Erosion-Wear Experimental Materials and Equipment
Experimental Materials
Tungsten carbide (WC) carbide?is a composite material produced using powder metallurgy techniques, with WC, a metal carbide that is difficult to dissolve, as the matrix and a binder added. It is characterized by high hardness and strong wear resistance. The WC carbide?used in this experiment is YG8, which is employed as the coating material for the valve core and outlet sleeve in coal direct liquefaction devices. YG8 is a tungsten-cobalt carbide?with a cobalt binder, a density of 14.6 g/cm3, a hardness of HV 1350, an elastic modulus of 540 MPa, a bending strength of 1500 MPa, and a compressive strength of 4470 MPa.
The experiment uses quartz sand (SiO?) particles as the erosion particles, which are commonly used in erosion-wear tests. The particles are sieved to achieve an average particle size of 150 μm, as shown in Figure 1.
Experimental Equipment
The experiment uses a self-made shock wave-driven gas-solid two-phase flow erosion-wear testing device. This device primarily consists of a shock wave generator, a velocity measurement system, a high-speed camera, a heating system, and a temperature control system.

In this setup, nitrogen gas is connected to the driving section to generate shock waves with a specific Mach number. The driving section and the driven section are separated by an aluminum film. Experimental particles are placed on a tin foil located between the driven section and the accelerating section. By adjusting the pressure relief valve, gas is introduced into the driving section of the shock tube. When the pressure difference across the film reaches a critical value, the film ruptures suddenly, generating a shock wave. The high-speed gas flow then propels the solid particles through the accelerating section to the desired experimental velocity. Upon impacting the specimen surface, the high-speed particles cause material loss, thus facilitating the erosion process.
The driving section, driven section, and accelerating section are each equipped with dynamic pressure sensors, charge amplifiers, and dynamic test analyzers to measure shock wave velocity. A high-speed camera in the experimental section captures the particle motion trajectories. The specimen holder is equipped with a temperature heating system and a temperature control system, allowing for adjustment to the required experimental temperature.
Erosion-Wear Experimental Parameters and Methods
Experimental Parameters
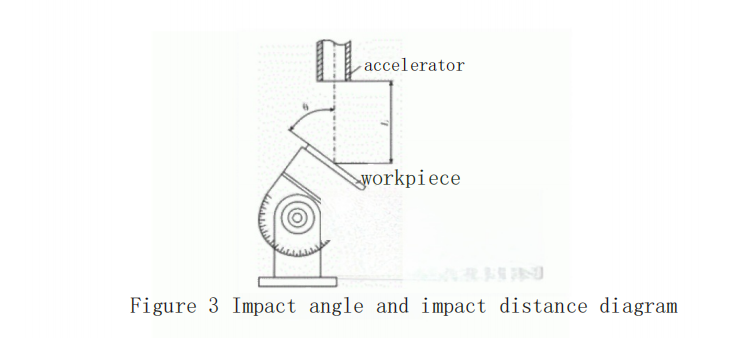
The impact angle, denoted as θ (see Figure 3), is defined as the angle between the axis of the shock tube and the surface of the specimen being eroded (0°to 90°). The desired impact angle is achieved by rotating the specimen holder.
The impact distance L is the distance between the center of the shock tube’s outlet and the center of the specimen’s surface. Typically, L is set between 30 and 50 mm during experiments. When conducting experiments at different impact angles, the position of the shock tube needs to be adjusted to maintain a consistent impact distance.
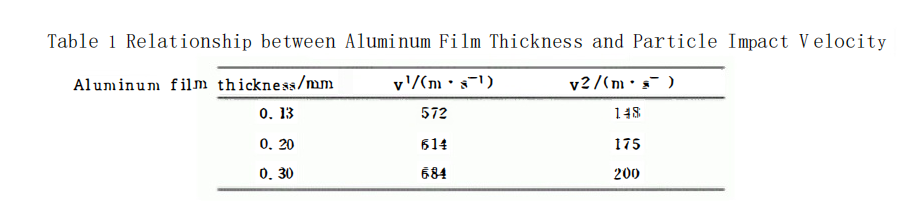
In the experiment, the impact velocity is adjusted by changing the thickness of the aluminum foil. Aluminum foils with thicknesses of 0.13 mm, 0.20 mm, and 0.30 mm are used for the erosion-wear tests. A high-speed camera is employed to record the particle trajectories. By analyzing these trajectories, the particle velocity v p is determined.
![]()
In the equation, ΔI represents the distance between the ends of the particle clusters in consecutive frames, measured in meters; Δn is the number of frames between measurements; and f is the filming frequency, measured in frames per second (FPS).
Using the high-speed camera, the velocity of 150 μm SiO? particles is tested. By replacing aluminum foils of different thicknesses, the corresponding membrane rupture pressure ratios are obtained, which in turn allows for the determination of the impact velocity. The velocities corresponding to different aluminum foil thicknesses are summarized in Table 1. The specific calculation method for particle velocity can be found in the referenced literature.
Experimental Method
Before the experiment, the nickel-based carbide specimens are first polished using 1000# sandpaper. The specimens are then cleaned with an ultrasonic cleaner, air-dried, and weighed to obtain an average value. The specimens are fixed onto the specimen holder, and the angle of the specimen and the distance between the shock tube and the specimen are adjusted. The temperature control system is activated, and the experimental temperature is set. Aluminum foils of the appropriate thickness are selected and solid particles are loaded simultaneously.
The lighting is turned on, and the dynamic testing analyzer and high-speed camera are activated. The camera lens height is adjusted so that the distance from the shock tube outlet to the specimen surface is within the field of view of the high-speed camera. The nitrogen gas valve is then opened to start the experiment. When the aluminum foil ruptures, the valve is immediately closed, and the high-speed camera captures the particle trajectories during the experiment.
At the end of the experiment, the specimen is cooled, cleaned, and dried. The specimen is weighed 10 times using an electronic balance to record the average weight. The erosion-wear rate is then calculated using equation (2).
![]()
In the equation, E represents the erosion-wear rate, measured in mg/g; Δm is the mass loss of the material, measured in mg; and m p is the mass of a single impact particle, measured in grams.
Analysis and Discussion of Erosion-Wear Experimental Results
Effect of Impact Angle on YG8 Wear Rate
Under an impact velocity of 175 m/s, the erosion-wear rates of the specimens were measured by varying the impact angles, as shown in Figure 4.?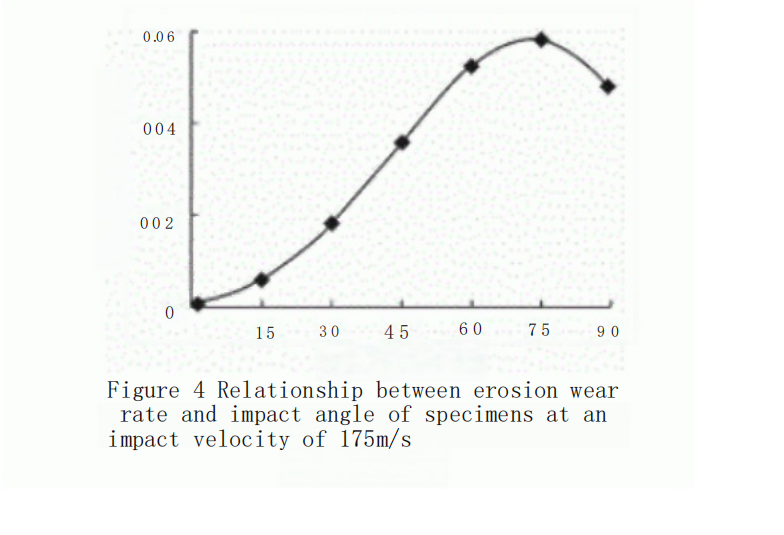
From Figure 4, it can be observed that the erosion-wear rate of the specimen initially increases and then decreases as the impact angle increases. The erosion-wear rate reaches its peak at an impact angle of 75°. The experimental results indicate that YG8 is a typical brittle material, with the maximum erosion-wear rate occurring at high impact angles. The erosion-wear characteristics of YG8 are consistent with the behavior of brittle materials, where the erosion-wear rate varies with the impact angle.
Impact Angle on Coating Erosion-Wear Performance
Particle velocity is a crucial factor affecting the wear rate of materials. Impact experiments were conducted on specimens at impact angles of 30°, 60°, and 90° under three different impact velocities: 148 m/s, 175 m/s, and 200 m/s. The relationship between erosion-wear rate and particle impact velocity is shown.
Figure 5 demonstrates that, at all three impact angles, the erosion-wear rate of the material increases with increasing impact velocity. There is a critical impact velocity at which erosion-wear begins, related to the abrasive properties and the material’s characteristics. Erosion-wear occurs only when the velocity exceeds this critical value. Extensive erosion tests indicate that the erosion-wear rate has the following relationship with particle velocity:
E=kv” (3)
where
v is the particle velocity in m/s;
k is a constant; and
n is the velocity index. A higher
n value indicates that the erosion-wear rate of the material is more influenced by the particle impact velocity.
Fitting the experimental data to equation (3) yields velocity indices of 2.34, 2.27, and 2.28 for impact angles of 30°, 60°, and 90°, respectively, for YG8 material.
Analysis of Erosion-Wear Mechanisms
Analysis of the erosion-wear morphology of specimens at an impact angle of 90° reveals that the erosion-wear is primarily driven by the impact forces of the solid particles directly striking the composite layer. Due to the high brittleness of both tungsten carbide particles and the composite layer matrix, high-velocity solid particle impacts more readily induce plastic deformation or crack formation, leading to the development of pits and cracks.
During the erosion process, the abrasive quartz sand continuously impacts the surface, creating numerous pits. The edges of these pits accumulate material that has been deformed and squeezed out, forming a lip-like flange. With continued particle impacts, this flange is progressively eroded and stripped away due to repeated compression. The wear mechanism can be summarized as erosion-induced compression leading to pit formation and material detachment.
As the reinforcement phase, WC particles have much higher hardness and stiffness compared to quartz sand, which helps them better withstand the abrasive impacts. During the erosion-wear process, the coating undergoes cutting and plowing effects from the sharp edges of the abrasive particles, resulting in plastic deformation, progressive fatigue, and delamination. The protruding WC particles bear the brunt of the abrasive impact. Table 2 shows the elemental chemical composition of the specimen surface before and after the erosion experiments.
Conclus?o
As the impact angle increases, the erosion-wear rate of YG8 material first increases and then decreases, reaching a maximum at an impact angle of 75°. YG8 exhibits the erosion-wear characteristics typical of brittle materials.
At impact angles of 30°, 60°, and 90°, the erosion-wear rate of YG8 material increases with rising impact velocity. The corresponding velocity indices, obtained from fitting the erosion-wear rate versus velocity relationship, are 2.34, 2.27, and 2.28, respectively.
The primary erosion-wear mechanism for YG8 material involves the formation of pits and microcracks on the material surface due to high-angle impacts. These features are caused by the detachment of Co and WC particles from the matrix and the development of microcracks under high-velocity impacts.









