Currently, in mechanical manufacturing, due to the rapid updating and upgrading of products, there are higher requirements for the selection of parts. Particularly in the manufacturing of industries such as aerospace, large power stations, and ships, some difficult-to-machine materials like high-temperature alloys, titanium alloys, heat-resistant stainless steels, and composite materials have been widely used. Among them, the efficient processing of widely used and commonly employed high-temperature alloy materials has received more attention.
Using high-performance high-speed steel bimetal saw blades (with M42 as the edge material) to cut difficult-to-machine high-temperature alloys results in low cutting efficiency and a very short service life. Subsequently, saw blades made of cemented carbide with high hardness were chosen. Through testing and practical application, cemented carbide saw blades have achieved significant results in the blanking processing of high-temperature alloys, meeting the requirements of production schedules.

Design and Selection of Cemented Carbide Saw Blades
Cemented carbide saw blades have different materials and structures. In practical applications, we have found that not every type of cemented carbide saw blade can achieve good results in the blanking processing of high-temperature alloys. Only by making reasonable choices and using them properly can the desired results be obtained. Therefore, we have selected and compared four aspects: the structure of the saw blade, the form of the tooth shape, the material, and the reasonable selection of cutting parameters. The details are as follows:
Tool Structure
Cemented carbide saw blades typically adopt a tipped and welded structure. The tips of the teeth on cemented carbide saw blades have the advantages of high hardness, high wear resistance, and high fatigue resistance. However, their main drawbacks are brittleness, low strength, and poor resistance to impact.
After testing and comparative application (especially based on the final sawing blanking data comparison results), we believe that for the blanking of high-temperature alloys, the saw blade structure is best suited with coarse teeth and variable pitch cemented carbide saw blades. The reason we believe this is optimal is that during the sawing blanking of high-temperature alloys (particularly nickel-based high-temperature alloys), the chips have strong adhesion, making it difficult for the chips to be discharged smoothly. The intermittent formation and disappearance of built-up edge can easily cause the cutting edge to chip and the tool’s flank wear to intensify. Choosing coarse teeth not only increases the strength of the cutting edge but also enlarges the chip space, facilitating the use of a larger feed rate to improve cutting efficiency. The adoption of variable pitch can reduce cutting noise and vibration, making the cutting process more stable, which is beneficial for improving the durability of the tool. A schematic diagram of the variable pitch saw blade structure can be seen in Figure 1.
Selection of Tool Tooth Shape
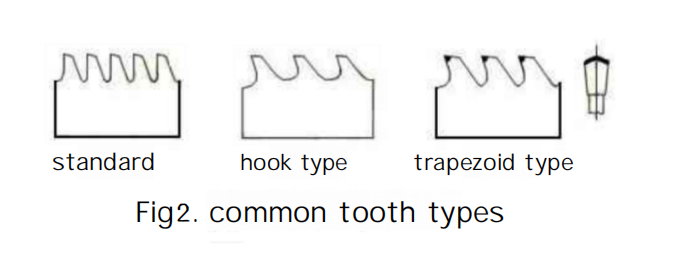
Common tooth shapes for saw blades include standard teeth, hook-shaped teeth, and trapezoidal teeth, as shown in Figure 2.
- Standard teeth have a cutting approach angle g=0°, with the tooth face perpendicular to the substrate, and the tooth slots are deep and narrow.
- Hook-shaped teeth have a cutting approach angle g=5°~10°, with the tooth slots deep and wide.
- Trapezoidal teeth have a cutting approach angle g=10°~15° and a back angle a=6°~8°, providing high tooth strength, suitable for heavy cutting.
For the processing of high-temperature alloy materials, in addition to selecting high-strength cemented carbide materials for the saw blades, the choice of tooth shape is also very important. Trapezoidal teeth have sufficient strength and are less prone to chipping during cutting. Due to the larger approach angle, the cutting resistance is also smaller than that of standard straight teeth. Practical verification has also proven that the choice of trapezoidal teeth results in better cutting performance compared to the other two tooth shapes.
Tool Material Grades
The grades of cemented carbide suitable for cutting high-temperature alloy materials mainly fall into two categories: Type M and Type K according to the ISO standard (now recommended as Type S). Based on the results of sawing comparison tests, the improvement in cutting efficiency between the two types of tool grades is not significant. However, in terms of sawing service life, the saw blades made of material equivalent to grade M15-M30 have a 15%~20% longer life span compared to those made of material equivalent to grade K05-K20 (when processing high-temperature alloys of the same specification and grade).
Selection of Cutting Parameters
The rational selection of cutting parameters is crucial for the blanking of high-temperature alloys. Proper cutting parameters ensure normal blanking of workpieces, significantly improve cutting efficiency and tool life, and also reduce the harsh noise generated by the adhesion and friction of chips between the tool and the workpiece during blanking. Based on our experimental application results for various nickel-based high-temperature alloy grades (considering efficiency and tool life comprehensively), the selected rational cutting parameters are as follows:
Cutting linear speed: 15~20 m/min
Feed rate (material removal rate): 6~8 cm2/min
The above cutting parameters have been determined through long-term experimental applications and are considered to be economically viable.
Actual Tool Benefits
Through the aforementioned four aspects of work, the use of cemented carbide saw blades for processing high-temperature alloys has achieved significant economic effects in the steam turbine factory:
After testing and comparing multiple data results, the current cemented carbide saw blades used for processing high-temperature alloys have improved the cutting efficiency by 5 to 8 times compared to the previously used bimetal saw blades. For example, when processing a GH4169 nickel-based high-temperature alloy blank with dimensions of 140×245, the original M42 bimetal saw blade took about 6 to 8 hours to blank one piece. However, with the selected cemented carbide saw blade for processing high-temperature alloys, the blanking time for one workpiece is only about 1 hour. Moreover, what is more prominent is the improvement in tool life.
When processing blanks of the above-mentioned grades and specifications, the original M42 bimetal saw blade could only blank one piece, whereas the current cemented carbide saw blade can generally blank 20 to 24 pieces (under reasonable cutting parameters and proper operation, one saw blade can even blank 40 to 50 pieces). Although the price of the current cemented carbide saw blade is about 5 times higher than that of the bimetal saw blade, in terms of cost-performance ratio and comprehensive economic benefits (especially as demonstrated by the comparison of the above typical example), using cemented carbide saw blades to process high-temperature alloys is very cost-effective. It achieves the goal of low cost, high tool life, and efficient processing.








