Currently, TiN is the primary coating used for cutting tools; however, traditional nitride coatings like TiN have low hardness, poor wear resistance, and particularly weak thermal stability, which limits their application in dry cutting tools. Improvements in TiN coatings have focused on developing new TiN-based alloys and multi-component composite layers, aiming to achieve wear-resistant, high-temperature coatings through the introduction of alloying elements (such as Al, Zr, Cr, V) into the TiN coating. This forms a new multi-element coating system that enhances coating hardness and improves wear resistance and thermal stability. The novel TiAlN coating, formed by implanting Al atoms into the TiN lattice, has become one of the most widely used tool coatings in global manufacturing.
In recent years, to further enhance the high-temperature hardness and oxidation resistance of tool coatings, as well as to improve the bonding strength between the coating and the substrate, research has shifted towards multi-element and multilayer composite coating systems. This paper employs unbalanced magnetron sputtering to prepare composite coatings such as TiN, TiAlN, TiN-MoS?, and CrAlTiN on carbide?tools. It conducts cutting comparison tests on TiN and its composite-coated tools under dry cutting conditions, investigating the mechanical and cutting performance of TiN-based composite coated tools. This research is significant for the further development and promotion of coated tools.
Experimental Methods
Composite coatings of TiN, TiAlN, TiN-MoS?, and CrAlTiN were deposited on YT14 carbide?tools using the closed-field unbalanced magnetron sputtering ion plating equipment from Teer. The nano-hardness and elastic modulus of the coatings were measured using a Nano Test 600 nano-hardness tester with a diamond tip under a load of 3 mN. To minimize experimental errors, the hardness and elastic modulus values reported are the averages of five measurements. Additionally, Vickers microhardness testing was conducted to validate the hardness measurements.
The morphology and phase structure of the tool coatings were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and an Advance 8 X-ray diffractometer (XRD). Cutting tests on the coated tools were performed in a CNC machining center, with the workpiece material being PCrNi3MoVA steel. The wear of the cutting edge was observed and measured using a 30x tool microscope. The tool life was evaluated based on the wear land width (VBc) on the flank face exceeding 0.6 mm as the criterion for tool lifespan, allowing for a comparison of the cutting life of the tools.
Experimental Results and Analysis
Hardness and Elastic Modulus Testing of Coatings
Figure 1 shows the loading-unloading curve obtained during the nano-hardness measurement of the CrAlTiN composite coating. This curve allows us to determine both the hardness and elasticity of the CrAlTiN film. The elastic recovery coefficient
R=(hmax-hres)/hmax ?is defined, where hmax?is the indentation depth at maximum load, and
hres?is the residual depth after unloading. A higher R value indicates greater elasticity. From the nano-indentation curve in Figure 2, the hardness of the CrAlTiN film is found to be 33 GPa, with an elastic modulus of 675 GPa.
Figure 2 also compares the nano-hardness of TiN, TiAlN, TiN-MoS?, and CrAlTiN coatings. The measured nano-hardness values are 18 GPa for TiN, 30 GPa for TiAlN, 15 GPa for TiN-MoS?, and 33 GPa for CrAlTiN. The order of nano-hardness for the four coatings is: CrAlTiN > TiAlN > TiN > TiN-MoS?. The addition of composite elements significantly alters the hardness of the TiN coating; in particular, the incorporation of Al increases the hardness by 12 GPa, while the addition of Cr and Al collectively raises the nano-hardness by 15 GPa. This indicates that Cr and Al form hard phases within the composite coating, enhancing its hardness. Conversely, the combination of TiN with MoS?results in a 3 GPa decrease in nano-hardness, suggesting that the MoS?phase exists as a soft phase within the coating, reducing hardness. However, this lubricating phase significantly improves the coating’s lubrication properties and lowers its friction coefficient.
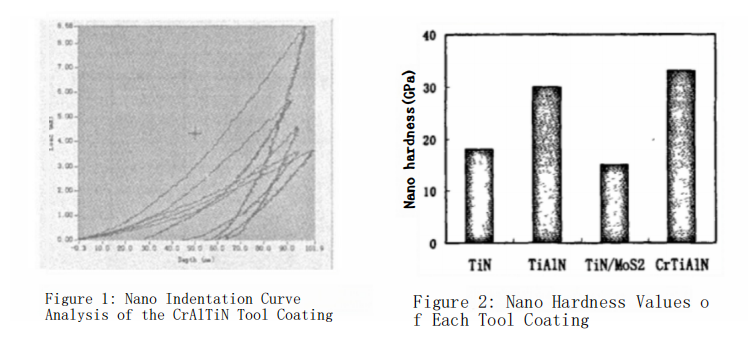
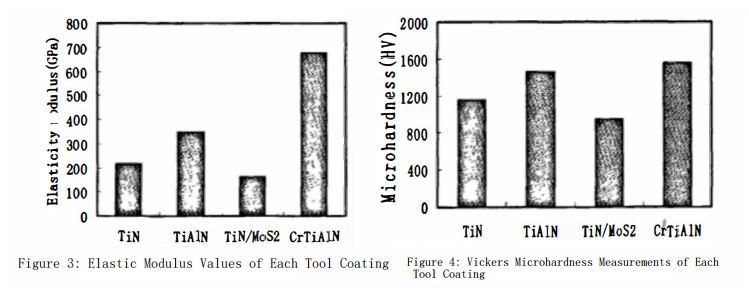
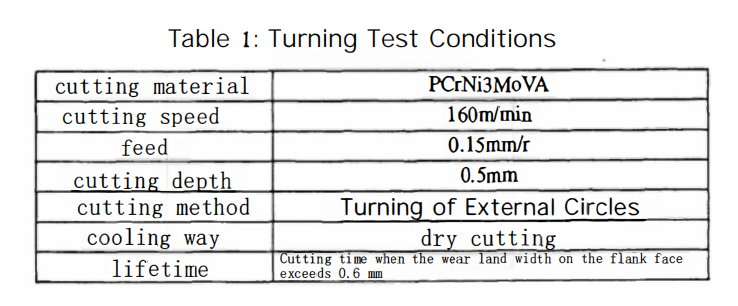
Figure 3 presents the measured elastic modulus values for each coating. From the figure, it can be observed that the elastic modulus of the TiN coating is 214 GPa, that of the TiAlN coating is 346 GPa, the TiN-MoS? coating has an elastic modulus of 164 GPa, and the CrAlTiN coating reaches 675 GPa. The order of elastic modulus for the four coatings is CrAlTiN > TiAlN > TiN > TiN-MoS?. This indicates that the elastic modulus of the coatings is directly proportional to their hardness. Notably, the CrAlTiN coating shows the greatest relative increase in elastic modulus, with a value significantly higher than the other coatings at 675 GPa. This demonstrates that the deposited CrAlTiN coating possesses both high hardness and high elasticity.
At the same time, Vickers microhardness tests were conducted on each tool coating using a Vickers hardness tester, with an applied load of 15 g for 10 seconds. The results are shown in Figure 4. Although the testing principles of the Vickers microhardness and nano-indentation methods differ, a comparison of the nano-hardness values in Figure 2 and the microhardness values in Figure 4 reveals that the trends in microhardness for each coating are consistent with those of nano-hardness. Notably, the CrAlTiN coating exhibits the highest Vickers microhardness, measuring HV1560.
Drilling Tests
The four types of coated carbide?tools—TiN, TiAlN, TiN-MoS?, and CrAlTiN—were used to process the same material, PCrNi3MoVA steel, and the wear of the tools was evaluated to compare the durability of the different coated tools. The surface morphology of the coatings for the TiN, TiAlN, TiN-MoS?, and CrAlTiN tools is shown in Figure 5, all at a magnification of 600x. The figure illustrates significant differences in surface morphology among the four coatings, indicating that the incorporation of composite elements has greatly altered the crystallization state of the TiN compound.
The TiN coating shows a uniform surface microstructure with relatively small grains. In contrast, the TiAlN coating has a rougher surface morphology with larger grain structures. The addition of Al results in numerous bright white hard particles of aluminum oxide or aluminum nitride appearing in the TiN lattice. The TiN-MoS? coating features a substantial distribution of flake-like mixed structures, mainly composed of MoS? uniformly dispersed within the TiN/MoS?coating, contributing to its self-lubricating properties. The CrAlTiN coating exhibits relatively fine grains and a dense, uniform structure with a significant presence of hard particles on the surface.
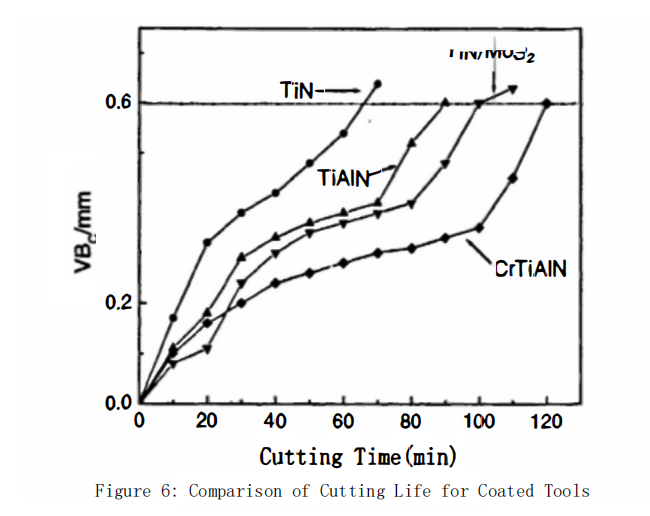
The cutting test conditions for the coated tools are shown in Table 1. During the experiments, the conditions were kept constant, and the cutting time was recorded until the wear land width (VBc) on the flank face exceeded 0.6 mm, which was used as the criterion for tool life evaluation. The comparison of cutting life for the tools is presented in Figure 6.
From Figure 6, the ranking of cutting life for the four coated tools is as follows: CrAlTiN > TiN-MoS? > TiAlN > TiN. This indicates that the Cr and Al elements in the TiN coating form hard phases, and the addition of Al is beneficial for the formation of aluminum oxides, which helps prevent further oxidation during the cutting process, thereby enhancing the tool’s oxidation resistance and contributing to an increase in cutting life. Additionally, the MoS? lubricating phase helps reduce the friction coefficient and improve the wear resistance of the tools, further extending their service life.
In summary, the analysis indicates that the multi-component composite coatings effectively leverage the advantages of various coating materials, resulting in enhanced overall performance, excellent wear resistance, toughness, and reduced friction. This helps to minimize built-up edge formation while providing resistance to mechanical and thermal shocks, significantly extending tool life. Therefore, it is anticipated that the usage of multi-component composite coated tools will continue to increase in the future.
XRD Analysis
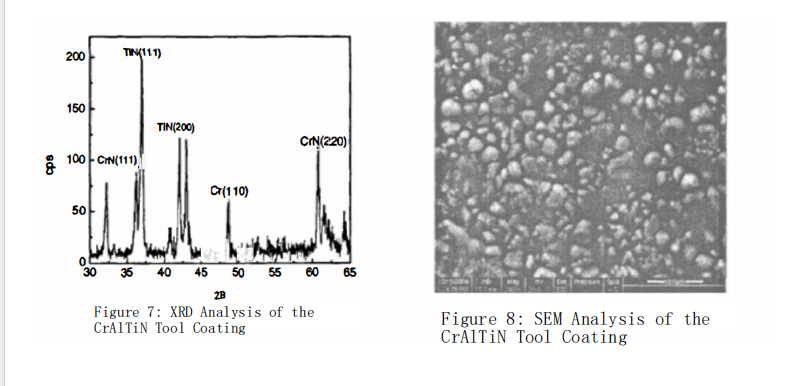
XRD analysis was conducted on the CrAlTiN tool coating, which exhibited the best cutting performance, with the results shown in Figure 8. The XRD patterns reveal that at room temperature, the crystalline phases of the coating are primarily composed of Cr, CrN, Cr?N, and TiN, with no amorphous phases detected. Further high-resolution scanning of the coating surface shows a significant distribution of hard phase particles. Combined with X-ray diffraction analysis, it is evident that these hard phases mainly consist of Cr, CrN, Cr?N, and TiN grains. These hard grains contribute to the improved cutting life of the coated tools.
Application Prospects
Coating technology for tools has proven to be an effective way to enhance the cutting performance of carbide?tools, improve cutting efficiency, and reduce processing costs. Since its introduction in the late 1970s, it has rapidly developed and been adopted worldwide. By the late 1980s, the proportion of complex carbide?tools using coatings in industrialized countries exceeded 60%, significantly improving cutting efficiency and yielding notable economic benefits. Currently, over 80% of carbide?tools used in CNC machines in Japan and Germany are coated, and the adoption of coatings in countries like Russia is also increasing.
However, the usage of coated tools in China remains limited, with even high-performance CNC machines often relying on standard carbide?tools with inferior cutting performance. This restricts the full potential of expensive equipment. Therefore, developing composite coating processes for carbide?tools is crucial for shifting China away from its reliance on imported high-performance tools and advancing the local coating technology.
Although coated carbide?tools are priced 50% to 100% higher than standard tools, their superior cutting performance, longer tool life, and higher production efficiency lead to lower costs per part compared to uncoated tools. This is particularly beneficial for complex tools with longer manufacturing cycles, such as gear cutters and broaches, where using coated tools not only offsets the coating costs but also provides significant economic benefits and better machining quality
Furthermore, coated tools facilitate dry cutting, eliminating the increased production costs and environmental pollution associated with cutting fluids, thus protecting worker health. Therefore, from both economic and social benefit perspectives, using coated carbide?tools is advantageous. In the future, as research into multi-component and multilayer composite coating technologies progresses, the lifespan of coated carbide?tools will further improve, significantly lowering manufacturing costs and broadening the application of these coatings.
????????
This study utilized the closed-field unbalanced magnetron sputtering PVD coating process to prepare composite coatings such as TiN, TiAlN, TiN-MoS?, and CrAlTiN. Comparative tests of the mechanical and cutting performance of these coatings yielded the following results:
1.Nano-indentation analysis showed the order of nano-hardness for the four tool coatings as follows: CrAlTiN > TiAlN > TiN > TiN-MoS?. The elastic modulus was found to be proportional to hardness, and Vickers microhardness measurements further validated the accuracy of the nano-indentation tests.
2.Under dry cutting conditions while drilling PCrNi3MoVA steel, the cutting life of the coated tools ranked as: CrAlTiN > TiN-MoS? > TiAlN > TiN, indicating that multi-component composite coatings offer significantly better cutting performance than standard TiN coatings, marking a promising direction for the future development of coated tools.








