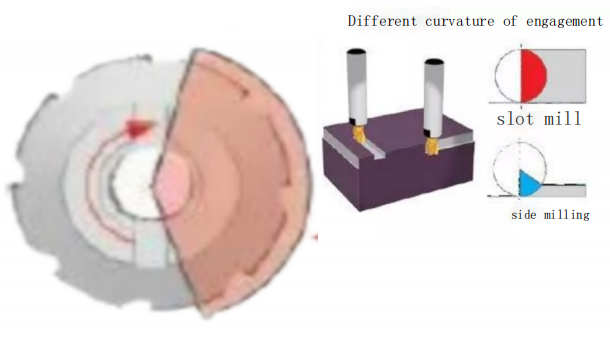
Due to the intermittent nature of the milling process, cutting teeth only generate heat during a portion of the machining time. The percentage of cutting time for the teeth is determined by the tool engagement arc of the milling cutter, which is influenced by the radial cutting depth and tool diameter.
Different milling processes have different tool engagement arcs. In slot milling, the workpiece material surrounds half of the tool, and the tool engagement arc is 100% of the tool diameter. Half of the cutting teeth’s machining time is spent on cutting, leading to a rapid accumulation of heat. In face milling, a relatively smaller portion of the tool engages with the workpiece, allowing the cutting teeth to have more opportunities to dissipate heat into the air.
скорость резки
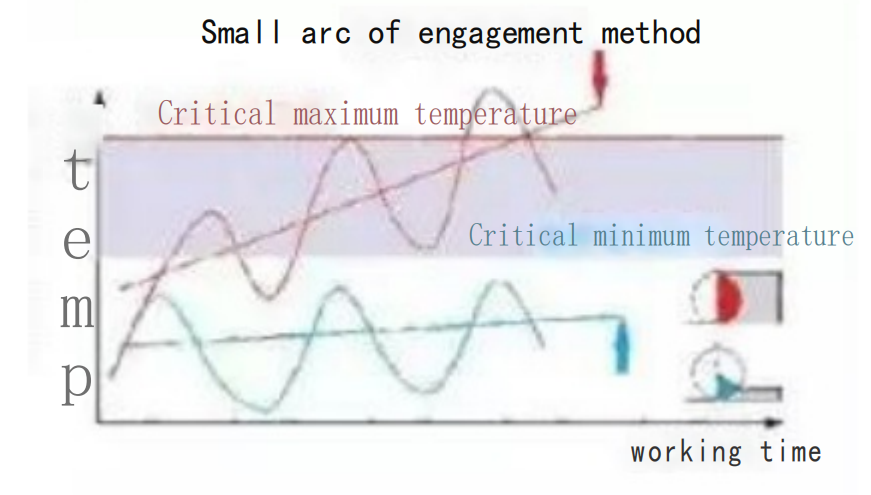
To maintain the thickness and temperature of the chips in the cutting zone equal to those during full slot cutting, tool suppliers establish compensation factors that increase the cutting speed when the tool engagement percentage decreases.
From a thermal load perspective, a smaller tool engagement arc may result in insufficient cutting time to generate the minimum temperature required for maximizing tool life. Increasing the cutting speed typically generates more heat, but combining a smaller tool engagement arc with a higher cutting speed helps elevate the cutting temperature to the desired level. Higher cutting speeds shorten the contact time between the cutting edge and the chips, thereby reducing the heat transferred to the tool. Overall, higher cutting speeds reduce machining time and increase productivity.
On the other hand, lower cutting speeds can lower the machining temperature. If excessive heat is generated during the process, reducing the cutting speed can bring the temperature down to an acceptable level.
cutting depth
The thickness of the chips has a significant impact on heat generation and tool life. When the chip thickness is too large, it creates excessive load that results in excessive heat and chip formation, and it may even lead to cutting edge fracture. Conversely, when the chip thickness is too small, the cutting process occurs only on a smaller portion of the cutting edge, and the increased friction and heat can cause rapid wear.
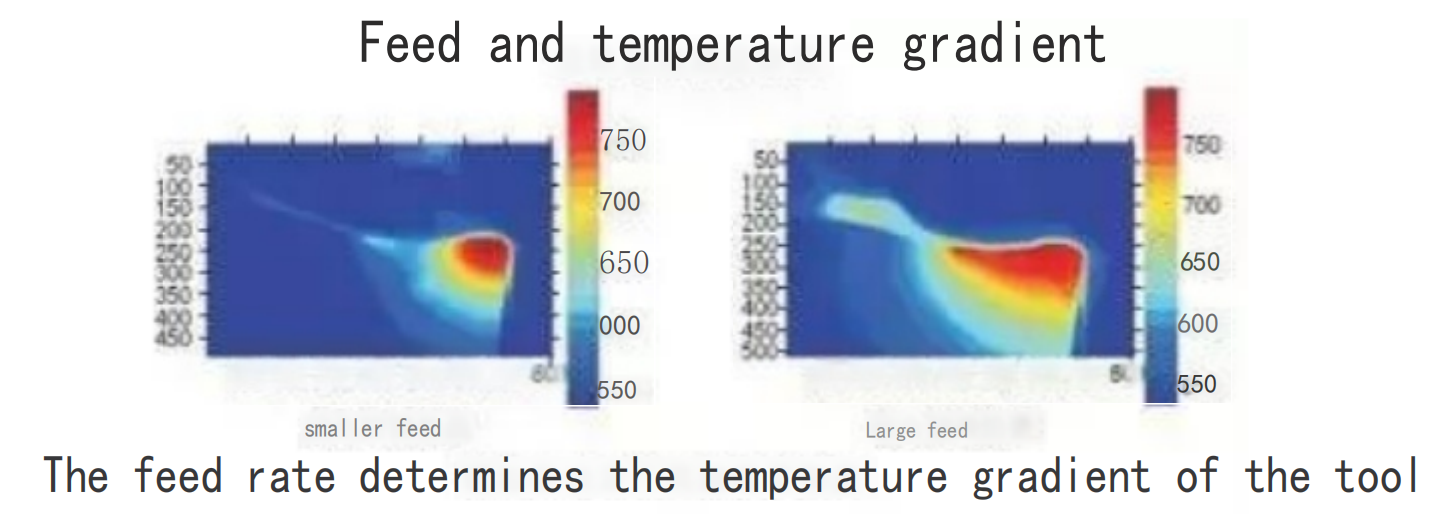
The thickness of chips generated in milling varies as the cutting edge enters and exits the workpiece. Therefore, tool suppliers utilize the concept of “average chip thickness” to calculate the tool feed rate aimed at maintaining the most efficient chip thickness.
Factors involved in determining the correct feed rate include the tool engagement arc or radial cutting depth and the primary relief angle of the cutting edge. A larger engagement arc requires a smaller feed rate to achieve the desired average chip thickness. Similarly, a smaller engagement arc necessitates a higher feed rate to achieve the same chip thickness. The primary relief angle of the cutting edge also affects the feed rate requirement. When the primary relief angle is 90°, the chip thickness is maximum. Thus, to achieve the same average chip thickness, reducing the primary relief angle requires an increase in the feed rate.
cutting edge groove
The geometric angles and cutting edges of milling cutters contribute to controlling the thermal load. The choice of tool rake angle is determined by the hardness of the workpiece material and its surface condition. Tools with a positive rake angle generate lower cutting forces and heat, allowing for higher cutting speeds. However, tools with a positive rake angle are weaker compared to tools with a negative rake angle, which can generate higher cutting forces and temperatures.
The groove geometry of the cutting edge can induce and control the cutting action and cutting forces, thus affecting heat generation. The cutting edge in contact with the workpiece can be chamfered, dulled, or sharp. Chamfered or dulled edges have higher strength and generate greater cutting forces and heat. Sharp edges can reduce cutting forces and lower machining temperatures.
The back angle of the cutting edge, known as the relief angle, is used to guide the chips. It can be positive or negative. Positive relief angles can simultaneously result in lower machining temperatures, while negative relief angles are designed for higher strength and generate more heat.
Milling is an intermittent cutting process, and the chip control features of milling tools are generally not as critical as in turning operations. Depending on the workpiece material and the engagement arc, the energy required to form and guide the chips may become crucial. Narrow or forced chip control groove geometry can curl up the chips immediately, generating higher cutting forces and more heat. Broader chip control groove geometry can produce lower cutting forces and lower machining temperatures, but may not be suitable for certain combinations of workpiece materials and cutting parameters.
охлаждение
One method of controlling the heat generated in metal cutting processes is through the application of coolant. Excessive temperature can cause rapid wear or deformation of the cutting edge, so it is essential to control the heat as quickly as possible. In order to effectively reduce the temperature, the heat source must be cooled.
Multiple interrelated factors collectively contribute to the load in metal cutting processes. These factors interact with each other during the machining process. This article explores the issue of heat generation in milling operations and its relationship with mechanical factors. Understanding the various factors involved in generating metal cutting loads and their overall impact will help manufacturers optimize their machining processes and maximize productivity and profitability.








