In order to make the metal parts have the required working performance, heat treatment process is often necessary. Heat treatment process generally includes heating, heat preservation and cooling. Due to different processes, it can be divided into quenching, tempering, normalizing, annealing, etc?
??? ???? ???
Quenching of steel is a heat treatment process in which the steel is heated to the critical temperature AC3 (hypoeutectoid steel) or AC1 (hypereutectoid steel), holding for a period of time, and then rapidly cooling to below MS (or isothermal near MS) at a cooling rate greater than the critical cooling rate for martensite (or bainite) transformation. Generally, the solution treatment of aluminum alloy, copper alloy, titanium alloy, tempered glass and other materials or the heat treatment process with rapid cooling process is called quenching.
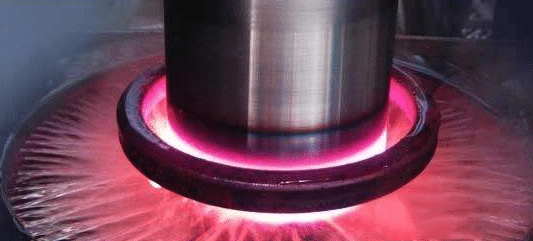
Purpose of quenching:
1) Improve the mechanical properties of metal products or parts.
2) ??? ????? ??????? ?? ????? ????? ?? ???????? ????? ??? ????? ????? ???? ???????? ????? ?? ???????? ???????? ??? ????? ???? ?? ??????? ????? ?? ?????? ???????? ?? ???????
The steel workpiece has the following characteristics after quenching:
① The unbalanced (i.e. unstable) structures such as martensite, bainite and retained austenite are obtained.
② There is a large internal stress.
③ The mechanical properties can not meet the requirements. Therefore, iron and steel parts are generally tempered after quenching.
????? ???? ???
Tempering is a heat treatment process in which the quenched metal products or parts are heated to a certain temperature and cooled in a certain way after holding for a certain time. Tempering is an operation immediately after quenching and is usually the last process for heat treatment of workpieces. Therefore, the combined process of quenching and tempering is called final treatment.

The main purpose of quenching and tempering is to:
1) In order to reduce the internal stress and brittleness, the quenched parts have great stress and brittleness. If not tempered in time, deformation and even cracking will occur.
2) ??????? ?? ???????? ????? ?? ???????? ????? ??? ?? ???, ??????? ??? ???? ?????? ?? ??????? ???? ??? ??????? ??????? ?? ??????? ???????? ?????????? ?? ???? ???? ?? ???, ??????, ?????, ???????????? ?? ??????? ?? ????? ?????? ???????? ???? ?? ???? ???
3) Stabilize workpiece size. The metallographic structure can be stabilized by tempering, so as to ensure no deformation in the later use.
4) Improve the machinability of some alloy steels.
The effect of tempering is as follows:
① Improve the stability of the structure, so that the structure of the workpiece will not change in the process of use, so that the geometric size and performance of the workpiece remain stable.
② In order to improve the performance of the workpiece and stabilize the geometric dimension of the workpiece, the internal stress should be eliminated.
③ Adjust the mechanical properties of steel to meet the requirements of use.
The reason why tempering has these effects is that when the temperature rises, the atomic activity ability is enhanced, and the atoms of iron, carbon and other alloy elements in iron and steel can be rapidly diffused to realize the rearrangement and combination of atoms, so that the unstable unbalanced structure gradually changes into stable equilibrium structure. The elimination of internal stress is also related to the decrease of metal strength with the increase of temperature. When tempered, the hardness and strength of steel decrease and the plasticity increases. The higher the tempering temperature, the greater the change of these mechanical properties. Some alloy steels with high content of alloying elements will precipitate some fine metal compounds when tempered in a certain temperature range, which will increase the strength and hardness. This phenomenon is called secondary hardening.
Tempering requirements: workpieces with different uses should be tempered at different temperatures to meet the requirements in use.
① Tools, bearings, carburized and quenched parts and surface hardened parts are usually tempered at low temperature below 250 ℃. After low temperature tempering, the hardness changes little, the internal stress decreases and the toughness increases slightly.
② High elasticity and necessary toughness can be obtained by tempering spring at 350 ~ 500 ℃.
③ The parts made of medium carbon structural steel are usually tempered at 500 ~ 600 ℃ to obtain a good combination of strength and toughness.
In production, it is often based on the performance requirements of the workpiece. According to different heating temperature, tempering can be divided into low temperature tempering, medium temperature tempering and high temperature tempering. Quenching and subsequent high-temperature tempering combined heat treatment process is called quenching and tempering, which has high strength and good plasticity and toughness.
1) Low temperature tempering: 150-250 ℃, m cycles, reduce internal stress and brittleness, improve plasticity and toughness, and have high hardness and wear resistance. It is used to make measuring tools, cutting tools and rolling bearings.
2) Medium temperature tempering: 350-500 ℃, t cycle, high elasticity, plasticity and hardness. It is used for making springs, forging dies, etc.
3) High temperature tempering: 500-650 ℃, s cycle, with good comprehensive mechanical properties. It is used to make gears, crankshafts, etc.
What is normalizing?
Normalizing is a heat treatment to improve the toughness of steel. After the steel members are heated to 30-50 ℃ above AC3 temperature, they are kept for a period of time and then cooled out of the furnace. The main feature is that the cooling rate is faster than that of annealing and lower than that of quenching. When normalizing, the crystallized grains of steel can be refined in a slightly faster cooling, which can not only obtain satisfactory strength, but also significantly improve the toughness (Akv value) and reduce the cracking tendency of the components. After normalizing some low alloy hot rolled steel plates, low alloy steel forgings and castings, the comprehensive mechanical properties of the materials can be greatly improved, and the cutting properties can also be improved.
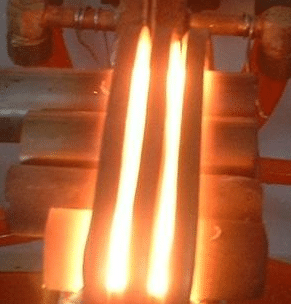
Normalizing has the following purposes and uses:
① For hypoeutectoid steel, normalizing is used to eliminate overheated coarse grain structure and widmanstatten structure in casting, forging and welding parts, and banded structure in rolled products, refine grain size, and be used as pre heat treatment before quenching.
② For hypereutectoid steel, normalizing can eliminate the network secondary cementite and refine the pearlite, which not only improves the mechanical properties, but also benefits the later spheroidizing annealing.
③ For low carbon deep drawing steel sheet, normalizing can eliminate free cementite at grain boundary to improve its deep drawing property.
④ For low carbon steel and low-carbon low alloy steel, more fine pearlite structure can be obtained by normalizing, and the hardness can be increased to hb140-190. The phenomenon of “sticking to the tool” can be avoided and the machinability can be improved. For medium carbon steel, it is more economical and convenient to normalize and anneal medium carbon steel.
⑤ For ordinary medium carbon structural steel, normalizing can be used instead of quenching and tempering at high temperature when the mechanical properties are not required. This method is not only easy to operate, but also stable in structure and size of steel.
⑥ High temperature normalizing (150-200 ℃ above AC3) can reduce the composition segregation of castings and forgings due to the high diffusion rate at high temperature. The coarse grains after high temperature normalizing can be refined by the second lower temperature normalizing.
⑦ For some low and medium carbon alloy steels used in steam turbines and boilers, the bainite structure is usually obtained by normalizing and then tempered at high temperature. It has good creep resistance when used at 400-550 ℃.
⑧ In addition to steel and steel, normalizing is also widely used in the heat treatment of ductile iron to obtain pearlite matrix and improve the strength of ductile iron.
Since the normalizing is characterized by air cooling, the ambient air temperature, stacking mode, air flow and workpiece size have effects on the microstructure and properties after normalizing. Normalizing structure can also be used as a classification method of alloy steel. Alloy steels are usually classified into pearlitic steel, bainite steel, martensite steel and austenitic steel according to the microstructure obtained by air cooling after heated to 900 ℃ for a sample with a diameter of 25 mm.
What is annealing?
Annealing is a kind of metal heat treatment process in which the metal is slowly heated to a certain temperature, maintained for enough time, and then cooled at an appropriate speed. Annealing is divided into complete annealing, incomplete annealing and stress relief annealing. The mechanical properties of annealed materials can be tested by tensile test or hardness test. Many steels are supplied in the state of annealing heat treatment. Rockwell hardness tester can be used to test HRB hardness. For thin steel plate, steel strip and thin-walled steel pipe, surface Rockwell hardness tester can be used to detect HRT hardness.
The purpose of annealing is to:
① It can improve or eliminate all kinds of structural defects and residual stresses in the process of casting, forging, rolling and welding, and prevent the deformation and cracking of the workpiece.
② Soften the workpiece for cutting.
③ The mechanical properties of the workpiece can be improved by refining the grain and improving the microstructure.
④ Prepare for the final heat treatment (quenching and tempering).
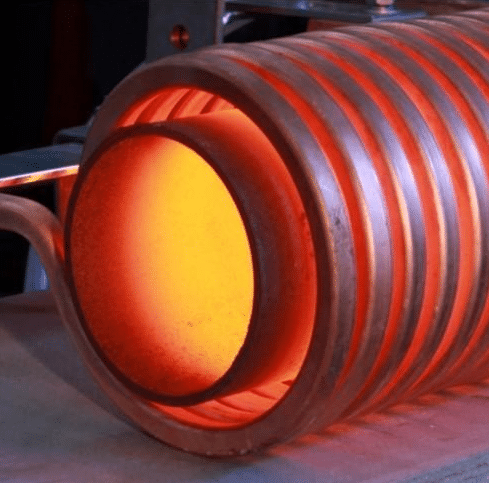
The common annealing processes are as follows:
① Fully annealed. It is used to refine the coarse overheated structure of medium and low carbon steel with poor mechanical properties after casting, forging and welding. When the workpiece is heated to 30-50 ℃ above the temperature at which all ferrite is transformed into austenite, keep it for a period of time, and then slowly cool down with the furnace. During the cooling process, the austenite transforms again, and the microstructure of the steel becomes finer.
② Spheroidizing annealing. It is used to reduce the high hardness of tool steel and bearing steel after forging. When the workpiece is heated to 20-40 ℃ above the temperature at which austenite begins to form, the lamellar cementite in pearlite becomes spherical during cooling, thus reducing the hardness.
③ Isothermal annealing. It is used to reduce the high hardness of some alloy structural steels with high nickel and chromium contents for cutting. Generally, the austenite is cooled to the most unstable temperature of austenite at a faster speed, and the austenite is transformed into troostite or sorbite, and the hardness can be reduced.
④ Recrystallization annealing. It is used to eliminate the hardening phenomenon of metal wire and sheet in the process of cold drawing and cold rolling (hardness increasing and plasticity decreasing). The heating temperature is generally 50-150 ℃ below the temperature at which austenite begins to form. Only in this way can the work hardening effect be eliminated and the metal softened.
⑤ Graphitization annealing. It is used to make the cast iron containing a lot of cementite into malleable cast iron with good plasticity. The technological operation is to heat the casting to about 950 ℃ and cool it properly after holding for a certain time, so that the cementite decomposes and forms flocculent graphite.
⑥ Diffusion annealing. It is used to homogenize the chemical composition of alloy casting and improve its service performance. On the premise of no melting, the casting is heated to the highest temperature as possible, and kept warm for a long time, and then slowly cooled after the elements in the alloy diffuse evenly.
⑦ Stress relief annealing. It is used to eliminate the internal stress of steel castings and weldments. For iron and steel products, when austenite begins to form after heating, the internal stress can be eliminated by cooling in air after heat preservation.









