As is familiar to us, elements to be put into some kind of steel alloy for improving or altering its properties are regarded as alloy elements. Commonly used alloying elements are chromium, nickel, molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium, titanium, niobium, zirconium, cobalt, silicon, manganese, aluminium, copper, boron, rare earth, etc. Phosphorus, sulphur and nitrogen also play the role of alloys in some cases.
Cr
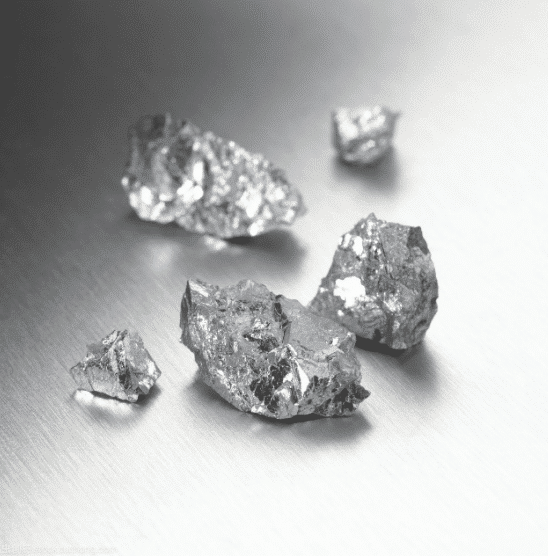

Chromium can increase hardenability and secondary hardening of steel. It can improve hardness and wear resistance of carbon steel without brittleness of steel. When the content exceeds 12%, the steel has good high temperature oxidation resistance and oxidation corrosion resistance, and also increases the thermal strength of the steel. Chromium is the main alloy element of stainless steel acid-resistant steel and heat-resistant steel.
Chromium can improve the strength and hardness of carbon steel during rolling, and reduce elongation and section shrinkage. When the content of chromium exceeds 15%, the strength and hardness will decrease, and the elongation and section shrinkage will increase accordingly. It is easy to obtain high surface quality of chromium-containing steel parts by grinding.
The main function of chromium in quenching and tempering structure is to improve hardenability, to make steel have better comprehensive mechanical properties after quenching and tempering, and to form chromium-containing carbides in carburized steel, so as to improve the wear resistance of material surface.
Spring steel containing chromium is not easy to decarbonize during heat treatment. Chromium can improve the wear resistance, hardness and red hardness of tool steel, and has good tempering stability. In electrothermal alloys, chromium can improve the oxidation resistance, resistance and strength of alloys.
Nickel (Ni)
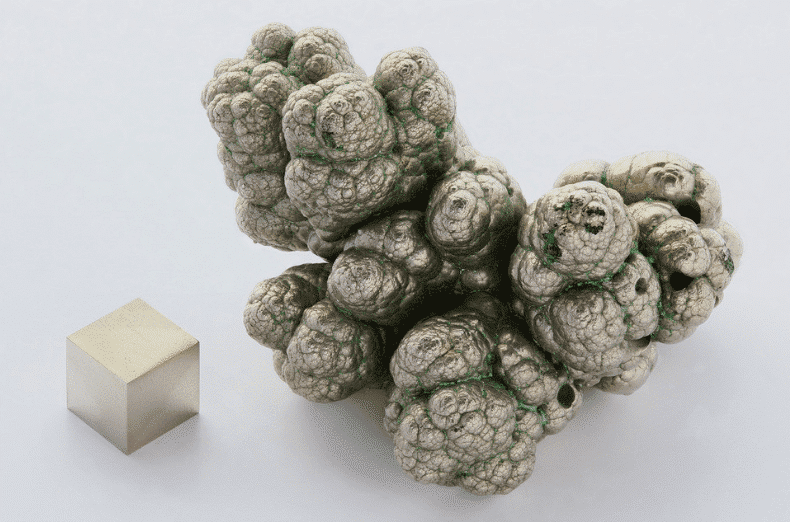

The total effect of nickel on strengthening ferrite and refining pearlite in steel is to increase strength, but the effect on plasticity is not significant.
Generally speaking, for low carbon steel used in rolling, normalizing or annealing without quenching and tempering treatment, a certain nickel content can improve the strength of the steel without significantly reducing its toughness.
According to statistics, every 1% increase in nickel can increase the strength by 29.4 Pa. With the increase of nickel content, the yield degree of steel increases faster than the tensile strength, so the ratio of nickel-containing steel is higher than that of common carbon steel. While increasing the strength of steel, nickel has less effect on toughness, plasticity and other process properties than other alloy elements.
For medium carbon steels, because nickel decreases pearlite transformation temperature and fines pearlite, and because nickel decreases carbon content at eutectoid point, the pearlite content of pearlite ferrite steels containing nickel is larger than that of carbon steels with the same carbon content, which makes the strength of pearlite ferrite steels containing nickel higher than that of carbon steels with the same carbon content. Conversely, if the strength of the steel is the same, the carbon content of the nickel-containing steel can be reduced appropriately, so that the toughness and plasticity of the steel can be improved.
Nickel can improve the fatigue resistance of steel and reduce the sensitivity of steel to notches. Nickel reduces the brittle transition temperature of steel at low temperature, which is of great significance for low temperature steel. The steel containing 3.5% nickel can be used at – 100 ~C, and the steel containing 9% nickel can work at – 196 ~C. Nickel does not increase the creep resistance of steel, so it is generally not used as a strengthening element of Hot-Strength steel.
The linear expansion coefficient of ferronickel alloys with high nickel content varies significantly with the increase or decrease of nickel content. Using this characteristic, precise alloys and bimetallic materials with very low or certain linear expansion coefficient can be designed and manufactured.
In addition, nickel can not only resist acid, but also alkali, and has corrosion resistance to atmosphere and salt. Nickel is one of the important elements in stainless steel.
Mo
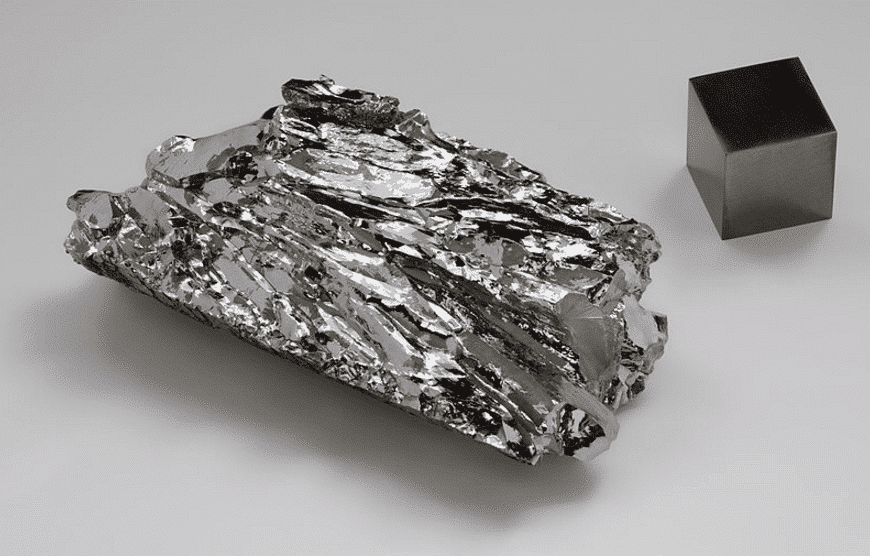
Molybdenum in steel can improve hardenability and thermal strength, prevent tempering brittleness, increase remanence and coercivity and corrosion resistance in some media.
In quenched and tempered steels, molybdenum can harden and harden parts with larger cross section, improve tempering resistance or tempering stability of steels, and enable parts to temper at higher temperatures, thereby effectively eliminating (or reducing) residual stress and improving plasticity.
In addition to the above effects, molybdenum in carburized steel can also reduce the tendency of carbide forming continuous network on grain boundary, reduce the retained austenite in carburized layer, and increase the wear resistance of surface layer.
In the forging die rigidity, molybdenum can also maintain a relatively stable hardness of steel and increase the pair of deformation. Resistance to cracking and wear, etc.
Molybdenum can further improve the corrosion resistance of stainless steel to organic acids (such as formic acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid, etc.) and hydrogen peroxide, sulfuric acid, sulfite, acid dyes, bleaching powder, etc. Especially due to the addition of molybdenum, the tendency of pitting corrosion caused by the presence of chloride ions is prevented.
The W12Cr4V4Mo high speed steel containing about 1% molybdenum has the properties of wear resistance, tempering hardness and red hardness.
Wolfram(W)
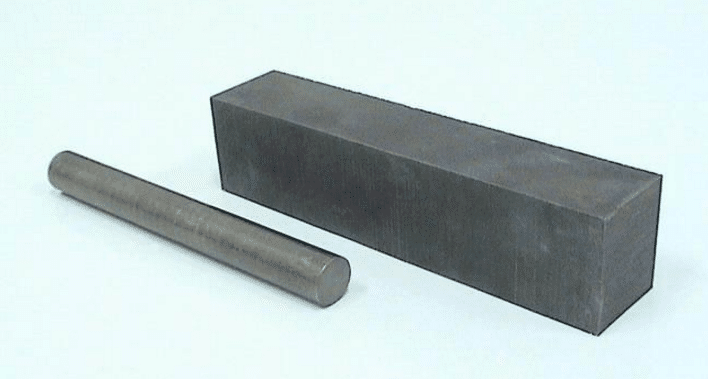
Tungsten dissolves partially into iron to form solid solution in addition to carbides in steel. Its effect is similar to that of molybdenum, and its general effect is not as significant as that of molybdenum in terms of mass fraction.
Tungsten is mainly used in steel to increase tempering stability, red hardness, thermal strength and wear resistance due to carbide formation. Therefore, it is mainly used for tool steel, such as high-speed steel, hot forging die steel and so on.
Tungsten forms refractory carbides in high quality spring steel. When tempered at higher temperature, it can alleviate the carbide aggregation process and maintain higher high temperature strength. Tungsten can also reduce the superheat sensitivity, increase hardenability and hardness of steel.
The air cooling of 65SiMnWA spring steel after hot rolling has very high hardness. The spring steel with 50mm2 cross section can harden in oil, and can be used as an important spring which can withstand heavy load, heat resistance (not more than 350 C) and impact. 30W4Cr2VA high-strength heat-resistant high-quality spring steel has great hardenability. It is quenched at 1050-1100 C and tempered at 550-650 C, and its tensile strength reaches 1470-1666 Pa. It is mainly used for manufacturing springs used at high temperature (not more than 500 C).
Tungsten is the main element of alloy tool steel, because tungsten can improve the wear resistance and cutting ability of steel remarkably.
Vanadium(V)
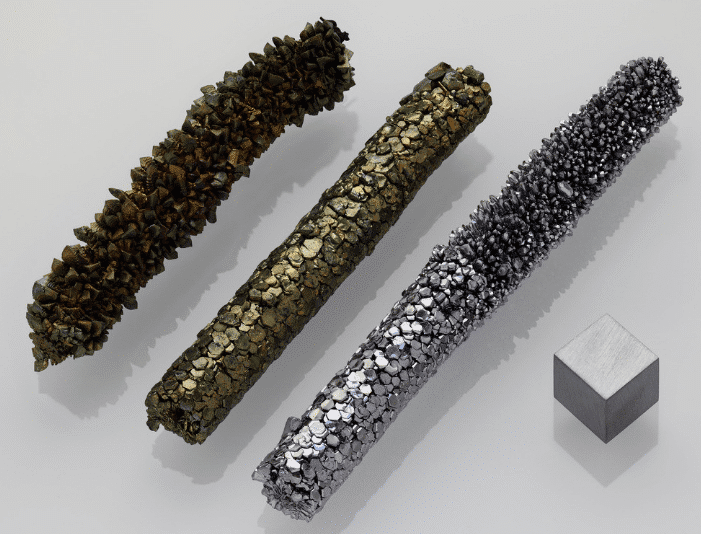
Vanadium has strong affinity with carbon, ammonia and oxygen, and forms corresponding stable compounds.
Vanadium exists mainly in the form of carbides in steel. Its main function is to refine the structure and grain size of steel and reduce the strength and toughness of steel. When the solid solution is dissolved at high temperature, the hardenability is increased; otherwise, if it exists in the form of carbide, the hardenability is reduced. Vanadium increases tempering stability of quenched steel and produces secondary hardening effect. The vanadium content in steel is generally not more than 0.5% except for high-speed tool steel.
Vanadium can refine grain size, improve strength and yield ratio and low temperature properties of normalized low carbon alloy steel, and improve weldability of steel.
Vanadium is often used in structural steels in conjunction with manganese, chromium, molybdenum and tungsten due to its low hardenability under general heat treatment conditions. Vanadium in quenched and tempered steel is mainly used to improve the strength and yield ratio of steel, refine grain size and pick up superheat sensitivity. In carburized steel, because the grain size can be refined, the steel can be quenched directly after carburizing without secondary quenching.
Vanadium in spring steel and bearing steel can increase strength and yield ratio, especially increase proportion limit and elastic limit, reduce decarburization sensitivity during heat treatment, and thus improve surface quality. Bearing steel containing vanadium with five chromium has high carbonization dispersion and good service performance.
Vanadium refines grains in tool steel, reduces superheat sensitivity, increases tempering stability and wear resistance, thus prolonging tool life.









