
Carbides are composed of refractory carbides with high compressive strength, hardness, and elastic modulus, which are difficult to plastically deform during the pressing process. To improve the formability of the powder and increase the strength of the compact, a binder must be added to the powder material before shaping.
As an intermediate auxiliary material, the binder must be completely removed during the degumming stage, as any residue can pose a quality risk to the product. The total carbon content in the alloy must be strictly controlled to produce high-quality carbide products. Although many factors can affect the total carbon content in carbide products, the application of the binder is a crucial aspect, especially when the quality of the tungsten carbide raw material is stable.
Therefore, the performance of the binder is a key factor directly affecting the properties of the blank and the final sintered product.
Research Status and Issues
Current Usage
According to surveys, some carbide manufacturers have used synthetic resins, dextrin, starch, methyl alcohol, and cellulose as binders in the past. For example, East Germany used a mixture of ceresin, paraffin wax, and mineral oil with an addition rate of 48%-59%; General Electric in the United States used starch, rubber, and synthetic resins; the United Kingdom applied water-soluble fibers and polyacrylamide; and some manufacturers even added surfactants.
Foreign carbide manufacturers, equipped with advanced production equipment and high automation levels, use pipeline conveying for mixed material preparation equipment, fully automatic high-precision presses, and multi-atmosphere pressure degumming and sintering integrated furnaces. The binders used in foreign carbide production are primarily paraffin and PEG, with paraffin acetone as the ball milling medium, and rubber as a binder is very rare.
Currently, the widely used binders in domestic carbide manufacturers are rubber, paraffin, and polyethylene glycol (PEG). Depending on the foreign manufacturer from which the technology was introduced and the time of introduction, each manufacturers usage may vary. Manufacturers that have introduced Sandvik technology generally use PEG as a binder and adopt a spray drying process. Some use paraffin as a binder and also adopt a spray drying process. Some enterprises use a combination of binders, and there are also mixtures of rubber and paraffin. SMEs basically use the rubber process, with each type of binder having its own advantages and disadvantages.
Rubber Binders
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the carbide industry in China used butadiene sodium rubber imported from the Soviet Union, which had stable rubber quality. Later, due to changes in the situation, domestically produced synthetic butadiene sodium rubber from Lanzhou was used. Due to manufacturing process technology and equipment issues, the quality stability of the rubber was poor. The butadiene sodium rubber dissolved in gasoline had a high gel content, and the solution was suspended, making filtration difficult, with high ash and impurity content, which affected the normal production of the alloy.
Rubber solvents have good formability and can press out products with complex shapes and larger volumes, and the compact is less likely to crack. However, the disadvantages include high ash content, high residual carbon, difficulty in precise carbon control, vacuum removal, and unstable product quality, and it is not suitable for the spray drying process.
Paraffin-Type Binders
Paraffin is derived from petroleum refining and is a mixture of various hydrocarbons, with a small amount of liquid “impurities” present as oil, and the solid component is saturated alkanes. The properties of paraffin are ultimately determined by its chemical composition, whether they are straight-chain, branched, or cyclic structures. Paraffins can be classified into: paraffin, microcrystalline wax, montan wax, vegetable wax, animal wax, and synthetic wax. There are dozens to hundreds of different varieties, each with different molecular weight, structure, performance, and uses.
The paraffin used for carbides is mainly composed of normal alkanes, with few straight-chain molecules and aromatic hydrocarbons. The molecular weight range is 360-540, with a melting point of 42-70 degrees and slight solubility in ethanol. Microcrystalline wax has a molecular weight of 580-700, mostly branched molecules, with more cyclic hydrocarbon compounds. Paraffin is brittle, while microcrystalline wax is stronger and more flexible, with higher tensile strength and melting point, greater adhesiveness, and is a saturated straight-chain hydrocarbon that can completely volatilize at high temperatures without leaving any residue and is easily removed under vacuum. This reduces the difficulty in controlling the carbon content and improves the precision of the carbon content in the alloy, but it has a low viscosity, resulting in low compaction strength and large elastic after-effect, which makes it prone to cracking at stress concentration areas, difficult to produce complex-shaped products, and the compacts are brittle and prone to chipping.
Water-Soluble Polymer Binders
PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) is a water-soluble polymer, and foreign literature classifies PEG as a synthetic wax. It is prepared by stepwise addition of ethylene oxide to water or ethylene glycol, with a molecular weight range of 200-20000. PEG is completely soluble in water and has very low solubility in ethanol at room temperature (less than 1%). It is compatible with many substances and shows the greatest compatibility with substances with high polarity. It is non-toxic and non-irritating. The formability of PEG is equivalent to that of paraffin, and it has less residual carbon. Therefore, it can be considered a safe and environmentally friendly binder suitable for spray drying. However, PEG has a serious tendency to absorb moisture, and its moisture absorption capacity decreases with increasing molecular weight. It has very strict requirements for humidity and temperature in the working environment. After absorbing moisture, the powder becomes hard, the pressing pressure increases, and higher requirements are placed on the press. Additionally, it is more difficult to form some complex products.
Water-Soluble Polymer Binders
PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) is a water-soluble polymer, and according to foreign literature, PEG is classified as a synthetic wax. It is prepared by stepwise addition of ethylene oxide to water or ethylene glycol, with a molecular weight range of 200-20000. PEG is completely soluble in water and has very low solubility in ethanol at room temperature (less than 1%). It is compatible with many substances and shows the greatest compatibility with substances with high polarity. It is non-toxic and non-irritating. The formability of PEG is equivalent to that of paraffin, and it has less residual carbon. Therefore, it can be considered a safe and environmentally friendly binder suitable for spray drying. However, PEG has a serious tendency to absorb moisture, and its moisture absorption capacity decreases with increasing molecular weight. It has very strict requirements for humidity and temperature in the working environment. After absorbing moisture, the powder becomes hard, the pressing pressure increases, and higher requirements are placed on the press. Additionally, it is more difficult to form some complex products.
Comparison in Actual Production
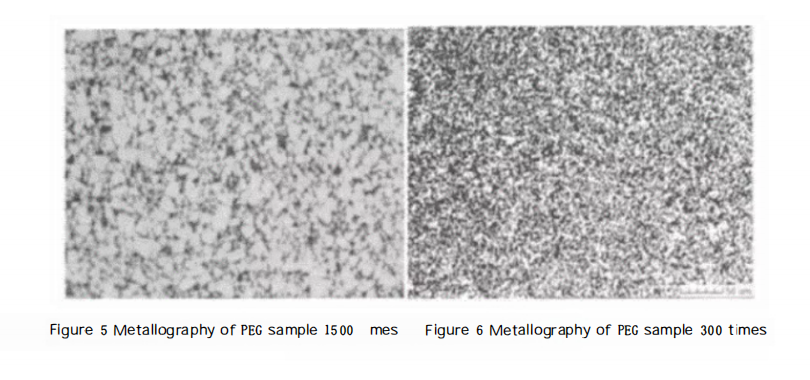
To compare the performance of the three binders, three batches of mixed materials were prepared using sodium butadiene rubber, paraffin, and PEG as binders. The basic composition of the mixture was WC-8%Co, and the blanks were compressed to the same weight and then sintered in a vacuum degassing integrated furnace to obtain metallographic and physical properties for comparison.
Experimental Section

The WC particle size used in this experiment was 6.5 m. The rubber used was sodium butadiene rubber, paraffin, and PEG.
The rubber and paraffin materials used aviation gasoline as the wet milling medium, while the PEG material used anhydrous alcohol as the ball milling medium. After ball milling, all materials were dried in a vacuum, screened, and granulated before pressing the compacts. They were then sintered under vacuum and pressure at a temperature of 1430°C.
From a direct analysis of the physical and mechanical performance data, it can be observed that the samples using paraffin and PEG as binders have increased strength and reduced magnetism, which is a significant advantage for mining carbides. Additionally, the metallographic photographs indicate that the microstructure using paraffin and PEG binders is more uniform compared to rubber binders. This is because paraffin and PEG have less residual carbon, while rubber binders are difficult to remove, leading to the growth of local grains due to the presence of a large amount of residual carbon.
Due to the lack of spray granulation equipment, the mixed materials using paraffin and PEG as binders were dried in a vacuum and then granulated using a manual screen. This had a significant impact on the pressing performance of the mixed materials, such as the accumulation of PEG in the drying process causing uneven distribution within the material, leading to agglomeration in the alloy phase. The poor effect of manually screening paraffin also posed a problem. However, from the perspective of the physical performance of the samples, it is still evident that PEG and paraffin have advantages over the rubber process.
During the experiment, the poor formability of paraffin due to manual screening was addressed by using manual weighing and pressing methods. However, in actual production, to accommodate large-scale production with self-pressing machines, increasing the pressing pressure and extending the holding time were necessary to avoid cracks or chipping of the paraffin material, which would reduce labor efficiency. Using a spray drying system to obtain a well-flowing mixture can effectively solve this problem.
The above discussion is a preliminary exploration of three commonly used binders in China. The research on binders is a systemic project involving a wide range of knowledge. To conduct in-depth research, one must possess knowledge in organic chemistry, polymer chemistry, and combine it with practical production knowledge of powder metallurgy to apply it to the production process of carbides. This will be a long-term and challenging task.
????????
With the continuous expansion of research and application fields of carbide materials, such as the emergence of ultra-fine and nano-carbides, and the extensive use of metal ceramics and ceramic materials, the raw materials for these products have undergone significant changes compared to the previous ordinary carbides. They have smaller particle sizes, lower bulk densities, poorer fluidity, and much worse forming performance than ordinary carbides. Therefore, a more excellent binder is needed. Specifically, research can be initiated in the following three aspects:
1.Studying the interaction between different types of powder materials and binders to understand the impact on forming performance.
2.Developing new polymer binders with different characteristics by combining different components.
3.Researching the thermal cracking characteristics of binders to meet the requirements of carbide production processes in terms of process characteristics and residual carbon content.
Through the above three aspects of research, it is expected to obtain a new generation of binders with good forming performance, environmental friendliness, stable performance, no toxicity, and no residue at the molecular level.









