
The Effect of Cobalt Content
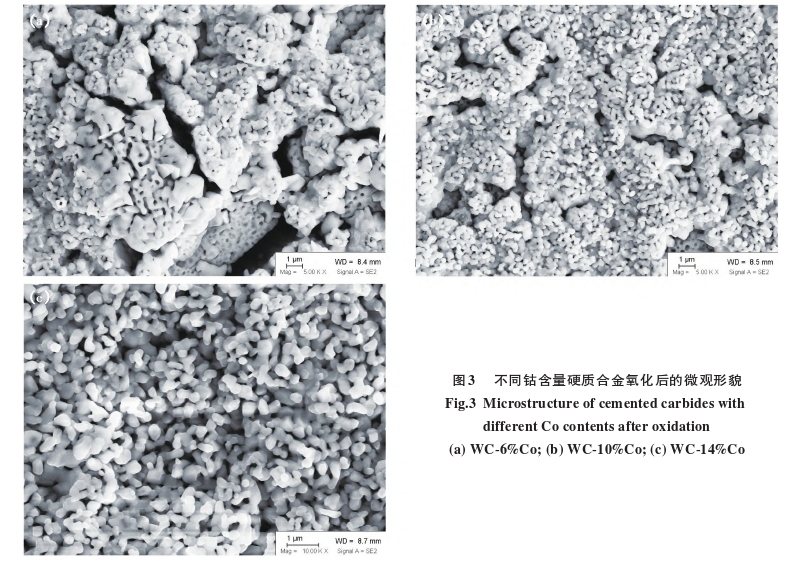
Figure 3 shows the microstructure after oxidation of carbides?with different cobalt contents (all WC materials are WC-1). As the cobalt content increases, the microstructure of the carbide?oxides changes significantly. The oxide of the WC-6%Co carbide?has more and larger pores, the pores in the oxide of the WC-10%Co carbide?are significantly reduced, and the oxide of the WC-14%Co carbide?has virtually no large pores.
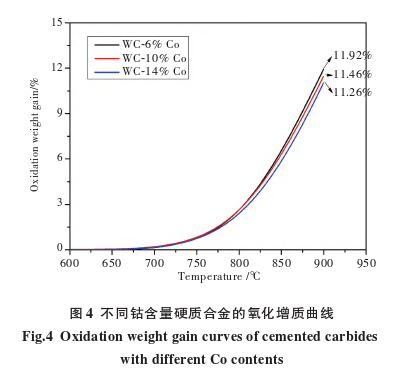
Figure 4 shows the oxidation weight gain curves of carbides?with different cobalt contents. As the cobalt content increases, the oxidation weight gain of the carbides decreases sequentially. At 900°C, the oxidation weight gain of WC-6%Co, WC-10%Co, and WC-14%Co carbides are 11.92%, 11.46%, and 11.26%, respectively. Compared to WC-6%Co carbide, the oxidation weight gain of WC-10%Co and WC-14%Co carbides?at 900°C decreased by 3.8% and 5.5%, respectively. Therefore, although increasing the Co content can improve the high-temperature oxidation resistance of carbides, the improvement is not significant.

Table 3 lists the oxidation reaction equations of each component in the carbide?and their Gibbs free energy. It is well known that during the oxidation of carbides, the oxidation of WC to WO3 results in significant volume expansion. The oxide WO3 is loose, porous, and volatile, producing volatile gases such as CO2, which provide more pathways for the oxidation diffusion process, thereby exacerbating the oxidation of the carbide. Although the binder phase is more prone to oxidation than the hard phase, the oxide formed from the binder phase is the relatively dense CoWO4, which can slow down the oxidation diffusion process of the carbide. Therefore, with the increase in cobalt content, more CoWO4 and less WO3 are formed, resulting in a denser microstructure of the oxides and consequently improving the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the carbide.
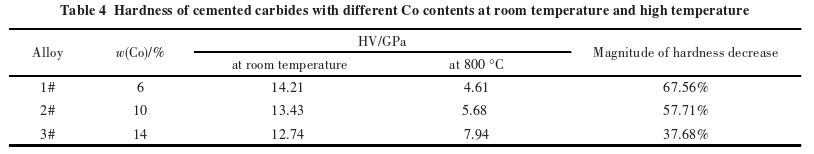
Table 4 shows the room temperature hardness and high-temperature hardness of carbides?with different cobalt contents. At room temperature, the more cobalt content, the lower the hardness of the carbide. When the temperature rises to 800°C, the hardness of the carbides decreases significantly, with the rate of decrease reducing as the cobalt content increases. At 800°C, the hardness of carbides with higher cobalt content is actually higher than that of carbides with lower cobalt content.
Both the hard phase and the binder phase exhibit some thermal expansion at high temperatures, with the binder phase experiencing greater thermal expansion and generating larger stress, which offsets some of the load force. This is one of the reasons why the high-temperature hardness of the carbide?increases with the increase in cobalt content.
The Effect of WC Grain Size
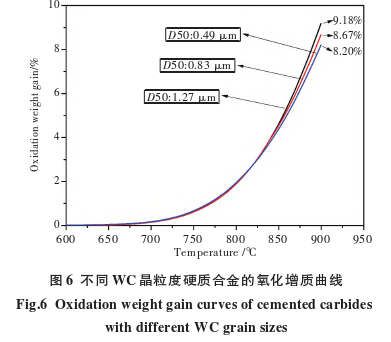
Figure 6 shows the oxidation weight gain curves of 4#, 5#, and 6# carbides?prepared with WC of different Fischer particle sizes. From room temperature to 825°C, the oxidation weight gain curves of the three carbides with different WC grain sizes overlap; however, in the range of 825-900°C, the finer the WC grains, the less the oxidation weight gain of the carbides. At 900°C, the oxidation weight gains of 4#, 5#, and 6# carbides?are 9.18%, 8.67%, and 8.20%, respectively. Compared to the 4# carbide, the oxidation weight gain of the 5# and 6# carbides?at 900°C decreased by 5.6% and 10.7%, respectively. Therefore, under the same Co content, refining the WC grains can improve the high-temperature oxidation resistance of carbides.
Figure 7 shows the XRD diffraction patterns after oxidation of carbides?with different WC grain sizes. Since the compositions of 4#, 5#, and 6# carbides?are the same, there is no significant difference in their oxidation products. Therefore, the diffraction patterns of the oxides of the three carbides?with different WC grain sizes are essentially identical.
The Oxidation Resistance and hardness Differences of Carbides with Different WC Grain Sizes
The differences in the oxidation resistance of carbides?with different WC grain sizes can be mainly attributed to the following two points:
In the case of a uniform carbide?structure, finer WC grains result in more phase boundaries between WC and the binder phase. The finer WC grains are better encapsulated by the binder phase, and the oxidation products of the binder phase can, to some extent, hinder the oxidation diffusion process, thereby improving the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the carbide.
Finer WC grains have fewer grain boundary defects and smaller grain boundary voids between the WC grains, which correspondingly reduce the oxidation diffusion channels, thus enhancing the high-temperature oxidation performance of the carbide.
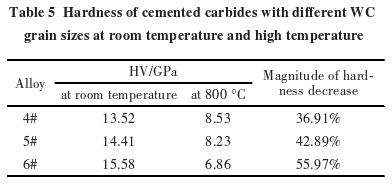
Table 5 shows the room temperature hardness and high-temperature hardness of carbides?with different WC grain sizes. At room temperature, the finer the WC grains, the higher the hardness of the carbide. When the temperature rises to 800°C, the hardness of the carbides decreases significantly, and the rate of decrease in high-temperature hardness increases as the WC grain size decreases. Clearly, although the room temperature hardness of the carbide?increases as the WC grain size decreases, the high-temperature hardness becomes lower.
The Effect of TaC/NbC/TiC Additives
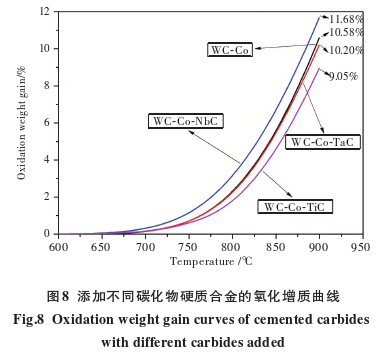
Figure 8 shows the oxidation weight gain curves of carbides?with different carbide additives (all WC materials are WC-3). The oxidation weight gain curves and oxide diffraction patterns of WC-Co and WC-Co-TaC carbides?are basically the same, with oxidation weight gains of 10.58% and 10.20% at 900°C, respectively. Among the four carbides, WC-Co-NbC carbide?has the highest oxidation weight gain, while WC-Co-TiC carbide?has the lowest oxidation weight gain, with oxidation weight gains of 11.68% and 9.05% at 900°C, respectively.
Figure 9 shows the XRD diffraction patterns of carbides?with different carbide additives after oxidation. The oxidation of the carbides produces corresponding oxides.
In WC-Co carbides, the added TaC, NbC, and TiC all exist in the form of W-containing solid solutions. The (Nb,W)C solid solution oxidizes earlier than WC and has many phase boundaries with WC. Without the protective “encapsulation” of the binder phase, the oxidation of the solid solution promotes the oxidation of WC, thereby accelerating the oxidation of the carbide. The oxidation weight gain of WC-Co-TaC carbide?is the same as that of WC-Co carbide. This is because the (Ta,W)C solid solution reacts simultaneously with WC, and since the hard phase WC is the main component, the loose and porous WO3 phase predominantly controls the oxidation rate of the carbide. Therefore, the addition of TaC does not significantly affect the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the carbide.
In summary, under the same conditions of grain size and cobalt content, the addition of TaC has no significant effect on the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the carbide. However, the addition of NbC significantly reduces the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the carbide, with a reduction of 10.4%, while the addition of TiC significantly improves the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the carbide, with an improvement of 14.5%.
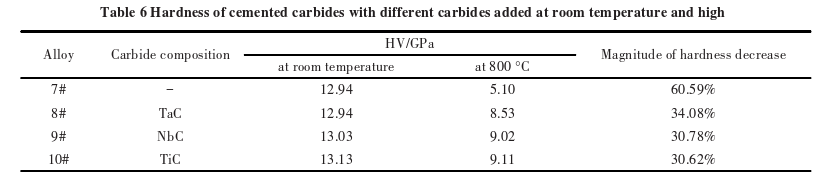
Table 6 shows the room temperature hardness and high-temperature hardness of carbides?with different carbide additives. At room temperature, the hardness of the carbides with TaC, NbC, and TiC additives is comparable to that of the WC-Co carbide. When the temperature rises to 800°C, the high-temperature hardness of the carbides with TaC, NbC, and TiC additives is higher than that of the WC-Co carbide, and the rate of decrease in high-temperature hardness is significantly reduced.
It is well known that solid solutions exhibit good red hardness and provide structural support to the overall carbide, helping it maintain high hardness under high-temperature conditions. Additionally, the solid solutions contribute to solid solution strengthening of the Co phase, which increases the hardness of the Co phase. Therefore, the addition of TaC, NbC, and TiC results in carbides?exhibiting good high-temperature hardness.
??
This study investigated the effects of cobalt content, WC grain size, and types of solid solutions on the high-temperature oxidation resistance and high-temperature hardness of carbides. The conclusions are as follows:
1.Increasing the cobalt content improves the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the carbide?and significantly increases the high-temperature hardness.
2.Reducing the WC grain size enhances the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the carbide?but significantly reduces the high-temperature hardness.
3.Compared to WC-Co carbides, the addition of TaC has no significant effect on the high-temperature oxidation resistance of the carbide, the addition of NbC decreases the high-temperature oxidation resistance, and the addition of TiC significantly improves the high-temperature oxidation resistance. All three additives, TaC, NbC, and TiC, significantly enhance the high-temperature hardness of the carbide.









