When the grain size of WC is reduced to around 100 nm, there will be a significant breakthrough in its hardness and strength. Stronger and harder ultrafine or nano carbide cutting tools are needed for the processing of difficult-to-machine metal materials such as high-temperature carbide in aviation materials, drilling of printed circuit boards in the electronics industry, processing of wood and composite flooring, needles for dot matrix printers, precision cutting of glass, and cutting of textiles.
In this article, we briefly introduce the synthesis and densification of nano carbide.
Synthesis of nano carbide powder
Due to the inevitable growth of grain during densification, in order to produce carbide with nano grains, it is necessary to first synthesize nano carbide powders with finer grains. The main methods currently used include the following:
Mechanical ball milling method to get nano carbide
Mechanical carbide is a method of synthesizing materials at low temperature using high-energy mechanical driving force. High-energy ball milling is commonly used as the mechanical driving force. Currently, research on the synthesis of nano carbide powders by mechanical alloying mainly includes two aspects:
Using mechanical mixing method to synthesize nano WC powder by W and C, some scholars mixed W, C, and Co for 100 hours to synthesize composite powder of 11.3 nm WC-Co. Another method is to prepare nano-sized WC using chemical mechanical mixing method. This method mixes WO and Mg with C powder in a ball mill under N or H-Ar protective atmosphere, and explosive reduction reaction occurs to generate W and MgO. Then, W undergoes diffusion reaction with C to generate WC and WC. The grain size is about 4-20 nm.
WC and Co powders are mixed and then finely crushed into nano-composites using high-energy ball milling. Chinese scholars used this method to obtain an average WC grain size of 10 nm by ball milling WC-10%Co for 40 hours, with WC particles separated and covered by Co. German scientists used the same method to ball mill at a speed of 55r/min for 300 hours, obtaining an average WC grain size of 7 nm.
The method of synthesizing nano carbide powder using mechanical mixing is simple and efficient, and the powder produced has small grain size. However, it often causes powder contamination due to friction with the container and balls.
Spray Conversion Method
A spray conversion method has been developed by researchers at New Jersey University in the United States to synthesize nano WC-Co composite powder. This chemical method uses ammonium metatungstate (CH4)6(H2W12O40)·4H2O and cobalt chloride CoCl2nH2O aqueous solution or Co(en)3WO4 and H2WO4 aqueous solution, followed by spray drying, fluidized bed reduction, and carbide reaction to generate uniform 20-50 nm grain size powder.
Carburizing Reduction Method
?US scholars have also reported a method using polyacrylonitrile as an in situ carbon source without requiring gas-phase carburation. Tungstic acid and cobalt salts are dissolved in a polyacrylonitrile solution, which is then moved to an atmosphere furnace at 800-900°C and directly reduced into WC-Co powder using a 90%Ar-10% H2 mixed gas. The obtained powder has a grain size of about 50-80 nm.
Co-Precipitation Method
This method uses sodium tungstate or ammonium tungstate (CH4)6(H2W12O40) and cobalt acetate co-precipitation to obtain WC-Co powder precursor containing H2Co2W11O40 solid salt. Then, through the H-reduction reaction and carbide reaction, 50 nm WC-Co powder is produced. However, this method is only suitable for powder with a W/Co atomic ratio close to 5.5. If (NH4)(H12W12O42) and cobalt hydroxide are co-precipitated, the W/Co atomic ratio can be changed, and a wider range of composite powders can be obtained.
Sintering of nano carbide
Due to the large proportion of surface and interface in nano particles, the sintering behavior of nanocrystalline WC-Co carbide is different from that of ordinary grain-sized WC-Co carbide due to the influence of small size effect, surface and interface effects during sintering.
Densification temperature
The sintering of ordinary carbides usually occurs above the eutectic temperature of WC-Co, which is 1320℃ and is called liquid-phase sintering. However, the starting temperature of densification is lower than the eutectic temperature, usually around 1280℃, so it is also called solid-phase sintering stage.
As for the composite WC-Co powders with ultrafine grains and nanoscale structures, their densification temperature is greatly reduced. For example, 0.4 μm WC with grain growth inhibitor CrC, VC, TaC added can significantly reduce the eutectic temperature of carbide, and the starting temperature of densification is between 770-850℃. The starting temperature of densification for WC-15Co with grain size of 30 nm is 600℃, and the maximum densification is achieved at 1200℃. The shrinkage starting temperature of 30 nm WC-Co powder synthesized by spray conversion method is 580℃.
From the above content, we can see that the nano carbide powder?synthesized by ball milling method has higher defect density and smaller nano?particles, and its solid-phase sintering temperature is significantly lower than that of nano carbide powder?synthesized by spray conversion method.
Grain growth of nano carbide and ordinary carbide
The smaller the particle size radius, the greater the sintering bonding strength. The sintering bonding strength of nano WC-Co powder is tens or even hundreds of times that of ordinary? carbide. Therefore, the trend of grain growth of WC-Co powder is significant.
Firstly, the influence of sintering time. It was found that the grain size had grown in the first 5 minutes of sintering when studying the densification of nano?WC-Co powder. Secondly, the influence of sintering temperature, the higher the sintering temperature, the more severe the grain growth, as shown in figure 1. In addition, the original size of the powder strongly affects the sintering grain size. As shown in the following figure, within the range of particle size less than 0.2μm, the smaller the original powder, the larger the grain size after sintering at a certain temperature and time.
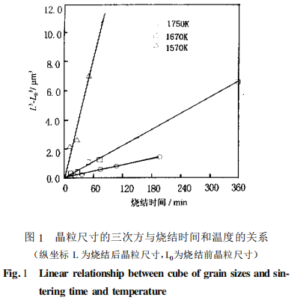
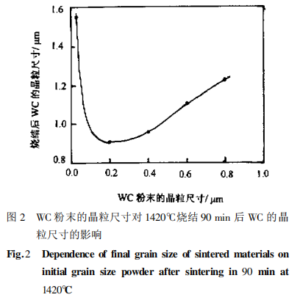
Thus, suppressing the growth of grains during the sintering process is the most critical step in obtaining nano carbide. On the one hand, we can add grain growth inhibitors such as carbides like VC, Cr3C2, TaC, NbC to affect the WC/Co interface energy and reduce the solubility of WC in the Co liquid phase, thus inhibiting the growth of WC grains. On the other hand, controlling grain growth can be achieved by controlling the sintering process or researching new sintering methods. The hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process can rapidly densify the material and reduce the degree of grain growth. In addition, microwave sintering, pulse discharge sintering, and plasma discharge sintering are very promising sintering methods for nano carbide. They can all efficiently heat the material to achieve densification of the hard carbide?grains and reduce grain growth.
Summary and outlook
the main problem currently faced in nano carbide?is the growth of grains during sintering. Although there are reports of nano carbide?products, their grain sizes are rarely around or less than 100nm. Therefore, we need to use more advanced sintering methods, such as microwave sintering, to accurately control the process parameters such as temperature, time, and pressure to obtain higher performance nano carbide.










