Fatigue: The change in the properties of metal materials under repeated stress or strain is called fatigue.
Fatigue fracture: When a material is subjected to alternating cyclic stress or strain, it causes continuous development of local structural changes and internal defects, resulting in a decrease in mechanical properties of the material, ultimately leading to complete fracture of the product or material. This process is called fatigue fracture, and can also be referred to as metal fatigue. The stress causing fatigue fracture is generally very low, and the occurrence of fatigue fracture often has characteristics of suddenness, high localization, and sensitivity to various defects.

Classification of fatigue fracture
High-cycle fatigue and low-cycle fatigue
If the stress level acting on the part or component is low, and the number of cycles of failure is greater than 100,000, it is called high-cycle fatigue. Products such as springs, drive shafts, and fasteners are generally characterized by high-cycle fatigue.
The stress level acting on the component parts is high, and the number of cycles of damage is low, generally less than 10,000 cycles of fatigue, which is called low-cycle fatigue. For example, the fatigue damage of pressure vessels and turbine parts belongs to low-cycle fatigue.
Stress and strain analysis
Strain fatigue – high stress, low cycle number, called low cycle fatigue;
Stress fatigue – low stress, high cycle number, known as high-cycle fatigue.
Composite fatigue, but in practice, it is often difficult to distinguish between stress and strain types, and in general, both types are present, which is called composite fatigue.
Classification by load type
Bending fatigue, torsional fatigue, tension-compression fatigue, contact fatigue, vibration fatigue, and fretting fatigue.
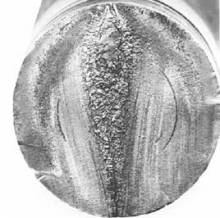
Characteristics of fatigue fracture
Macro: crack source → propagation zone → instantaneous fracture zone.
Crack source: The presence of grooves, defects, or areas of stress concentration on the surface is a prerequisite for the generation of crack sources.
Fatigue propagation zone: The section is relatively flat, with fatigue propagation perpendicular to the stress direction, resulting in a clear fatigue arc, also known as a beach or shell line.
Transient fracture zone: It is the area where fatigue cracks rapidly expand to instantaneous fracture. The fracture surface has traces of metal slip, and some products have radioactive stripes and shear lip zones in the transient fracture zone.
Microscopic: The typical characteristic of fatigue fracture is the appearance of fatigue striations.
Some microscopic samples also exhibit cleavage and quasi-cleavage phenomena (crystallographic terms for small planes that appear in microscopic images), as well as microstructural features such as toughness pockets.
Characteristics of fatigue fracture
(1) There is no obvious macroscopic plastic deformation during fracture, and there is no obvious precursor before fracture. It often occurs suddenly, causing damage or fracture of mechanical parts, which is very harmful.
(2) The stress causing fatigue fracture is very low, often lower than the stress load at the yield strength under static load.
(3) After fatigue failure, the three regions of crack initiation, propagation, and final fracture can usually be clearly observed at the fracture surface.
The cause of fatigue fracture of carbide tools
The service conditions of cemented carbide tools are generally harsh, often requiring cyclic loading, alternating temperature changes between hot and cold, and corrosive environments. Fatigue is a major cause of damage to cemented carbide workpieces.
Generally speaking, fatigue types include mechanical fatigue, thermal fatigue, corrosion fatigue, etc. In practical applications, several types of fatigue act together and promote each other. Currently, most of the reports on the properties of cemented carbides are related to static load, mainly including hardness, bending strength, fracture toughness, etc.
Fatigue fracture of carbide cutting tool
Cemented carbide tools are constantly subjected to alternating bending stresses, frequent shocks, and thermal fatigue caused by rapid cooling during idle periods during use, which inevitably leads to stick-slip and chipping. These are the various cracks that occur in the cutting area due to fatigue, which gradually expand under cyclic loading until failure.
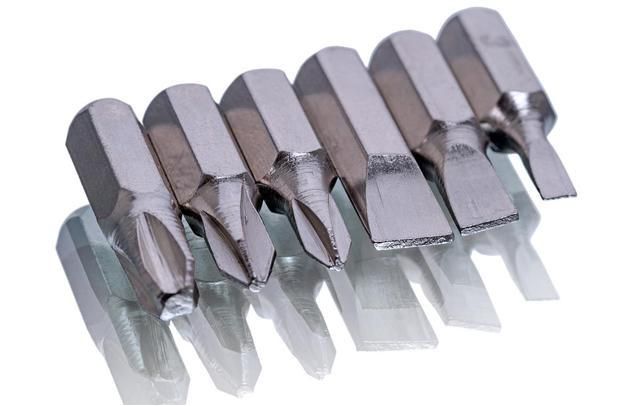

Fatigue fracture of carbide mining tools
In mining and excavation, it is necessary to achieve this through the rotation, impact, and combination of the two effects of carbide tools. During frequent contact with rock, carbide tools produce impact fatigue, and at the same time generate a large amount of heat due to severe friction, with local temperatures reaching over 1000°C. Meanwhile, under the action of water cooling or air cooling, thermal fatigue effects occur. For mining conditions in medium and soft hardness rocks, due to the small impact load on the rock, the main cause of damage is the expansion of crack sources caused by thermal fatigue under the combined action of impact load and thermal cycle, which ultimately leads to instability and final fracture of the workpiece. The final damage characteristics of this tool are the presence of “snake skin” cracks caused by thermal fatigue. During hard rock mining, the drill teeth mainly bear a large impact load, so the main damage is caused by impact fatigue. Physical or chemical changes in the surface area induce crack nucleation, which then grows and destroys. The increase in temperature accelerates this physical or chemical change, thereby exacerbating the material damage.
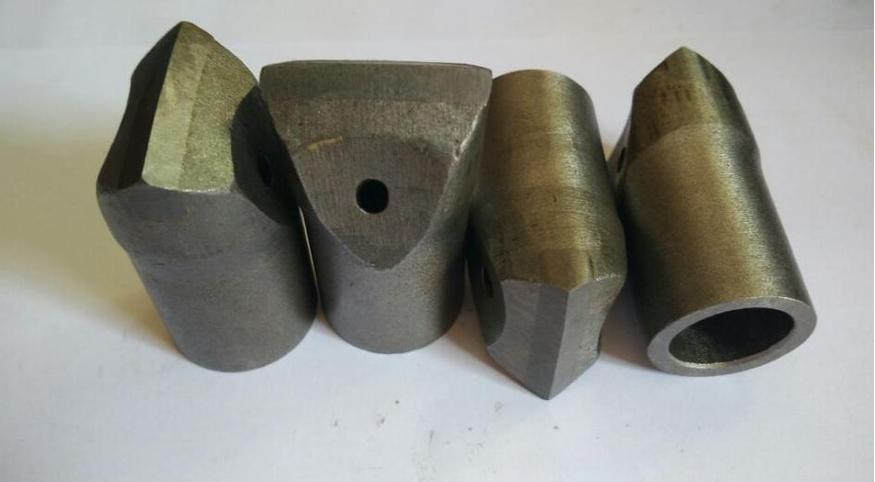

As a coal mining tool, carbide pick is subjected to high reciprocal compressive stress, shear stress, and impact load, and is also affected by temperature changes, making its service conditions quite complex.The main causes of fracture in coal mining pick blades are the combined effects of surface cracking caused by brazing, thermal fatigue, and impact fatigue.
Fatigue fracture of carbide die
Cemented carbide molds have been subjected to dynamic loads such as drawing, extrusion, and impact during use, as well as to thermal cycles due to friction or high-temperature operations, and even to the corrosive effects of cooling fluids. For example, the YG alloy used in drawing steel wire molds is ultimately destroyed due to stress corrosion cracking caused by selective dissolution of the Co binder phase in the lubricating fluid, leading to formation of a fracture source.
fatigue fracture of cemented carbide roll

During the normal use of the roll (ring), the general damage begins with surface “cracks”. This kind of crack is usually caused by thermal fatigue cracks generated by the interaction of friction heat and cooling water generated during the use of the surface. As this network-like cracks extend, it gradually causes alloy peeling and even crushing of the roll. Research indicates that the actual damage analysis of wire and rod rolls shows that the fracture source mainly originates from the voids inside the material and the groove bottom or groove surface of the roll.
Methods for improving material fatigue limit or fatigue strength
It is generally difficult to change the service conditions of parts, and it is necessary to improve the design of parts as much as possible, such as starting with surface effects. As long as the structural materials and mechanical parts are prevented from surface stress concentration, dislocation slip accumulation, and plastic deformation, fatigue cracks are not easy to nucleate and expand, which will increase the fatigue limit or fatigue strength.
Measures to slow down stress concentration
Square or sharp-angled holes and slots should be avoided in the design.
For sudden changes in cross-sectional dimensions (such as the shoulder of a stepped shaft), use a transition fillet with a sufficiently large radius to reduce stress concentration.
When it is difficult to increase the radius of the transition fillet due to structural reasons, a thinning groove or relief groove can be cut on the part of the shaft with a larger diameter.
Strengthen the surface strength
Mechanical methods are used to strengthen the surface layer (such as rolling, shot blasting, etc.), which results in a pre-stressed layer on the surface of the component, reducing the surface tensile stress that is prone to causing cracks, thereby improving fatigue strength. Alternatively, thermal and chemical treatments such as high-frequency quenching, carburizing, nitriding, etc. can be used.
Use small gravel with a diameter of 0.1-1mm to impact the surface of the sample at high speed to remove sharp corners, burrs, and other areas prone to stress concentration, and compress the surface to a depth of 1/4-1/2 the diameter of the steel ball, causing residual stress on the surface of the part and inhibiting the propagation of fatigue cracks.








