Typically, nano-WC powders are prepared using gas-phase reaction methods or high-energy ball milling techniques. The most widely used method for preparing WC-Co composite powders is through hydrogen reduction/carbonization of tungsten oxide. Therefore, controlling the microstructure and preparation process of tungsten oxide can yield nano-tungsten powder. However, there is currently a lack of in-depth research on how different carbonization methods affect the carbonization process of nano-tungsten powder. Research in this area holds significant practical value for the production of nano-tungsten carbide powders and the fabrication of nano-crystalline WC-Co carbides.
This study uses ball-milled tungsten oxide as the raw material and prepares nano-tungsten powder by controlling the hydrogen reduction process. Different carbonization methods, namely wet ball milling and dry milling, are employed to mix carbon, resulting in W+C mixed powders with varying morphologies. After carbonization, WC powder is obtained, aiming to enhance the uniformity of the dispersion of tungsten and carbon black particles through suitable carbonization methods and to explore a cost-effective industrial method for preparing homogeneous nano-WC powder.

The Importance of Carbon Content in Carbide?Powders
Carbon content is a crucial factor influencing the performance of carbides. Even minor fluctuations in carbon content can lead to changes in the alloy’s phase composition and microstructure, thus affecting its performance. When the carbon content in an alloy is insufficient, decarburized phases, which are brittle and unstable, may form, resulting in reduced strength and increased susceptibility to fracture and chipping during use. Conversely, when carbon content is too high, free graphite may form within the alloy, disrupting the continuity of the matrix and adversely affecting properties such as bending strength, toughness, and wear resistance.
Even fluctuations in carbon content within the normal phase range can significantly impact alloy performance. At the upper limit, strength and toughness are high while hardness and coercivity are low; at the lower limit, the opposite is true. This is because changes in carbon content, while not altering the number of phases, do modify the composition of the bonding phase. The hardness of the bonding phase is determined by tungsten content, which can be controlled by the total carbon in the raw materials during the sintering process. Thus, the overall carbon content of the alloy is vital for the material’s hardness and toughness. Studies of high-lifetime micro-drills and stamping dies have shown that the saturation magnetization of long-lasting alloys is typically controlled within 75% to 80%, indicating that their carbon content is maintained at the lower limit of the normal phase range.
Experimental Method
To further improve the uniformity of the powder and reduce particle agglomeration, mechanical milling and classification were used to preprocess WO. The preprocessed powder (MWO?) was then subjected to hydrogen reduction in a tubular furnace at 760°C to obtain nano-W powder. Following this, an appropriate dispersant was added for wet mechanical alloying and carbon mixing. After vacuum drying, the mixture was carbonized in a hydrogen molybdenum wire furnace at 1140°C, followed by crushing to obtain nano-WC powder. Additionally, dry milling was also employed for carbon mixing under the same carbonization conditions for comparative analysis. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to observe the morphology of WO?, W, and WC powders, while powder properties such as particle size, specific surface area, and total carbon content were measured. Specific surface area and particle size of the nano-W powder were measured using a SA3100 specific surface area analyzer and a particle size analyzer, and the morphology and uniformity of the powder were examined with a QUANTA-200 SEM.
Results and Discussion of the Experiment
Morphology and Properties of Nano-WC Powder
Figure 1 shows SEM images of the raw powder and nano-W powder. The results indicate that mechanical milling significantly refines the WO? powder, achieving a particle size of 1.1 μm and a specific surface area of 4.52 m2/g. After mechanical nano-sizing, the morphology of the WO? powder changed significantly, with smooth surfaces and a dense structure consisting of nano-particles. The large agglomerated WO? particles were crushed into finer particles with maximum agglomerates not exceeding 20 μm. Using MWO as a raw material under specific processing conditions, nano-sized W powder (20-30 nm) was produced, exhibiting inherited structural characteristics from its oxide precursor and showing varying degrees of loose agglomeration, with maximum agglomerate sizes not exceeding 20 μm.
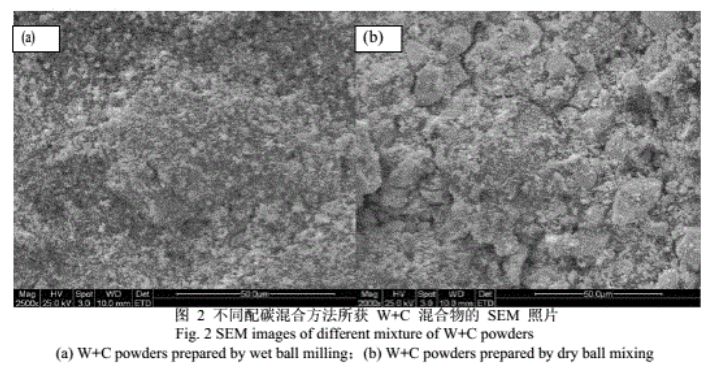
Morphology of W+C Mixture after Carbon Mixing
Figure 2 presents SEM images of the W+C mixtures obtained through different methods. After wet mechanical alloying with an appropriate dispersant, significant changes in the powder morphology were observed: most agglomerated W particles were effectively broken up and dispersed, with carbon black uniformly distributed. In contrast, the dry milling method resulted in noticeable agglomeration of W powder, with non-uniform distribution of carbon black.
Morphology and Structure of Nano-WC Powder
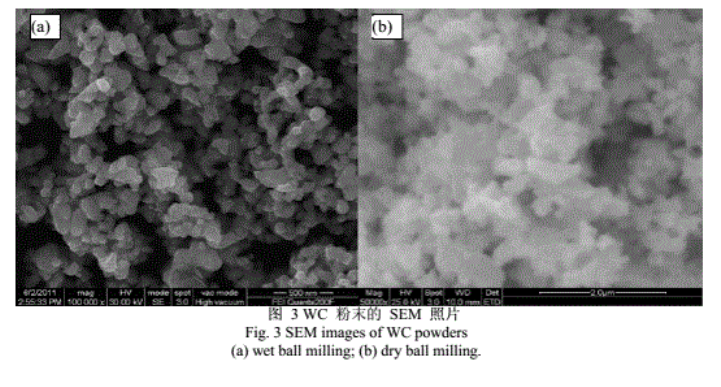
Figure 3 shows SEM images of different nano-WC powders. The nano-WC powder obtained through wet alloying with carbon was smaller and more uniform, with a well-defined morphology and minimal agglomeration, containing a total carbon content of 6.10-6.30%, a combined carbon content of 6.06%, and an average particle size of about 85 nm. In contrast, the WC powder produced through dry milling exhibited more tightly bound agglomerates and larger particle sizes, with an average size of approximately 189 nm. This discrepancy is attributed to the insufficient breaking of tungsten powder agglomerates during carbon mixing in the latter method, resulting in poor contact between carbon black and tungsten powder and non-uniform carbon distribution. During high-temperature solid-state reactions, the chemical migration process is lengthy and requires significant chemical driving force, making complete carbonization challenging; high temperatures can also cause tungsten particles within agglomerates to grow larger due to sintering.
Conclus?o
1.Using wet mechanical alloying for carbon mixing followed by carbonization at 1140°C, a well-dispersed and uniform nano-WC powder was produced, with a total carbon content of 6.10-6.30% (controllable), a combined carbon content of 6.06%, and an average particle size of approximately 85 nm.
2.The use of wet milling for carbon mixing altered the agglomerated appearance of the nano-tungsten particles, improving the uniformity of the dispersion of W and C powders. This approach facilitates lower carbonization temperatures and results in uniformly sized and chemically stable nano-WC powders.









