The development of nanotechnology has played a crucial role in scientific research in recent decades. The endless nanomaterials are now widely used in many fields from catalysis to biomedicine. Among various nanomaterials, colloidal nanocrystals may be one of the most important branch materials, and it has strong application prospects in many fields. Paul Alivisatos of the University of California at Berkeley has done a lot of groundbreaking work in the nano-field. He made such a question in the inaugural issue of the famous journal Nano Letters [1]: Why can such a specific scale range define one? Science and a scientific journal? What is the special point of such a compelling nanometer scale? Here, we have compiled a small footnote for trying to solve this problem by summarizing the development of quantum dots (which is what Paul Alivisatos played a pivotal role in the development of quantum dot materials) in various fields.
1. Definition
In general, colloidal nanocrystals are fragments of a crystal having a size of 1-100 nm in a metastable form in solution. Because of its physical size and the critical size of many properties, considerable surface atomic ratio, many properties of colloidal nanocrystals show a unique phenomenon related to size [3]. Traditionally, colloidal nanocrystals are mainly classified into noble metal colloidal nanocrystals and semiconductor colloidal nanocrystals. According to the classical quantum confinement effect, when the geometric radius of the semiconductor colloidal nanocrystal is smaller than the exciton Boole radius of the bulk material, the energy levels of the valence band and the conduction band will appear in a discrete distribution form. It has to be related to size. Thus, classical studies have referred to semiconductor nanocrystals with radius sizes less than or close to the exciton Boer radius as quantum dots.
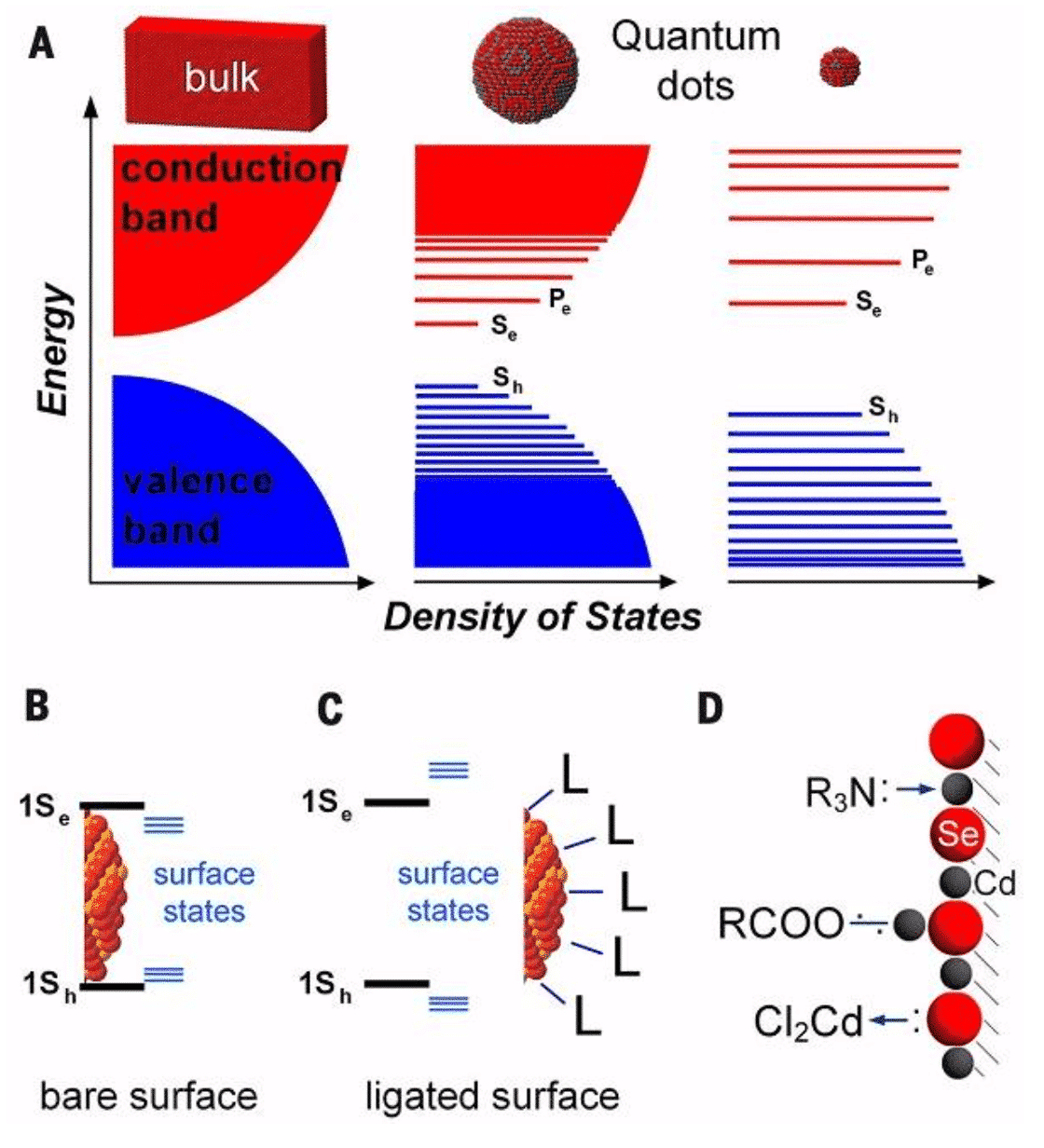
Figure 1 Structure of quantum dots (surface and core) [2]
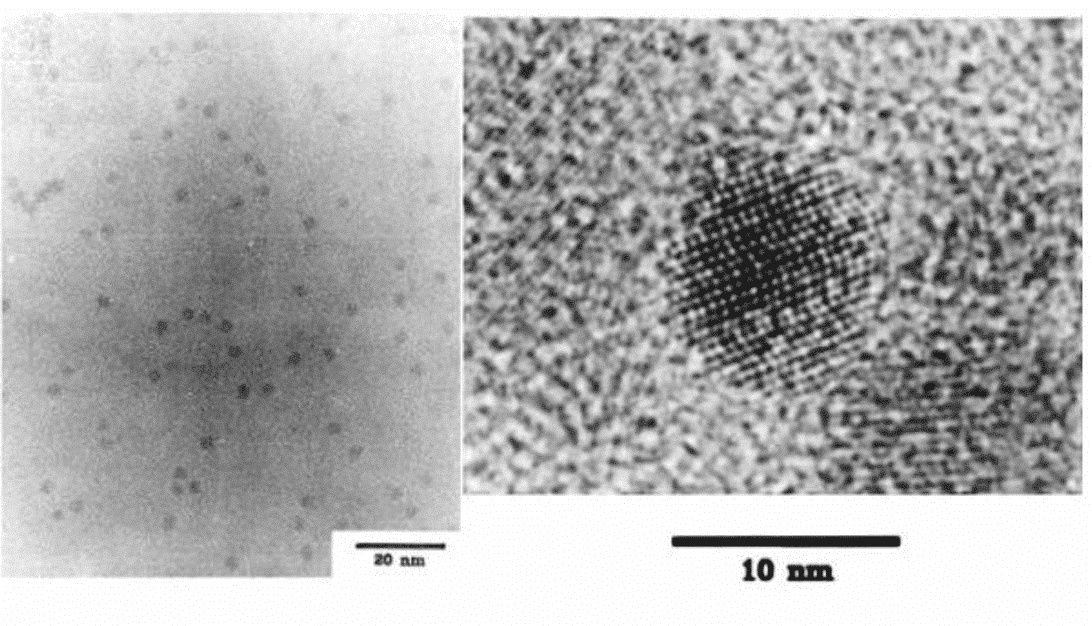
Figure 2 TEM image of monodisperse CdSe nanocrystals [4]
At the initial stage of development of quantum dots, research has focused on the field of metal chalcogenides. In 1993, MIT’s Bawendi group [4] injected organometallic compounds into high-temperature solvents, and the compounds were thermally decomposed and nucleated in solution to obtain metal chalcogenides such as cadmium selenide (CdSe) with good dispersibility. Nanocrystalline. These high-quality semiconductor nanocrystals have a diameter size distribution in the range of about 1 nm to 12 nm, have a uniform crystal structure, and exhibit size-dependent light emission and absorption characteristics. This is an early classic of the systematic study of quantum dots in the rapid development of semiconductor nanocrystal research. However, after decades of development research, the concept of quantum dots has also been extended from the original semiconductor nanocrystals, and nowadays, materials such as perovskite quantum dots, carbon quantum dots, and inorganic quantum dots without cadmium have become Research hotspots. Therefore, the application of these emerging materials will also be involved.
2.Led
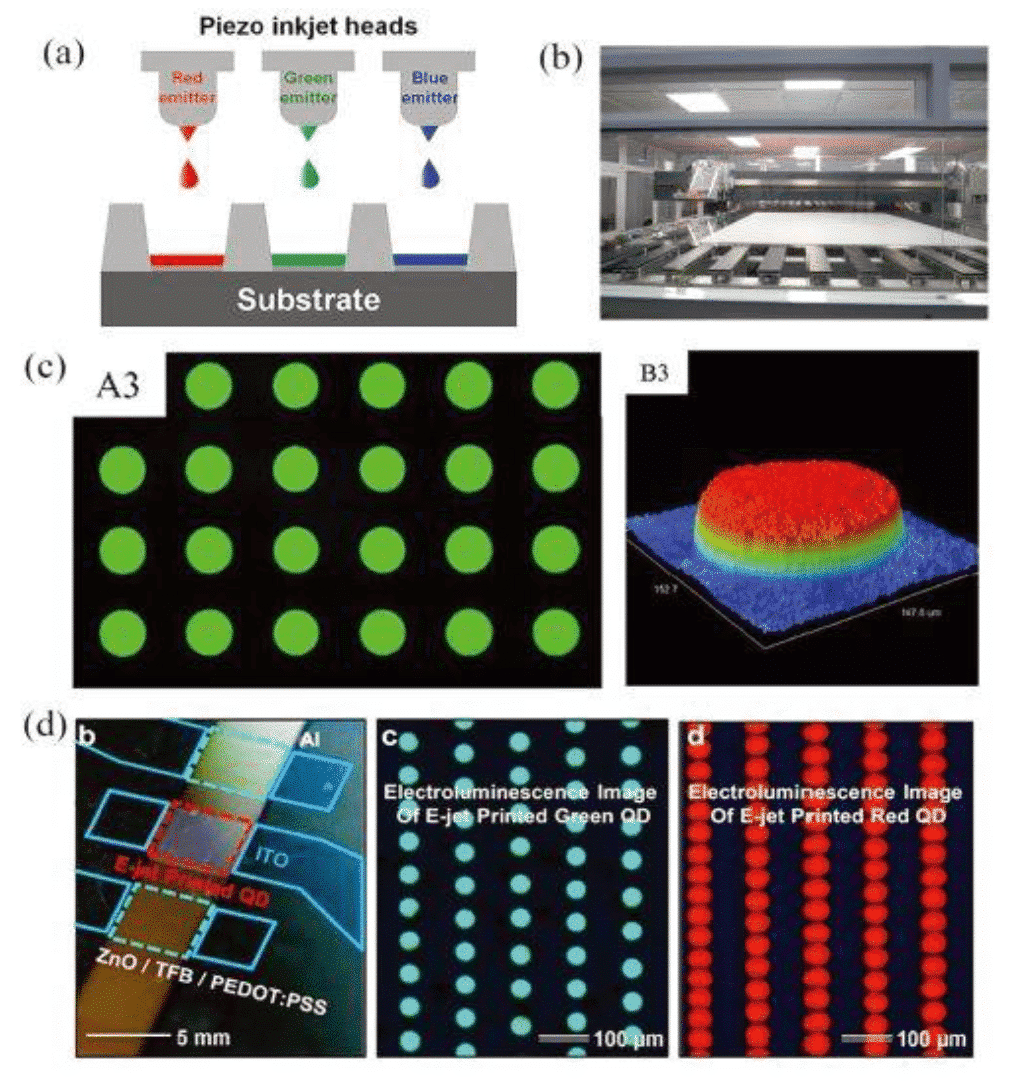
Figure 3 QLED inkjet printing [7]
As early as 1994, P. Alivisatos et al. first combined CdSe quantum dots with semiconducting polymers for the manufacture of novel organic-inorganic hybrid electroluminescent diodes. By developing new assembly techniques, researchers have constructed multi-layer quantum dots that enable charge transport. The advantages of traditional bulk inorganic semiconductor diodes in thermal, chemical, and mechanical stability have also been retained [5]. However, the organic layer in these devices will have very low carrier mobility and nanocrystalline conductivity, which directly drags the efficiency of the photovoltaic device. By around 2006, S. J. Rosenthal [6] and others prepared an ultra-small CdSe nanocrystal as a white phosphor. The quantum dots are very uniform in size and large in specific surface area, which significantly increases the probability of electrons and holes interacting on the surface of the nanocrystals, so that the Stokes shift of the nanocrystals can reach 40-50 nm and exhibit broad spectrum emission in the visible region. Characteristics. The invention of this new white phosphor has greatly expanded the application prospects of quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs). In recent years, laboratory preparation of QLED prototype devices has gradually matured in design and mechanism research [7], and the promotion of industrial production of large-area RGB pixel arrays has also become a research hotspot. Nowadays, the development of patterning technologies such as inkjet printing and transfer printing has laid the foundation for the maturity of QLED’s large-area display technology, and has significantly promoted the commercial application of QLED.
3. Living imaging
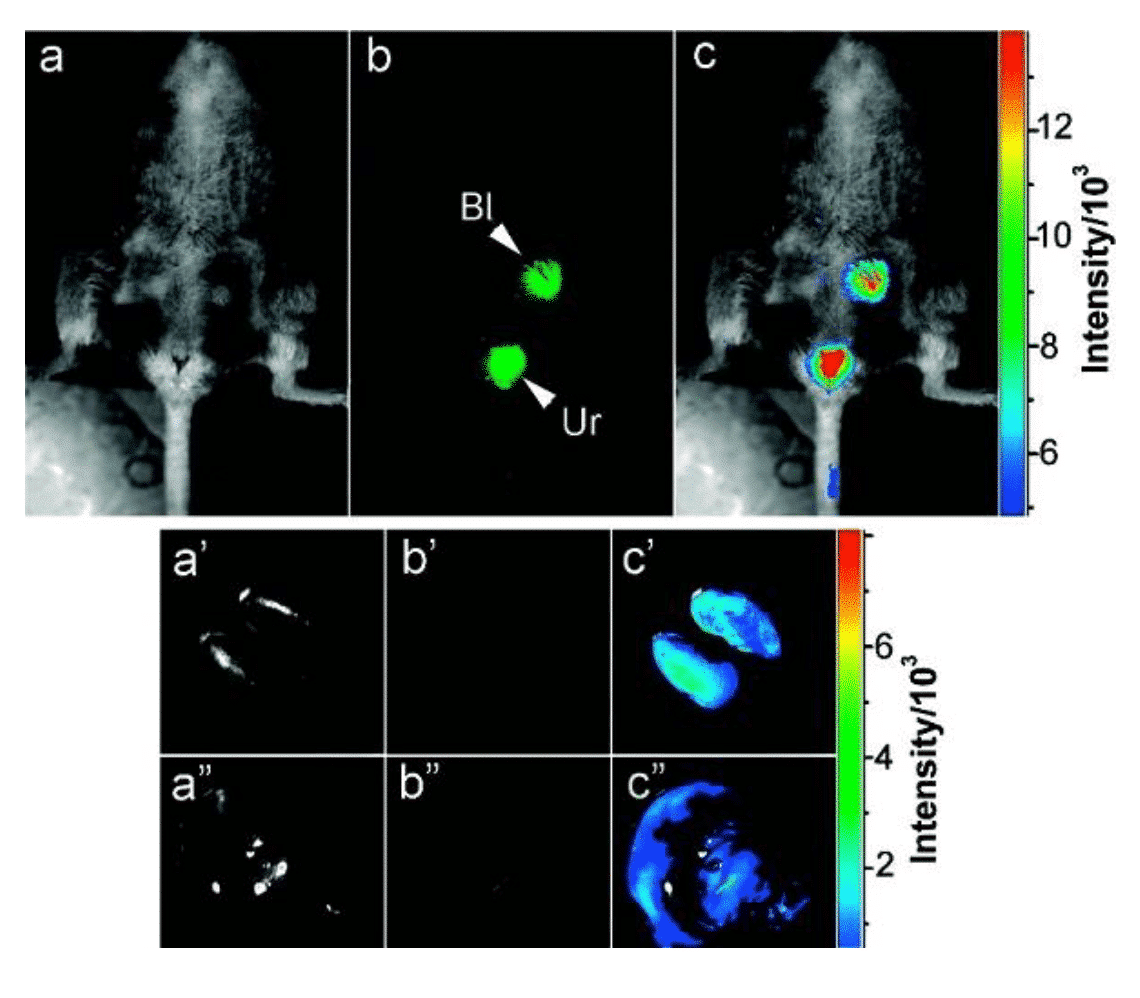
Figure 4 Carbon dots for in vivo optical imaging [11]
Fluorescence is a tool that has a wide range of applications in the biological field. Compared with traditional fluorescent dyes, quantum dots have the characteristics of high emission brightness, large molar extinction coefficient, and broad absorption spectrum, and can be used as a substitute for fluorescent dyes or fluorescent proteins. P. Alivisatos et al. [8] used quantum dots for fibroblast labeling in 1998, which has opened up the application of quantum dots as fluorescent probes for biomedical imaging. Nie Shuming’s research team also made pioneering work in the field of imaging. The research team not only used the covalent coupling of zinc sulfide/cadmium selenide core-shell quantum dots with biomacromolecules as early as 1998 to achieve ultra-sensitive non-isotopic tracing [9], they also realized for the first time in living animals. Tumor targeting and imaging studies [10] have developed diagnostic studies for quantum dot disease. Inorganic nanocrystals, especially cadmium-based nanocrystals, can cause toxic effects on organisms, so the synthesis of quantum dots with excellent biocompatibility has been a research hotspot. For example, research on synthetic copper-based or silver-based quantum dots can effectively reduce the biological toxicity of materials. In addition, the development of metal-free quantum dots is also an important strategy. The carbon dots synthesized by Ya-Ping Sun et al. still retain considerable fluorescence intensity after injection into mice [11]. In addition to toxicity, optimizing the emission region of quantum dots to better conform to near-infrared bio-optical windows is also a challenge for nanocrystalline medical applications.
4.Cancer treatment
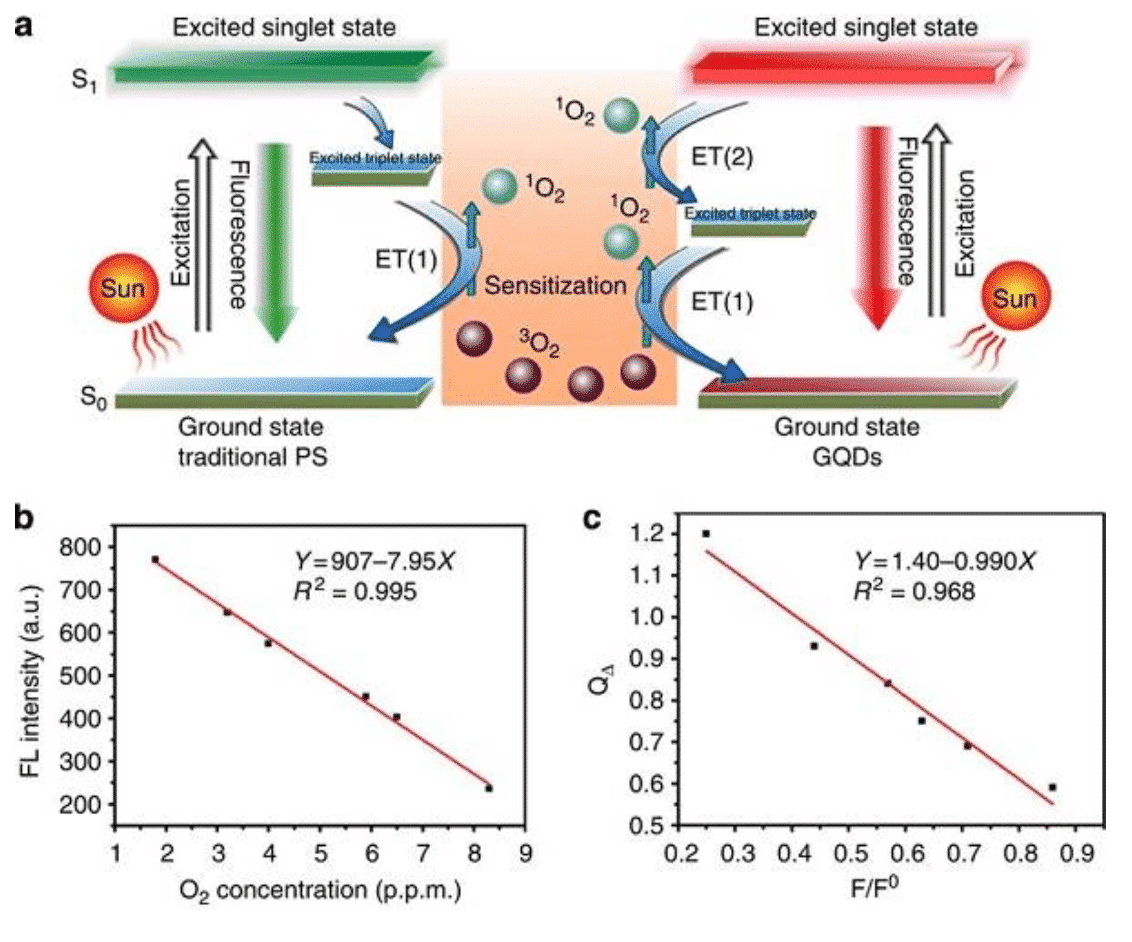
Figure 5 Singlet oxygen generation mechanism of graphene quantum dots [13]
Photodynamic therapy has now evolved into an FDA-approved cancer treatment program. In general, photosensitizer drugs are stimulated in the body to produce reactive oxygen species that kill tumor cells. However, the photosensitizer is poor in water solubility and tends to lose photochemical activity due to aggregation in the body. In 2003, the Burda team [12] first explained the development potential of CdSe quantum dots as a photosensitizer. The optical properties of quantum dots determine that it is a powerful photon absorber that transfers energy efficiently and its surface functionalization enhances dispersion in the body. In order to solve the problem of toxicity, Wang Pengfei of the Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the joint team of Wenjun Zhang of the City University of Hong Kong [13] found that graphene quantum dots can efficiently produce singlet oxygen and act on living tumors to kill tumors. In addition, recent research has extended quantum dot materials to the application of tumor photothermal therapy and radiation therapy.
5.Artificial photosynthesis
Figure 6 Application advantages of quantum dots in the field of artificial photosynthesis [14]
According to the quantum confinement effect, the band gap of the quantum dots can be artificially adjusted by an appropriate method, so that the absorption emission region of the quantum dots can cover the entire visible light spectral range as compared with the corresponding bulk materials and molecular dyes. Moreover, the exciton generation and charge separation effects of quantum dots are more controllable, so the application of quantum dots in the field of catalysis is also a very important issue. In the 1980s, research on the modification of quantum dots to platinum or ruthenium oxide [15] and other promoters can catalyze hydrolysis. Since then, researchers have been working on building quantum dot-based artificial photosynthesis and continually optimizing its performance. In 2012, an important breakthrough was made in the photocatalytic hydrogen production of quantum dot catalytic systems. Krauss et al. [16] found that after the CdSe quantum dots were coated with lipoic acid, the quantum dots were easily bonded to the nickel ion-lipoic acid system to form a hybrid catalytic system. Under visible light irradiation, this system can maintain active hydrogen production for at least 360 hours (quantum yield up to 36%), greatly improving the application prospects of non-precious metal catalysts. So far, after decades of development of artificial photosynthesis systems have entered the stage of exploring mass production and large-scale use, quantum dots have established advantages over precious metals in terms of source of acquisition and production cost, but the development of cadmium-free environment Friendly and visible light-responsive quantum dots (such as zinc selenide quantum dots) remain a challenge for implementing new energy conversion systems.
6.Perovskite quantum dot

Figure 7 Structure and properties of bismuth-lead halide perovskite quantum dots [17]
So far, metal sulfide nanocrystals are the best-developed and most in-depth quantum dot materials, and they have the widest range of applications. In the past five years, quantum dots with a crystal structure of perovskite have become an emerging research hotspot. This new type of quantum dot is no longer a metal sulfide. Instead, it is a metal halide. A metal halide with a perovskite structure exhibits unique properties such as superconductivity and ferroelectric properties that are not available in conventional quantum dots. The earliest organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite nanocrystals have the disadvantage of being extremely sensitive to environmental factors such as oxygen and humidity, which limits the development of this material. Almost at the same time, Kovalenko’s research group [17] pioneered the preparation of all-inorganic bismuth-lead halide perovskite quantum dots in 2014. This colloidal quantum dot has a cubic perovskite crystal structure, while the exciton Bohr radius It does not exceed 12 nm and therefore exhibits dimensionally related spectral properties. This emerging material combines the advantages of quantum dots and perovskite materials to extend the potential applications of quantum dots. In the past year or two, perovskite quantum dots have not only been used in photovoltaic cells and optoelectronic display devices, but have not yet been manufactured. New laser materials [18] offer new strategies.
7.Summary
Quantum dots are representative materials for explaining the “size effect” of so-called nanomaterials. They have been applied more widely in more and more fields, from optoelectronic devices to photocatalysis to biodetection, covering almost the present and Future daily needs. However, due to space limitations, many quantum dot family member materials such as silicon quantum dots have not been mentioned, and the introduction of material applications has remained in representative research. By summarizing these classic research paradigms, it is expected that the development of quantum dots can be summarized to some extent.
?? ??
Welcome to Nano Letters. Nano Letters. 2001, 1, 1.
? R. Kagan, E. Lifshitz, E. H. Sargent, et al. Building devices from colloidal quantum dots. Science. 2016, 353(6302), aac5523.
? Peng. An Essay on Synthetic Chemistry of Colloidal Nanocrystals. Nano Research. 2009, 2, 425-447.
? B. Murray, D. J. Norris, M. G. Bawendi. Synthesis and Characterization of Nearly Monodisperse CdE(E = S, Se, Te) Semiconductor Nanocrystallites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8706-8715.
? L. Colvin, M. C. Schlamp, A. P. Alivisatos. Light-emitting diodes made from cadmium selenide nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer Nature. 1994, 370, 354-357.
? J. Bowers, J. R. McBride, S. J. Rosenthal. White-Light Emission from Magic-Sized Cadmium Selenide Nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 127, 15378-15379.
? Dai, Y. Deng, X. Peng, et al. Quantum-Dot Light-Emitting Diodes for Large-Area Displays: Towards the Dawn of Commercialization. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29, 1607022.
? Bruchez, M. Moronne, P. Gin, et al. Semiconductor Nanocrystals as Fluorescent Biological Labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013-2016.
? C. W. Chan, S. Nie. Quantum Dot Bioconjugates for Ultrasensitive Nonisotopic Detection. Science, 1998, 281, 2016-2018.
? Gao, Y. Cui, R. M. Levenson, et al. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotech., 2004, 22, 969-976.
? S-T. Yang, L. Cao, P. G. Luo, et al. Carbon Dots for Optical Imaging in Vivo. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11308-11309.
? C. S. Samia, X. Chen, C. Burda. Semiconductor Quantum Dots for Photodynamic Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 15736-15737.
? Ge, M. Lan, B. Zhou et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4596.
? X-B. Li, C-H. Tung, L-Z. Wu. Semiconducting quantum dots for artificial photosynthesis. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 160-173.
? Kalyanasundaram, E. Borgarello, D. Duonghong, et al. Cleavage of Water by Visible‐Light Irradiation of Colloidal CdS Solutions; Inhibition of Photocorrosion by RuO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1981, 20.
? Han, F. Qiu, R. Eisenberg, et al. Robust Photogeneration of H2 in Water Using Semiconductor Nanocrystals and a Nickel Catalyst. Science 2012, 338, 1321-1324.
? Protesescu, S. Yakunin, M. I. Bodnarchuk, et al. Nanocrystals of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, and I): Novel Optoelectronic Material Showing Bright Emission with Wide Color Gamut. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3692-3696.
? Wang, X. Li, J. Song, et al. All‐Inorganic Colloidal Perovskite Quantum Dots: A New Class of Lasing Materials with Favorable Characteristics. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27, 7101-7108.









