
Experimental Materials and Methods
Tungsten carbide (WC) powders were used as the raw material. Four different particle sizes of WC powder were selected: 4.0 μm, 2.2 μm, 1.1 μm, and 0.5 μm, which were labeled as WC1, WC2, WC3, and WC4, respectively. Metal cobalt (Co) powder was used as the binder phase, and paraffin was used as the forming agent. Four different WC-Co mixtures with varying particle sizes were prepared.
The mixtures were processed into green bodies with specific shapes and densities using extrusion forming equipment. The pressed green bodies were then placed in a sintering furnace and subjected to high-temperature sintering at 1400°C for 30 minutes, followed by cooling, to form cemented carbide bars.
The magnetic properties of the cemented carbide bars were tested using a magnetic performance tester, measuring parameters such as coercive force (Hc) and saturation magnetization (Bs), and the results were analyzed.
Experimental Results and Analysis
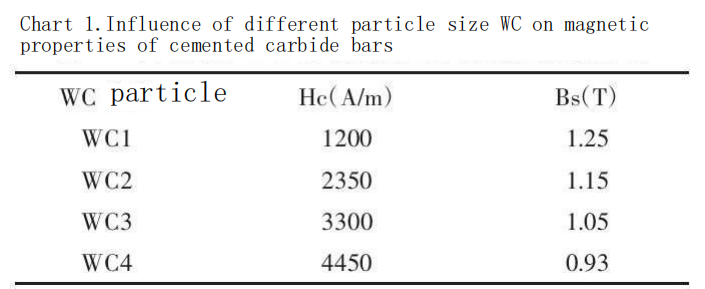
Effect of Particle Size on Coercive Force
As shown in Table 1, the coercive force of cemented carbide bars increases with decreasing WC particle size, while the saturation magnetization also increases. This indicates that cemented carbide bars made with fine and ultrafine WC particles exhibit poorer magnetic properties. Among the samples, the ultrafine WC (WC4) shows the highest coercive force of 4450 A/m, followed by medium-sized WC (WC3) with a coercive force of 3300 A/m. Coarse WC (WC2) and very coarse WC (WC1) have lower coercive forces, at 2350 A/m and 1200 A/m, respectively. The increase in coercive force with decreasing WC particle size is primarily due to the increase in internal defects and dislocations within smaller particles. These defects and dislocations create resistance to domain wall movement, making the magnetization process more difficult and requiring a larger external magnetic field to achieve saturation, thereby increasing the coercive force.
Effect of Particle Size on Material Magnetic Performance Stability
For fine and ultrafine WC particles, the larger grain boundary area facilitates grain boundary diffusion and reactions, which reduces the material’s magnetic properties. As the WC particle size decreases, the magnetic saturation of cemented carbide bars gradually increases. Specifically: coarse WC (WC1) exhibits the lowest magnetic saturation at only 1.25 T; medium-sized WC (WC2) has a magnetic saturation of 1.15 T; fine WC (WC3) and ultrafine WC (WC4) show higher magnetic saturations at 1.05 T and 0.93 T, respectively. This is likely because fine and ultrafine WC particles have higher chemical reactivity, promoting the diffusion and bonding of the Co binder, thereby improving the stability of the material’s magnetic performance.
Magnetic saturation is an indicator of the remaining proportion of magnetizable material and is closely related to magnetic properties such as coercive force and remanence. The impact of WC particle size on magnetic saturation can be attributed to the degree of solubility of the binder phase in the cemented carbide bars. Coarse and medium-sized WC particles, having larger specific surface areas, have more contact with the Co binder, which enhances the solubility of Co in the cemented carbide bars. This effectively improves the material’s magnetic performance stability, resulting in higher coercive force and better magnetic stability. Conversely, fine and ultrafine WC particles, with smaller specific surface areas, reduce the effectiveness of the Co binder, potentially affecting the material’s hardness and magnetic properties. Thus, selecting the appropriate particle size during the preparation of cemented carbide bars is crucial for achieving the best overall performance based on specific application needs.
Impact of Gamma Phase on Material Performance
For cemented carbide materials, the proportion of the gamma phase directly affects the material’s hardness and magnetic properties. Variations in carbon and oxygen content also influence the gamma phase proportion and must be considered during material preparation. Generally, higher carbon content leads to an increase in the gamma phase proportion, thereby enhancing the material’s hardness and magnetic performance. Therefore, different WC particle sizes may have varying carbon and oxygen contents, which also affects the gamma phase proportion and the overall performance of the material.
Discussion on Sintering Atmosphere
In the sintering process of cemented carbides, the choice and control of the atmosphere have a decisive impact on the final microstructure and magnetic properties of the material. The atmosphere not only affects the chemical reactions during sintering but also directly relates to the microstructure and final performance of the cemented carbide. The types of sintering atmospheres are as follows:
Oxidizing Atmosphere:? air.
Reducing Atmosphere: Contains components such as H? or CO: hydrogen atmosphere for cemented carbide sintering.
Inert or Neutral Atmosphere: Argon, helium, vacuum.
Carburizing Atmosphere: Contains high components that cause carburization of the sintered body, such as CO, methane, and hydrocarbon gases.
Nitrogen-Based Atmosphere: High nitrogen content sintering atmosphere: 10% H? in N?.
We mainly selected vacuum, argon, and hydrogen atmospheres for discussion. The variations in coercive force and magnetic saturation of cemented carbides sintered in argon, vacuum, and hydrogen atmospheres differ depending on the atmosphere, as shown in Table 2.
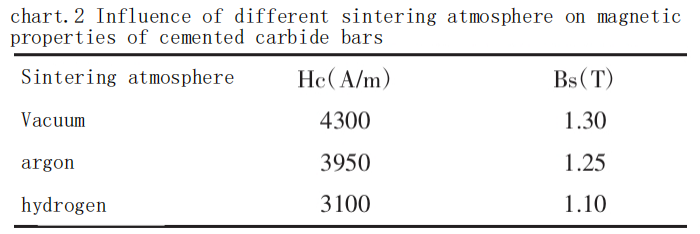
From Table 2, it can be observed that under vacuum and argon atmospheres, the coercive force (Hc) of cemented carbide bar is higher compared to that in a hydrogen atmosphere. Conversely, the saturation magnetization (Bs) is lowest in a hydrogen atmosphere compared to vacuum and argon atmospheres.
Under vacuum and argon atmospheres, the effective control of oxygen partial pressure and the exclusion of volatile elements result in fewer pores and inclusions, clearer grain boundaries, and better grain growth, thereby enhancing the magnetic properties of the material. In contrast, in a hydrogen atmosphere, the reducing nature of hydrogen may reduce some elements in the cemented carbide, leading to the presence of uncertain phase components, poor grain growth, and subsequently affecting the material’s magnetic properties.
For coercive force (Hc), it is largely dependent on the material’s microstructure and magnetic anisotropy. Under vacuum and argon atmospheres, effective control of oxygen partial pressure and exclusion of volatile elements reduce magnetic anisotropy in the cemented carbide, which improves coercive force. However, in a hydrogen atmosphere, hydrogen’s reducing effect can lead to the reduction of some elements in the cemented carbide, resulting in grain defects and inclusions that directly affect magnetic anisotropy and reduce coercive force.
Regarding saturation magnetization (Bs), the relative magnetic saturation value in cemented carbide is influenced by factors affecting carbon content in the alloy. In vacuum or argon atmospheres, effective control of oxygen content reduces carbon loss. Although the pressed green body contains oxygen, which can be reduced by free carbon and carbon in WC (MeO + C = Me + CO), the oxygen content in these atmospheres is relatively low. In a hydrogen atmosphere, decarburization reactions (WC + 2H? → CH? + C) begin at around 100°C. Throughout the preparation process, the material is exposed to a decarburizing atmosphere, leading to a lower relative magnetic saturation value.

結(jié)論
This experiment investigated the effects of different particle sizes and sintering atmospheres on the magnetic properties of cemented carbide bars. By comparing the magnetic properties of cemented carbide under different WC particle sizes (coarse, medium, fine, and ultrafine) and sintering atmospheres (vacuum, argon, and hydrogen), it was found that both particle size and atmosphere have a significant impact on the magnetic performance of the material.
From the perspective of particle size, as the WC particle size decreases, the coercive force of the cemented carbide bars increases, while magnetic saturation also increases. This indicates that particle size has a substantial effect on the magnetic properties of cemented carbide. Fine and ultrafine WC particles, due to their higher chemical reactivity and good sintering performance, can promote the diffusion and bonding of the Co binder, thus enhancing the stability of the material’s magnetic performance. However, smaller particle sizes may lead to increased porosity and inclusions, affecting the material’s hardness and magnetic performance. Therefore, the choice of particle size should be tailored to the specific application needs when preparing cemented carbide.
Regarding the atmosphere, cemented carbide bars sintered under vacuum and argon atmospheres exhibited higher coercive force and better magnetic stability. This is because these atmospheres effectively control the oxygen content and volatile elements, reducing porosity and inclusions, and promoting clearer grain boundaries and grain growth. In contrast, cemented carbide bars sintered in a hydrogen atmosphere showed significantly lower magnetic saturation. This is likely due to the decarburizing effect of hydrogen. Therefore, selecting the appropriate sintering atmosphere is crucial for obtaining cemented carbide bars with excellent magnetic properties. Further improvements in cemented carbide performance can be achieved by optimizing sintering process parameters and adding suppressants.









