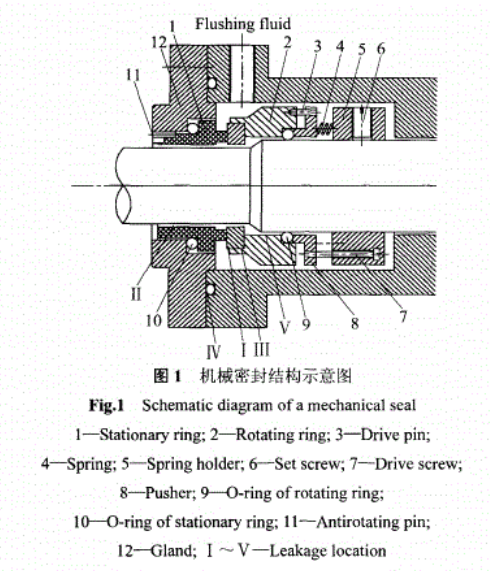
Requirements for Seal Face Materials in Mechanical Seals
To ensure the proper operation of sealing rings in mechanical seal devices, they are typically configured as a pair consisting of a hard ring and a soft ring with different hardness levels, considering aspects such as wear reduction, corrosion resistance, and prevention of galling. During operation, the sealing rings may come into contact and generate friction when starting, stopping, or experiencing fluctuations in working conditions. Therefore, the material for the hard ring needs to have sufficient strength, rigidity, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity. Friction and fluid shear forces can elevate the temperature of the sealing rings, so the sealing material must exhibit good thermal conductivity, heat resistance, and thermal shock resistance. To ensure a long service life, the sealing ring must also have good corrosion resistance. Additionally, the hard ring should possess good formability and machinability, low density and permeability, and excellent self-lubricating properties. No single material can fully meet all these requirements, so typically, the main performance criteria for sealing materials are defined based on the operating environment, and suitable materials are selected accordingly.
Application of WC-Ni carbide as Mechanical Seal Materials
To ensure the longevity and stable operation of mechanical seal materials, the sliding materials should have appropriate thermal compatibility and thermal conductivity, as well as suitable coefficients of thermal expansion, elastic modulus, and friction factors. WC-Ni carbides are known for their excellent performance in mechanical seals, making them suitable for applications in high-pressure, high-speed, high-temperature, corrosive environments, and media containing solid particles.

Characteristics of WC-Ni carbide
Since the introduction of carbides in the 1920s, cobalt has been regarded as the best binder phase and continues to play a significant role in the preparation of carbides. With the rapid advancement of science and technology, the applications of carbides have expanded, leading to a surge in demand. Due to the scarcity of cobalt resources, scientists worldwide have prioritized cobalt as a strategic material and have been researching ways to reduce or substitute cobalt in carbides. Nickel, being close to cobalt in the periodic table, with similar density, melting point, and atomic radius, can effectively wet and support the hard phase and has lower radioactivity compared to cobalt, making it a common substitute.
The characteristics of WC-Ni and WC-Co carbides during the sintering process are similar. However, due to the different strengthening effects of Ni and Co on the hard phase, WC-Ni may exhibit slightly lower performance in certain aspects compared to WC-Co carbides. By adding a small amount of metal elements to enhance the binder phase, using fine low-carbon WC particles, and employing vacuum sintering processes, WC-Ni carbides with lower porosity and a uniform, fine-grained structure can be achieved. Their hardness, bending strength, and tribological properties can meet or exceed those of WC-Co carbides, while their corrosion resistance is also significantly improved. Additionally, as Ni replaces the radioactive element Co, it provides good radiation protection when used under radioactive conditions. By carefully controlling the total carbon content and grain size of the alloy, and adding appropriate amounts of Mo and Cr, WC-Ni carbides can be produced with non-magnetic properties and excellent physical and mechanical performance, thereby mitigating the effects of special working conditions and environmental factors.

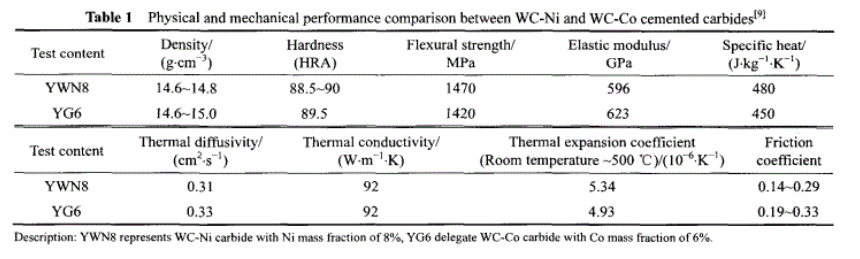
Physical and Mechanical Properties of WC-Ni carbide for Mechanical Seals
WC-Ni carbides are made by mixing WC and Ni powders in a specific ratio, adding a binder, and then pressing and sintering the mixture. With a melting point of approximately 2700°C, WC particles are primarily bonded together during the sintering process through the melting of Ni. At high temperatures, some WC dissolves into Ni, forming a WC-Ni eutectic with a lower melting point than Ni. Consequently, the sintering temperature varies with changes in Ni content and WC grain size. For composite materials, physical parameters such as elastic modulus, coefficient of thermal expansion, Poisson’s ratio, thermal diffusivity, and thermal conductivity can vary based on the proportion and distribution of each phase.
Application of WC-Ni carbide Materials in Mechanical Seals
Due to their exceptional toughness, rigidity, high hardness, good wear resistance, high bending strength, and high thermal conductivity, both WC-Ni and WC-Co carbides are notable. WC-Ni carbides offer superior corrosion resistance compared to WC-Co alloys and do not emit radiation under neutron exposure, making them suitable for use in mechanical seals operating under high pressure, high speed, high temperature, corrosive media, media containing solid particles, and radioactive environments. Currently, WC-Ni carbides have significant application value in vehicle transmission shaft seals, power shift transmissions, pumps in special operating conditions, and rotary seals for aircraft, as well as in the petrochemical industry and nuclear power seals.
Influence of Microstructure on the Properties of WC-Ni carbides
The unevenness in microstructure can adversely affect the strength of carbides. Minor variations in the binder phase content and distribution, WC grain size, carbon content, and any form of impurity contamination can lead to an uneven microstructure that negatively impacts the mechanical properties of WC-Ni carbides.
Influence of WC Grain Size on the Properties of WC-Ni carbides
WC-Ni carbides use Ni as the binder metal. During the sintering process, Ni melts at the sintering temperature and bonds the WC particles together into a solid mass. These alloys exhibit very high hardness, are difficult to machine, and possess excellent wear resistance. Variations in the processing methods can lead to significant differences in the alloy’s composition and properties, and the morphology of the WC grains can also affect the performance of WC-Ni carbides.
3.2Changes in WC Grain Morphology During Liquid Phase Sintering of WC-Ni carbides
The coarseness of WC grains can significantly affect the bending strength of carbides, while uneven distribution of Ni can lead to brittle fracture of the alloy. To improve the fracture toughness of the product, it is essential to strengthen the interface between WC and the binder phase or to enhance the strength of the binder phase. Therefore, controlling the sintering process and conditions will impact the mechanical properties of WC-Ni carbides.
During sintering, the shape of WC grains in the carbide?is also influenced by shape relaxation and the grain growth process. The higher the ratio of the average intercept length of the binder phase (the average length of each grain intersected by any testing line on a cross-section) to the WC grain size, the less impact it has on the shape of the WC grains, resulting in a more equiaxed grain morphology.

Effect of Binder on Temperature Residual Stress in WC-Ni carbides
When the content of the metallic binder Ni in WC-Ni alloy materials is relatively high, the compressive stress in fine WC grains is greater than that in coarse grains. This is because, with a constant WC content, the average free path of the binder in fine powder is shorter than in coarse powder. When the WC-Ni alloy contains less binder, the difference in the average free path of the binder is minimal, and the variation in residual stress with temperature is not significant. Therefore, if conditions allow, the Ni content in WC-Ni alloy sealing rings should be reduced to minimize the uneven distribution of residual stress due to temperature changes, thus reducing or even preventing thermal cracking in the sealing rings.
Current Research Status on the Application Performance of WC-Ni carbides
?Corrosion Resistance of WC-Ni Alloys
Compared to WC-Co carbides, WC-Ni carbides exhibit superior wear resistance. This is due to the binder in WC-Ni alloys having excellent corrosion resistance, with both passivation and electrochemical corrosion rates for WC-Ni carbides being significantly lower than those for WC-Co carbides. Under acidic conditions in practical production processes, WC alloys with Ni as the binder show better acid resistance than those with Co as the binder.
Table 2 compares the corrosion resistance of WC-Ni and WC-Co carbides. The results show that substituting Co with Ni significantly enhances the corrosion resistance of WC carbides. However, the corrosion resistance of a material is specific to its alloy composition, grain size, and the corrosive conditions (including temperature, concentration, time, and corrosion state). For example, the corrosion resistance of YWN8 in 68%-90% HNO? is not significantly different from, and even slightly lower than, that of YG6 alloy. This is primarily due to the poor resistance of metallic Ni to strong oxidizing acids like HNO?; as the concentration of HNO? and the Ni content in the alloy increase, its corrosion resistance decreases.
Table 2 Corosion resistance performance comparison between WC-Ni and WC-Co cemented carbides
Tribological Performance of WC-Ni Alloy Mechanical Seal Rings
WC-Ni carbide?sealing rings exhibit excellent wear resistance. This is because WC-Ni carbides possess strong oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance in fluid sealing media, which contributes to their superior wear resistance. The friction coefficient of WC-Ni carbides is related to the content, grain size, and distribution of the binder phase. A softer binder phase can lead to adhesion during friction. Additionally, the content and composition of the binder phase can affect the hardness of WC-Ni, thereby influencing the wear resistance of the WC-Ni carbide.
Conclusion
Mechanical seal materials are a crucial area of research in sealing technology. With the advancement of modern science and technology and the increasing demands of production and daily life, the requirements for sealing technology have become more stringent. However, research in this field in our country is still relatively behind. Strengthening interdisciplinary collaboration and continually improving experimental and theoretical research are key to overcoming the technological barriers in mechanical seals imposed by foreign countries.






