Overview
In recent years, research on coarse grain carbide grades and materials has been advancing in two different directions: ultra-coarse and ultra-fine grains. Ultra-coarse grain cemented carbides have been widely applied in mining rock drilling tools, roll mills, and stamping molds.
Studies have revealed several primary forms of carbide failure during drilling: impact fatigue, abrasive wear, and thermal fatigue. For hard rock formations, such as granite (drilled with impact or rotary impact drills), abrasive wear is relatively lower, and carbide failure is primarily caused by impact and impact fatigue. The compressive strength and bending strength of the carbide are directly related to its impact fatigue resistance; additionally, this resistance is associated with the carbide’s purity, WC grain size, and Co phase’s average free path. Furthermore, the carbide’s impact fatigue resistance is directly related to the impact energy.
Reasons for Issues in Cemented Carbide Rock Drilling
For medium-hard rock formations, such as quartzite (drilled with impact drills), abrasive wear dominates. Abrasive wear generally consists of two aspects: micro-cracks at the contact points of abrasive particles and premature wear of the Co phase. The former primarily occurs on hard and brittle carbides, especially when abrasives have high fracture strength; the latter occurs on softer carbides with higher Co content, particularly when abrasives are very brittle. Figure 1 shows a scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of the wear surface of a GF20D grade drill tooth, produced by Xiamen Jinlu Special Carbide Co., Ltd., after drilling about 500 meters into quartzite. The YG6 grade carbide, composed of 94% WC with a grain size of 2-3 μm and 6% Co, has a hardness of HV30:1430. The image illustrates typical abrasive wear, characterized by premature Co phase wear and cracking and spalling of the WC phase.
For soft rock formations, such as sandstone, thermal fatigue is the primary cause of carbide failure, accompanied by abrasive wear. For ultra-soft rock formations, such as calcite and limestone, thermal fatigue is the main cause of carbide failure. The propagation of cracks and premature wear of the Co phase directly impact the drill tooth’s lifespan. Especially when drilling magnetite, thermal fatigue cracks, also known as creep cracks, dominate. Figure 2 shows a typical undulating cracking morphology of cemented carbide drill teeth formed while drilling magnetite. Figure 3 is an SEM image of a traditional polished cross-section of a carbide drill tooth that drilled about 5 meters into magnetite, composed of 94% WC with a grain size of 5 μm and 6% Co, with a hardness of 1230 HV. The image reveals that the thermal fatigue cracks on the carbide surface have extended into the carbide’s interior.
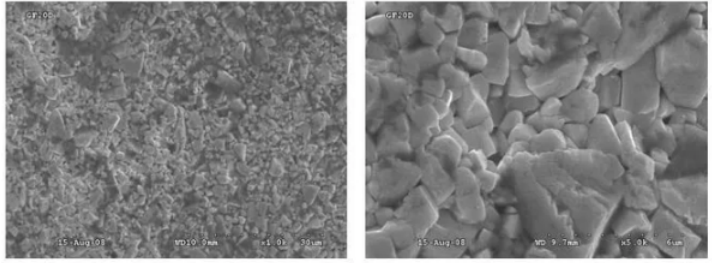
Figure 1: SEM photo of the wear surface of the quartzite at a depth of about 500 meters on the YG6 drill tips inserted in drill bits
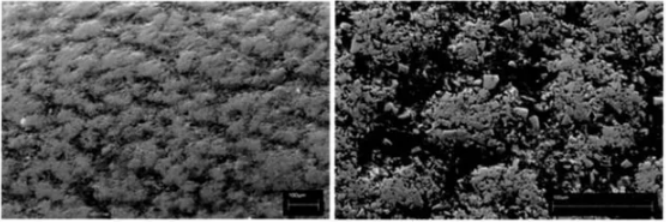
Figure 2. Typical ups and downs of crack morphology formed when carbide drill teeth drill magnetite
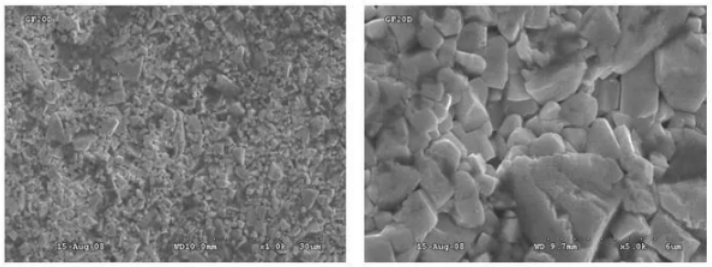
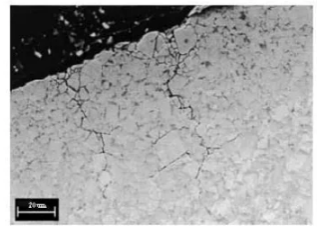
Figure 3. The carbide drill teeth drill a conventional polished cross-section of about 5m into the magnetite. The grade consists of 94% WC with a grain size of 5um and 6% Co with a hardness of 1230HV(SEM).
Reasons for Developing New Rock Drilling Cemented Carbides
The fundamental reason for developing new rock drilling carbides lies in the continuous advancement of mining and drilling technology both domestically and internationally. As drilling equipment becomes more advanced and drilling efficiency improves, there is a growing use of fully hydraulic, high-power, and high-efficiency rock drilling rigs and rotary-percussion drills. This advancement has raised higher demands for the quality and lifespan of rock drilling cemented carbides. When drilling tools penetrate rock, the pressure rises from 0 to 10 tons within 1/10 of a second, and the temperature increases from 20°C to 1000°C. During impact and rotation, drilling carbides generate extremely high temperatures. Especially when drilling magnetite, rapid formation of thermal cracks, commonly referred to as “snake skin” or “tortoise shell” cracks, occurs.
To meet the requirements of modern rock drilling technology, the performance of rock drilling cemented carbides needs to be improved and optimized in several key areas: the thermal conductivity (the ability of the material to conduct heat) should be as high as possible; the thermal expansion coefficient (the linear expansion of the material when heated) should be as low as possible to ensure minimal growth rate of thermal cracks; high-temperature hardness should be further enhanced to guarantee good wear resistance at high temperatures; in addition, the transverse rupture strength (TRS) and fracture toughness (Kic, the material’s ability to resist sudden fractures caused by micro-cracks) should also be improved.
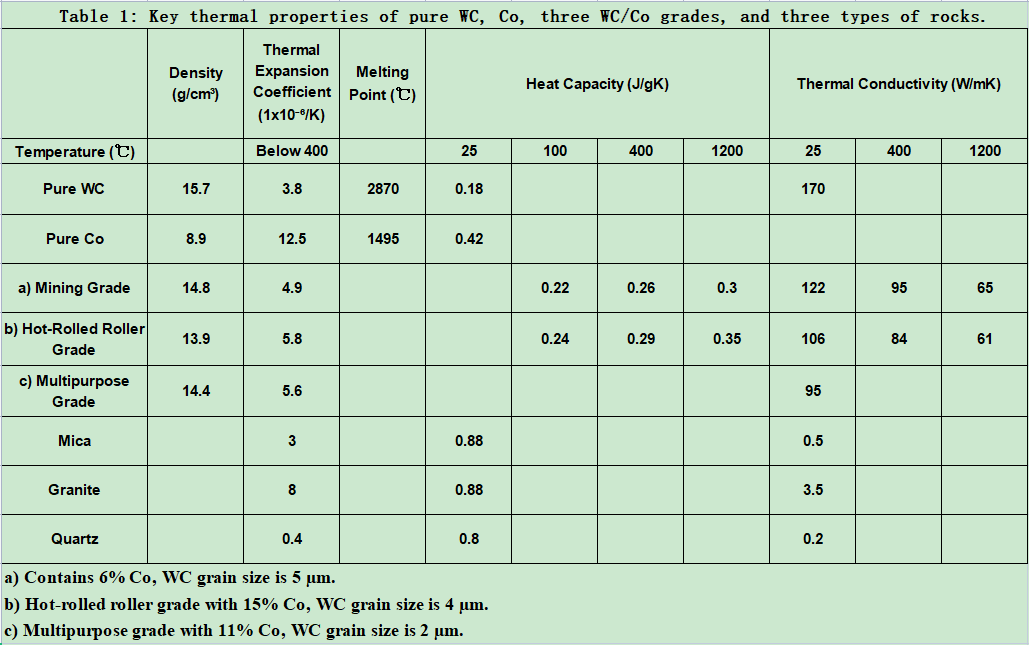
Table 1 lists the thermal performance data of pure WC, pure Co, three commonly used WC-Co carbide grades, and three types of rock. These three grades, with varying Co content and WC grain sizes, are suitable for different rock drilling teeth, hot-rolled rolls, and multi-purpose applications.
Directions for Developing New Rock Drilling Cemented Carbides
It is well known that Co has low thermal conductivity and a high thermal expansion coefficient. Therefore, the Co content should be minimized as much as possible. On the other hand, cemented carbides with high Co content exhibit better strength and fracture toughness. From a mechanical perspective, especially when carbide drill bits penetrate rock surfaces at high speeds, the drill bits endure high impact and loads, or mechanical vibrations under hard cutting conditions, necessitating improved strength and fracture toughness in the carbide. Additionally, compared to fine-grained carbides, coarse WC grain sizes contribute to greater strength and fracture toughness of the cemented carbide.
As a result, the preparation of rock drilling cemented carbides tends to use lower cobalt content and increase WC grain size to achieve good mechanical properties and the required high-temperature wear resistance. This approach results in ultra-coarse grain carbides. Traditionally, the production of ultra-coarse grain cemented carbides involves high-temperature reduction of coarse grain tungsten powder followed by high-temperature carburization to produce coarse grain WC powder. This powder is then mixed with Co powder and ball-milled to form a mixture, which is subsequently pressed and sintered to create the cemented carbide. However, coarse grain WC powder produced from tungsten powder via high-temperature carburization generally consists of polycrystalline particles, where each WC particle is composed of multiple WC single crystals.
Figure 4 shows a scanning electron microscope image of coarse grain carbide powder with a Feret diameter of 23.20 μm. The image reveals that each WC particle contains multiple WC single crystals. Although the original powder has a coarse grain size, after grinding, the polycrystalline particles easily break down into fine single crystal particles. Consequently, the ground WC powder has a Feret diameter of only 4.85 μm. Figure 5 shows the metallographic photo of a cobalt-containing carbide with 6% Co produced using conventional carbide production processes. The average grain size of this carbide is approximately 4.0 μm.

Figure 4: SEM image of coarse grain WC powder with a particle size of 23.20 μm.
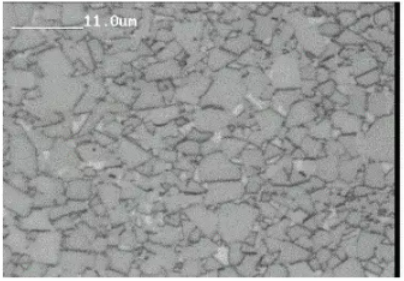
Figure 5: Metallographic photo of WC-6% Co alloy produced from coarse grain WC powder with a particle size of 23.20 μm using conventional processing methods.
U.S. Patents 5505902 and 5529804 disclose methods for producing ultra-coarse grain cemented carbides. The methods outlined in these patents involve the dispersion and classification of coarse grain WC powder through jet milling and sieving to remove fine WC particles, selecting only the coarse-grained carbide, and then coating these WC particles with Co. Patent 5505902 utilizes the sol-gel method, where WC, methanol, and triethanolamine are mixed in a reactor. During heating, methanol evaporates, and Co precipitates onto the WC grains, forming a sol-gel.
Patent 5529804 employs the polyol method, where Co acetate, water, and WC are mixed and then spray-dried. The mixing process is optimized to prevent the breaking of coarse WC particles. The mixture produced using these patented methods is then subjected to conventional pressing and sintering processes to create cemented carbides with 6% Co and an average grain size of 13-14 μm, with porosity easily controlled between A02 and B02. This new carbide shows better WC matrix adjacency compared to carbides produced by traditional ball milling. Consequently, this new carbide has been successful in specific applications where conventional carbides fall short, such as in hard rock layers like granite and hard sandstone. In these cases, conventional column teeth fail due to Co dissolution at high temperatures, leading to spalling of elongated or hexagonal WC grains, and eventually, complete spalling of the drill bit within minutes, causing rapid crack propagation and subsequent fracture. In contrast, carbides produced with new technology can be used for extended periods in hard rock layers, displaying stable wear resistance without deep cracks. Due to the high adjacency of the WC matrix, the thermal conductivity of the 6% Co carbide with a WC average grain size of 14 μm can reach 134 W/m°C, which is 20% higher than that of coarse-grained carbides with the same Co content produced by traditional methods and comparable to the thermal conductivity of pure WC.

Application Examples of New Ultra-Coarse Grain Cemented Carbide Production Technologies
Two types of impact drilling cemented carbides were simultaneously produced using both traditional and new methods and tested in iron ore. Both samples had a WC average grain size of 8 μm, 6% Co, and 94% WC content.
Sample A: Produced using traditional ball milling, drying, pressing, and sintering processes. This carbide has a wide distribution of crystal sizes.
Sample B: The WC powder was subjected to jet dispersion and classification to remove coarser and finer WC particles, selecting 6.5-9 μm WC powder. The WC grains were pre-coated with 2% Co, and then 4% pure Co was added to achieve a 6% Co content. After wet mixing (without ball milling) to obtain the desired slurry, a thickening agent was added if necessary to prevent coarse grain WC sedimentation. The slurry was dried, shaped, and sintered, resulting in a narrower particle size distribution, with over 95% of the grains ranging from 6.5 to 9 μm. The adjacency of these carbides was measured: Sample A had an adjacency of 0.41, while Sample B had an adjacency of 0.61.
Testing was conducted in magnetite, which is prone to generating high heat and thermal fatigue. After drilling 100 μm, Sample A exhibited thermal cracking. Cross-sectional observation of the used carbide revealed small cracks extending into the carbide, damaging its microstructure and reducing its lifespan. With regrinding after every 100 μm of drilling, the carbide’s drilling lifespan was 530 meters. Sample B showed no or only minimal thermal cracking after drilling 100 meters. Cross-sectional observation showed no internal cracks, only some fractured surface grains. With regrinding after every 200 meters, the average drilling lifespan was 720 meters.







