Microscopia eletr?nica de transmiss?o de alta resolu??o (HRTEM ou HREM) é o contraste de fase (o contraste de imagens de microscopia eletr?nica de alta resolu??o é formado pela diferen?a de fase entre a onda projetada sintetizada e a onda difratada, é chamada de contraste de fase). Microscopia, que fornece um arranjo at?mico da maioria dos materiais cristalinos.
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy began in the 1950s. In 1956, JWMenter directly observed parallel strips of 12 ? copper phthalocyanine with a resolution of 8 ? transmission electron microscope, and opened high-resolution electron microscopy. The door to surgery. In the early 1970s, in 1971, Iijima Chengman used a TEM with a resolution of 3.5 ? to capture the phase contrast image of Ti2Nb10O29, and directly observed the projection of the atomic group along the incident electron beam. At the same time, the research on high resolution image imaging theory and analysis technology has also made important progress. In the 1970s and 1980s, the electron microscope technology was continuously improved, and the resolution was greatly improved. Generally, the large TEM has been able to guarantee a crystal resolution of 1.44 ? and a dot resolution of 2 to 3 ?. HRTEM can not only observe the lattice fringe image reflecting the interplanar spacing, but also observe the structural image of the arrangement of atoms or groups in the reaction crystal structure. Recently, Professor David A. Muller’s team at Cornell University in the United States used laminated imaging technology and an independently developed electron microscope pixel array detector to achieve a spatial resolution of 0.39 ? under low electron beam energy imaging conditions.
Atualmente, os microscópios eletr?nicos de transmiss?o geralmente s?o capazes de realizar HRTEM. Esses microscópios eletr?nicos de transmiss?o s?o classificados em dois tipos: alta resolu??o e analítico. O TEM de alta resolu??o é equipado com uma pe?a de pólo objetivo de alta resolu??o e uma combina??o de diafragma, o que torna o angulo de inclina??o da mesa de amostra pequeno, resultando em um menor coeficiente de aberra??o esférica objetivo; enquanto o TEM analítico requer uma quantidade maior para várias análises. O angulo de inclina??o do estágio de amostra, de modo que o suporte da haste da lente objetiva é usado de maneira diferente do tipo de alta resolu??o, afetando a resolu??o. Em geral, um TEM de alta resolu??o de 200 kev tem uma resolu??o de 1,9 ?, enquanto um TEM analítico de 200 kev tem um 2,3 ?. Mas isso n?o afeta a TEM analítica que captura a imagem de alta resolu??o.
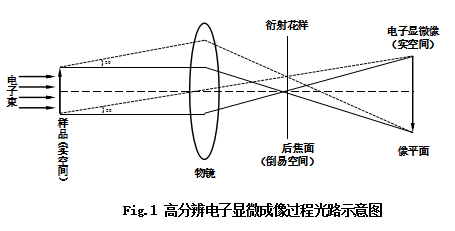
As shown in Fig. 1, the optical path diagram of the high-resolution electron microscopy imaging process, when an electron beam with a certain wavelength (λ) is incident on a crystal with a crystal plane spacing d, the Bragg condition (2dsin θ = λ) is satisfied, A diffracted wave is generated at an angle (2θ). This diffracted wave converges on the back focal plane of the objective lens to form a diffraction spot (in an electron microscope, a regular diffraction spot formed on the back focal plane is projected onto the phosphor screen, which is a so-called electron diffraction pattern). When the diffracted wave on the back focal plane continues to move forward, the diffracted wave is synthesized, an enlarged image (electron microscopic image) is formed on the image plane, and two or more large objective lens stops can be inserted on the back focal plane. Wave interference imaging, called high-resolution electron microscopy, is called a high-resolution electron microscopic image (high-resolution microscopic image).
Como mencionado acima, a imagem microscópica eletr?nica de alta resolu??o é uma imagem microscópica de contraste de fase formada pela passagem do feixe transmitido do plano focal da lente objetiva e dos vários feixes difratados através da pupila objetiva, devido à sua coerência de fase. Devido à diferen?a no número de feixes difratados participantes da gera??o de imagens, s?o obtidas imagens de alta resolu??o de nomes diferentes. Devido às diferentes condi??es de difra??o e espessura da amostra, as micrografias eletr?nicas de alta resolu??o com diferentes informa??es estruturais podem ser divididas em cinco categorias: franjas de treli?a, imagens estruturais unidimensionais, imagens de treli?a bidimensional (imagens de célula única), bidimensionais imagem da estrutura (imagem em escala at?mica: imagem da estrutura cristalina), imagem especial.
Franjas de treli?a: Se um feixe de transmiss?o no plano focal traseiro for selecionado pela lente objetiva e um feixe de difra??o interferir entre si, é obtido um padr?o de franja unidimensional com uma mudan?a periódica de intensidade (como mostrado pelo triangulo preto em Fig. 2 (f)) Essa é a diferen?a entre uma franja de rede e uma imagem de rede e uma imagem estrutural, que n?o exige que o feixe de elétrons seja exatamente paralelo ao plano da rede. Na verdade, na observa??o de cristalitos, precipitados e similares, as franjas de treli?a s?o frequentemente obtidas por interferência entre uma onda de proje??o e uma onda de difra??o. Se um padr?o de difra??o de elétrons de uma substancia como cristalitos for fotografado, um anel de adora??o aparecerá como mostrado na (a) da Fig. 2.
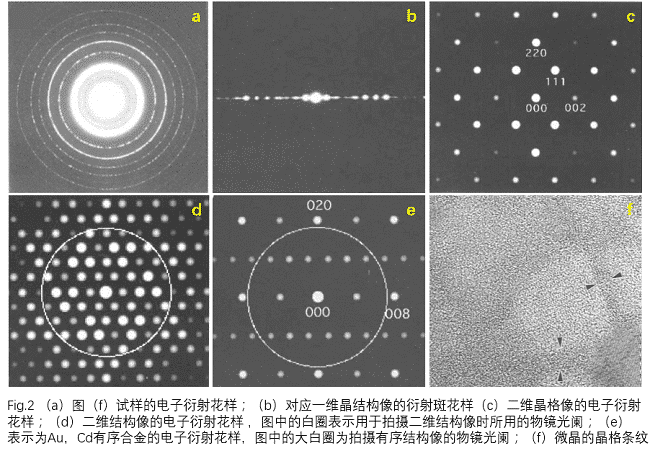
Imagem da estrutura unidimensional: se a amostra tiver uma certa inclina??o, de modo que o feixe de elétrons seja paralelo a um determinado plano de cristal do cristal, ele pode satisfazer o padr?o de difra??o de difra??o unidimensional mostrado na Fig. 2 (b) ( distribui??o simétrica em rela??o ao ponto de transmiss?o) Padr?o de difra??o). Nesse padr?o de difra??o, a imagem de alta resolu??o obtida sob a condi??o de foco ideal é diferente da franja da rede e a imagem da estrutura unidimensional contém as informa??es da estrutura do cristal, ou seja, a imagem da estrutura unidimensional obtida, como mostrado na Fig. 3 (uma imagem estrutural unidimensional de alta resolu??o do óxido supercondutor de base bi-mostrada.
Two-dimensional lattice image: If the electron beam is incident parallel to a certain crystal axis, a two-dimensional diffraction pattern can be obtained (two-dimensional symmetric distribution with respect to the central transmission spot, shown in Fig. 2(c)). For such an electron diffraction pattern. In the vicinity of the transmission spot, a diffraction wave reflecting the crystal unit cell appears. In the two-dimensional image generated by the interference between the diffracted wave and the transmitted wave, a two-dimensional lattice image showing the unit cell can be observed, and this image contains information on the unit cell scale. However, information that does not contain an atomic scale (into atomic arrangement), that is, a two-dimensional lattice image is a two-dimensional lattice image of single crystal silicon as shown in Fig. 3(d).
Two-dimensional structure image: a diffraction pattern as shown in Fig. 2(d) is obtained. When a high-resolution electron microscope image is observed with such a diffraction pattern, the more diffraction waves involved in imaging, the information contained in the high-resolution image is also The more. A high-resolution two-dimensional structure image of the Tl2Ba2CuO6 superconducting oxide is shown in Fig. 3(e). However, the diffraction of the high-wavelength side with higher resolution limit of the electron microscope is unlikely to participate in the imaging of the correct structure information, and becomes the background. Therefore, within the range allowed by the resolution. By imaging with as many diffracted waves as possible, it is possible to obtain an image containing the correct information of the arrangement of atoms within the unit cell. The structure image can only be observed in a thin region excited by the proportional relationship between the wave participating in imaging and the thickness of the sample.
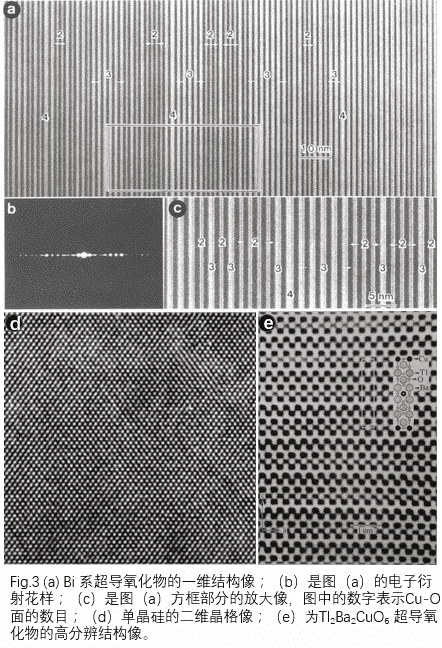
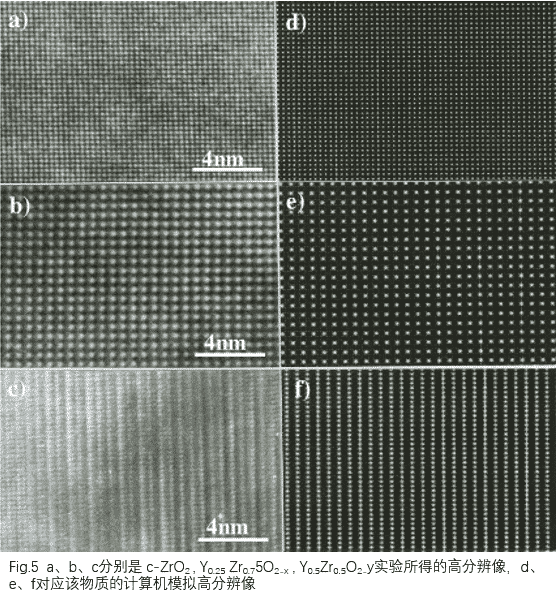
Imagem especial: No padr?o de difra??o do plano focal traseiro, a inser??o da abertura seleciona apenas a imagem de onda específica para poder observar a imagem do contraste da informa??o estrutural específica. Um exemplo típico disso é uma estrutura ordenada como. O padr?o de difra??o de elétrons correspondente é mostrado na Fig. 2 (e) como o padr?o de difra??o de elétrons da liga ordenada por Au, Cd. A estrutura ordenada é baseada em uma estrutura cúbica centrada na face na qual os átomos de Cd s?o organizados em ordem. Fig. 2 (e) os padr?es de difra??o de elétrons s?o fracos, exceto pelas reflex?es básicas da rede dos índices (020) e (008). Reflex?o ordenada da estrutura, usando a lente objetiva para extrair a reflex?o básica da estrutura, usando ondas de transmiss?o e imagens ordenadas da reflex?o da estrutura, apenas átomos de Cd com pontos brilhantes ou pontos escuros, como alta resolu??o, como mostrado na Fig. 4.
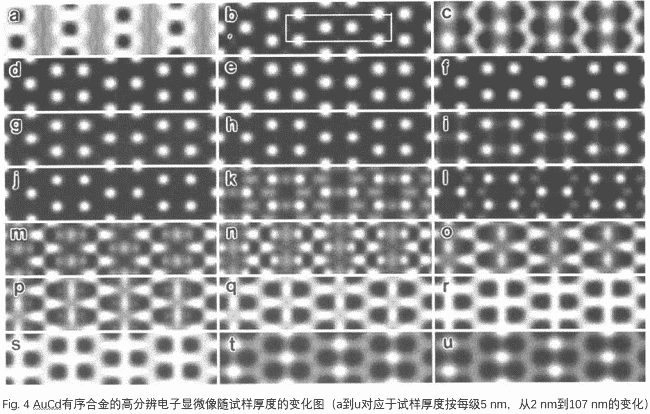
As shown in Fig. 4, the high resolution image shown varies with the thickness of the sample near the optimum high resolution underfocus. Therefore, when we get a high-resolution image, we can’t simply say what the high-resolution image is. We must first do a computer simulation to calculate the structure of the material under different thicknesses. A high resolution image of the substance. A series of high-resolution images calculated by the computer are compared with the high-resolution images obtained by the experiment to determine the high-resolution images obtained by the experiment. The computer simulation image shown in Fig. 5 is compared with the high resolution image obtained by the experiment.